Embark on your MySQL journey
Despite the emergence of modern NoSQL databases such as MongoDB, Firebase, and Redis in recent years, SQL databases remain extremely popular among developers.
SQL (Structured Query Language) is a language used for interacting with data in a variety of databases, including popular databases such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, and MS SQL Server.
In this article, you’ll learn everything you need to know to get started with MySQL, the open source database that powers content management systems like WordPress, e-commerce platforms like Shopify, and social media platforms like Twitter.
You will learn how MySQL works, relational databases and some of its key concepts, how to install and interact with a MySQL database using the command line, and modern SQL syntax for creating, reading, updating, and deleting data in MySQL .
Understanding the Object Relational Mapper (ORM)
Most developers working with relational databases don't actually write raw SQL. More commonly, they use libraries that perform object-relational mapping, or ORM.
These libraries basically make your database tables look like objects on the server side of your site, so you can easily manipulate the data using any object-oriented programming language of your choice.
Examples of ORMs include Sequelize (JavaScript), Eloquent (Laravel), SQLAlchemy (Python), and Active Record (Ruby on Rails).
ORM eliminates the need to write raw SQL code. Instead, you can use your knowledge of object-oriented programming to create, read, update, and delete data on a SQL database. ORM makes using relational databases easier and more intuitive.
Relational Database Management System (RDMS)
Essentially, a relational database management system consists of two main components: a database and a query language.
The database itself is just a collection of tables. In each table, your actual data is organized into columns and rows, just like a spreadsheet. Tables in a relational database can be linked or related based on data common to each table.
Query language is used to operate and read data in the database. For most relational databases, the query language used to manipulate data is a variation of SQL.
Some key concepts in SQL database
If you want to learn how to use MySQL, we must first understand some basic concepts in order to explain the following SQL database concepts in a visual way. I will use a database visualization tool called DrawSQL. First, we will learn about schema and data types.
Schema and data typesYou can think of a schema as a blueprint that defines the overall structure of a table and its relationship to other tables.
For example, consider the following
user table schema:
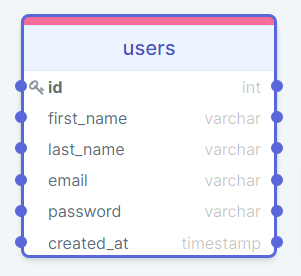 user table
user tableThere are multiple data types in MySQL, and different SQL database data types are also different.
You will also notice that the
id key that accepts integer values is also preceded by a key. This indicates that id is defined using primary key constraints.
id of each column cannot be empty and must be unique. Therefore, two or more users can never share the same primary key, and each row can be identified by its primary key.
users table.
Let’s take a deeper look at constraints in a MySQL database.constraint
We saw earlier the primary key constraint, which ensures that the value of a specified key is unique for every column in the table.
In MySQL, constraints are rules that allow or restrict which values are stored in a table. They help limit the type of data that will be inserted into the table, ensuring the accuracy and completeness of the data within the table.
The following constraints are commonly used in MySQL:
- NOT NULL
: Ensure that the column cannot have NULL values - UNIQUE
: Ensure that all values in the column are distinct from each other - Primary key
: A combination of NOT NULL and UNIQUE - uniquely identifies each row in the table - Foreign key
: used to link two tables together - CREATE INDEX
: Used to quickly create a database and retrieve data from the database - CHECK
: Ensure that the values in the column meet the specified conditions - DEFAULT
: If no value is specified, set a default value for the column
To add more context, let's assume that the
Users table is used to store registered users in an online shopping website.
Usually, there must be a product table and a shopping cart table in the database of an online shopping website. Products will contain all the products available to the user and Shopping Cart will contain the specific items that a specific user intends to purchase along with the quantity of each item. p>
All tables created so far are as follows:
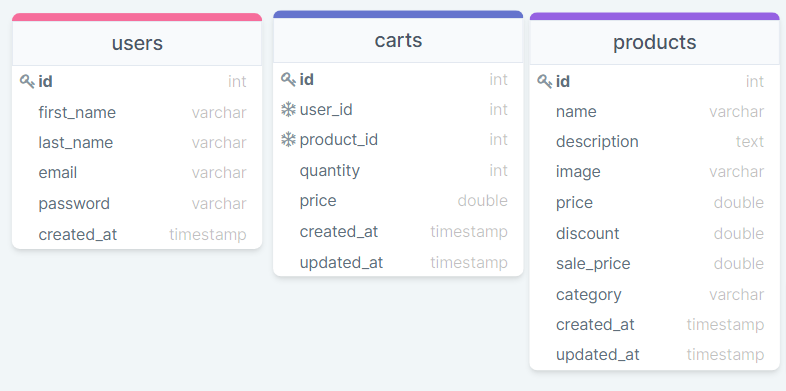
All these tables are unique entities. This means, for example, that the carts table does not need to store any information about the user.
Technically, there is nothing stopping us from merging the shopping cart data into the Users table. After all, both sets of information are related (the user has a shopping cart). However, this approach eventually leads to a crowded table that is very difficult to manage.
Instead, we took a more sustainable approach and created a separate Shopping Cart table to store all shopping cart related data. We then create references to the other tables by placing the foreign keys user_id and product_id in the carts table.
This way the shopping cart has access to any information about the user who owns the cart and the products present in the cart, although no such information is actually stored in it.
Install and learn how to use MySQL
Now that we have a higher level understanding of MySQL and MySQL Server, let's practice by installing MySQL on our system.
To install MySQL on your system, go to the MySQL Community Downloads page and download the MySQL installer.
After the download is complete, run the installer and complete the installation wizard to install MySQL.
When selecting the installation type, make sure to include the MySQL server product. I recommend using the Developer Default option.
After successful installation, you should be able to access MySQL server commands from the command line.
However, to use MySQL from the command line, you first need to authenticate yourself. Run the following command, filling in the placeholders with your username:
mysql -u <your username> -p
You will be prompted for your administrator password, and if both details are correct, you will be granted access to MySQL from the command line.
Please remember that the default username for MySQL is root and the default password is blank.
How does MySQL handle common SQL operations?
Create MySQL server and database
To create a database in MySQL, we use the CREATE DATABASE statement, followed by the database name:
CREATE DATABASE shopping_site;
statement is code that tells the system to do something. SQL statements always end with a semicolon. Capitalized words are reserved SQL keywords, and SQL will interpret them to perform certain operations.
Running the above command will create an empty database named shopping_site in MySQL.
To view all databases present in a MySQL instance, run SHOW DATABASE.
Create table in database
To create a table in a new database, use the CREATE TABLE statement, followed by the table name and parentheses containing the list of columns we want to include in this table:
CREATE TABLE users(
id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
first_name VARCHAR(255),
last_name VARCHAR(255),
email VARCHAR(255) UNIQUE NOT NULL,
password VARCHAR(255),
created_at TIMESTAMP,
updated_at TIMESTAMP
);
For each column in User, we specify the data type of the column. We also added a series of constraints to the id and email columns.
Running this command will create an empty but structured table named users in the database.
Create new record in table
To create a new record in a table, use the INSERT INTO statement, followed by the table into which the value is to be inserted:
INSERT INTO users(first_name, last_name, email, password)
VALUES(
'Kingsley',
'Ubah',
'ubahthebuilder@gmail.com',
'12345678'
);
In the first bracket, we specify the column into which we want to insert the value. Then, in the second bracket, we specify the values to be inserted in the correct order.
Running this command will insert these values into the specified columns in the users table.
从表中读取
要从数据库查询数据,请使用 SELECT 语句。
例如,如果我们想从 users 表中选择所有内容,我们可以使用以下语句:
SELECT * FROM users;
星号 (*) 代表我们数据库中的所有内容。该语句将返回整个表以及每一列。
如果我们只需要列的子集,例如 id 和 email,我们可以指定列来代替星号:
SELECT id, email FROM users;
在选择数据方面,我们的能力是无限的。
删除表格
要从 MySQL 中完全删除表,请使用 DROP 语句,后跟表名称:
DROP TABLE users;
现在,使用此命令时需要小心!它将永久删除users表中的所有数据。另外,不要将其与 DROP DATABASE 语句混淆,该语句会删除整个数据库。
就是这样!现在您知道如何使用 MySQL!
MySQL 是一个开源关系数据库管理系统,即使在今天,它仍然为网络的重要部分提供支持。结构化查询语言或 SQL 用于在 MySQL 数据库中操作和存储数据。
在这篇文章中,我们回顾了 SQL 的一些关键概念,包括 ORM、模式、约束和数据库规范化。我们还回顾了 MySQL 的安装和设置过程。
最后,我们介绍了一些负责在 MySQL 中操作数据的 SQL 语句。
The above is the detailed content of Embark on your MySQL journey. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Explain JSON Web Tokens (JWT) and their use case in PHP APIs.
Apr 05, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Explain JSON Web Tokens (JWT) and their use case in PHP APIs.
Apr 05, 2025 am 12:04 AM
JWT is an open standard based on JSON, used to securely transmit information between parties, mainly for identity authentication and information exchange. 1. JWT consists of three parts: Header, Payload and Signature. 2. The working principle of JWT includes three steps: generating JWT, verifying JWT and parsing Payload. 3. When using JWT for authentication in PHP, JWT can be generated and verified, and user role and permission information can be included in advanced usage. 4. Common errors include signature verification failure, token expiration, and payload oversized. Debugging skills include using debugging tools and logging. 5. Performance optimization and best practices include using appropriate signature algorithms, setting validity periods reasonably,
 How does session hijacking work and how can you mitigate it in PHP?
Apr 06, 2025 am 12:02 AM
How does session hijacking work and how can you mitigate it in PHP?
Apr 06, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Session hijacking can be achieved through the following steps: 1. Obtain the session ID, 2. Use the session ID, 3. Keep the session active. The methods to prevent session hijacking in PHP include: 1. Use the session_regenerate_id() function to regenerate the session ID, 2. Store session data through the database, 3. Ensure that all session data is transmitted through HTTPS.
 What are Enumerations (Enums) in PHP 8.1?
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:05 AM
What are Enumerations (Enums) in PHP 8.1?
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:05 AM
The enumeration function in PHP8.1 enhances the clarity and type safety of the code by defining named constants. 1) Enumerations can be integers, strings or objects, improving code readability and type safety. 2) Enumeration is based on class and supports object-oriented features such as traversal and reflection. 3) Enumeration can be used for comparison and assignment to ensure type safety. 4) Enumeration supports adding methods to implement complex logic. 5) Strict type checking and error handling can avoid common errors. 6) Enumeration reduces magic value and improves maintainability, but pay attention to performance optimization.
 Describe the SOLID principles and how they apply to PHP development.
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Describe the SOLID principles and how they apply to PHP development.
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:04 AM
The application of SOLID principle in PHP development includes: 1. Single responsibility principle (SRP): Each class is responsible for only one function. 2. Open and close principle (OCP): Changes are achieved through extension rather than modification. 3. Lisch's Substitution Principle (LSP): Subclasses can replace base classes without affecting program accuracy. 4. Interface isolation principle (ISP): Use fine-grained interfaces to avoid dependencies and unused methods. 5. Dependency inversion principle (DIP): High and low-level modules rely on abstraction and are implemented through dependency injection.
 Explain late static binding in PHP (static::).
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Explain late static binding in PHP (static::).
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Static binding (static::) implements late static binding (LSB) in PHP, allowing calling classes to be referenced in static contexts rather than defining classes. 1) The parsing process is performed at runtime, 2) Look up the call class in the inheritance relationship, 3) It may bring performance overhead.
 What is REST API design principles?
Apr 04, 2025 am 12:01 AM
What is REST API design principles?
Apr 04, 2025 am 12:01 AM
RESTAPI design principles include resource definition, URI design, HTTP method usage, status code usage, version control, and HATEOAS. 1. Resources should be represented by nouns and maintained at a hierarchy. 2. HTTP methods should conform to their semantics, such as GET is used to obtain resources. 3. The status code should be used correctly, such as 404 means that the resource does not exist. 4. Version control can be implemented through URI or header. 5. HATEOAS boots client operations through links in response.
 How do you handle exceptions effectively in PHP (try, catch, finally, throw)?
Apr 05, 2025 am 12:03 AM
How do you handle exceptions effectively in PHP (try, catch, finally, throw)?
Apr 05, 2025 am 12:03 AM
In PHP, exception handling is achieved through the try, catch, finally, and throw keywords. 1) The try block surrounds the code that may throw exceptions; 2) The catch block handles exceptions; 3) Finally block ensures that the code is always executed; 4) throw is used to manually throw exceptions. These mechanisms help improve the robustness and maintainability of your code.
 What are anonymous classes in PHP and when might you use them?
Apr 04, 2025 am 12:02 AM
What are anonymous classes in PHP and when might you use them?
Apr 04, 2025 am 12:02 AM
The main function of anonymous classes in PHP is to create one-time objects. 1. Anonymous classes allow classes without names to be directly defined in the code, which is suitable for temporary requirements. 2. They can inherit classes or implement interfaces to increase flexibility. 3. Pay attention to performance and code readability when using it, and avoid repeatedly defining the same anonymous classes.






