Docker quick start, core concepts and common instructions
#A friend asked about Docker-related issues over the weekend. Today I will share with you a quick start, core concepts and common instructions for Docker.
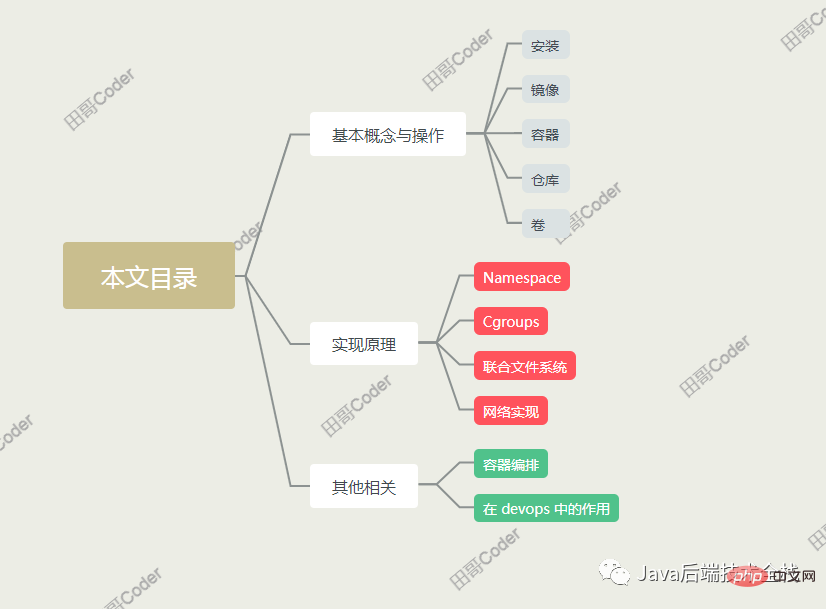
##1. Basic concepts and operations
Linux is Docker’s native support platform, so it is recommended to install it under Linux. Installing Docker under CentOS requires distribution version 7 and above. It is recommended to use the overlay2 storage driver.# 卸载已有 docker sudo yum remove docker \ docker-client \ docker-client-latest \ docker-common \ docker-latest \ docker-latest-logrotate \ docker-logrotate \ docker-engine # 添加安装源 sudo yum-config-manager \ --add-repo \ https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo # 安装最新版 sudo yum install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io # 启动 sudo yum install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.ioCopy after login
is essentially a read-only combination of files and folders, including container running All basic files and configuration information required. Operation: 1. Pull the image docker pull For example: docker pull nginx2, rename the image docker tag For example: docker tag nginx:latest mynginx:latest3. View the image docker image ls or docker images4. Delete the image docker rmisuch as: docker rmi mynginx5. Build the image docker build or docker commit For example: docker commit nginx mynginx:lastest docker build is relatively complex, but used more
1.3. Container
Container is the running entity of the image. One image can create multiple containers. The essence of running a container is Create a read-write copy of the file system inside the container.
Life cycle:
created: initial creation state
running: running state
stopped: stopped state
paused: paused state
deleted: deleted status
Operation: 1. Create and start the container
Create: docker create -it --name=mynginx mynginx
Start: docker start mynginx
Create and start: docker run -it --name=mynginx mynginx
2. Terminate the container docker stop mynginx
3. Enter the container docker attach mynginx docker exec -it mynginx sh (used more)
4. Delete the container docker rm mynginx Delete the running container: docker rm -f mynginx
5. Export the container docker export mynginx > mynginx.tar
6. Import container docker import mynginx.tar mynginx:import
1.4, warehouse
stores and distributes Docker images; the registration server is The actual server storing the warehouse can contain many warehouses, and each warehouse can contain multiple mirrors.
Public warehouse docker hub https://hub.docker.com/ Login: docker login Push the image to the warehouse: docker push
Use distribution to build a private warehouse https://github.com/distribution/distribution
docker run -d -p 5000:5000 --name registry registry:2.7 docker push localhost:5000/mynginx
1.5. Volumes
can bypass the default joint file system and exist directly on the host in the form of files or directories. superior. It solves the problems of data persistence and sharing data between containers. Operation: 1. Create: docker volume create volume-name
2. -v specifies the path to be persisted. Docker will automatically create the volume for us and bind it to the container. docker run -d --name=nginx-volume -v /usr/share/nginx/html nginx
3. View: docker volume ls
4. Volume details: docker volume inspect volume-name
5, --mount parameter specifies the name of the volume docker run -d --name=nginx --mount source=volume-name,target=/usr/share/nginx/html nginx
6. Delete volume: docker volume rm volume-name
7. Data sharing between volumes: docker run --mount source=lv,target=/tmp/log --name=v-producer -it test docker run -it --name consumer --volumes-from v-producer test
8. Data sharing between volumes and hosts: docker run -v /data:/usr/local/data -it test
1.6. Important components
1. Docker
docker, It is the Docker client, sends requests dockerd, the server entrance, is responsible for receiving requests and returning results docker-init, 1 of the container Process number, manages sub-containers docker-proxy, forwards the host’s network traffic to the container 2, containerd
containerd, responsible for the life cycle management of the container, such as container start, stop, etc... containerd-shim, as the parent process of the container process, decouples containerd and real The container process ctr, the client of containerd, sends a request to containerd during development and debugging 3. Runtime
runc, creates and destroys containers through the system interface
1.7. Container monitoring
docker stats can view the resource usage of CPU, memory, network IO, disk IO, PID and other resources of all containers on the host. cAdvisor is a general container monitoring solution open sourced by Google. Installation reference:
https://www.jianshu.com/p/91f9d9ec374f
View monitoring: http://localhost:8080 http://localhost:8080/containers/ http://localhost:8080/docker/
1.8. Security issues
Self-security vulnerability There are security issues in the image Linux host kernel isolation is not enough
2. Implementation principle
2.1. Namespace
Namespace is a feature of the Linux kernel that can isolate resources such as process ID, host name, user, file name, network and inter-process communication in the same host system.
Docker uses six types: Mount Namespace, mount point isolation PID Namespace, process isolation UTS Namespace, hostname isolation IPC Namespace, inter-process communication isolation User Namespace, user and user group isolation Net Namespace, isolation of network devices, IP addresses and ports
2.2, Cgroups
Restrict processes or process groups Resources, such as CPU, memory, disk IO, etc. Functions of cgroups:
Limit resource usage Different groups can have different usage priorities for CPU, disk IO and other resources Calculate the resource usage of the control group Control the suspension or resumption of the process
2.3. Union File System
Union File System is a layered lightweight file system that can jointly mount the contents of multiple directories into the same directory. Thus forming a single file system.
There are three most commonly used union file systems in Docker: AUFS, Devicemapper and OverlayFS.
AUFS is the earliest and most mature; Devicemapper, a framework provided by the Linux kernel, is a technical framework for mapping block devices. The core concepts include mapped device, target device, and map table, including loop-lvm mode and direct-lvm mode (for production use); overlay2, the update is more stable and has higher requirements for the Linux kernel and Docker versions.
2.4. Network implementation
CNM (Container Network Model) is released by Docker Container networking standard. Libnetwork is open source, written in Golang, fully follows the CNM network specification, and is the official implementation of CNM.
Libnetwork contains four main network models:
null Empty network mode, no container network is provided bridge Bridge mode, containers can communicate with each other host host network mode, the container communicates with the host network container network mode, the container is placed on the same network and accessed through localhost
3. Other related
3.1. Container orchestration
Docker Three commonly used orchestration tools: Docker Compose, Docker Swarm and Kubernetes.
Docker Compose was acquired by Docker. It is essentially a python script that can manage and orchestrate multiple containers on a single node. Docker Swarm is a container cluster management tool officially launched by Docker. It natively supports Docker API. It is simple to operate, supports TLS two-way authentication, and uses the Raft protocol to achieve distribution. Kubernetes, Google draws on the technical design and implementation accumulated by the internal Borg system. It is powerful and aims to support the operation of hundreds of millions of containers; however, its architecture is relatively complex and the threshold for getting started is high.
3.2. Role in devops
The overall goal of DevOps is to promote development Cooperate with operation and maintenance personnel, and shorten the entire delivery cycle of software through automated means to improve software reliability.
Quickly install the development environment through Docker, quickly integrate the Dockerfile to build the image, pull the image and run the container to complete the deployment, and combine with the container orchestration tool to achieve blue-green release.
Promotes the development of DevOps.
Can quickly continuously integrate and deliver.
The above is the detailed content of Docker quick start, core concepts and common instructions. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to exit the container by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:15 PM
How to exit the container by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:15 PM
Four ways to exit Docker container: Use Ctrl D in the container terminal Enter exit command in the container terminal Use docker stop <container_name> Command Use docker kill <container_name> command in the host terminal (force exit)
 How to copy files in docker to outside
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
How to copy files in docker to outside
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
Methods for copying files to external hosts in Docker: Use the docker cp command: Execute docker cp [Options] <Container Path> <Host Path>. Using data volumes: Create a directory on the host, and use the -v parameter to mount the directory into the container when creating the container to achieve bidirectional file synchronization.
 How to restart docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:06 PM
How to restart docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:06 PM
How to restart the Docker container: get the container ID (docker ps); stop the container (docker stop <container_id>); start the container (docker start <container_id>); verify that the restart is successful (docker ps). Other methods: Docker Compose (docker-compose restart) or Docker API (see Docker documentation).
 How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
You can query the Docker container name by following the steps: List all containers (docker ps). Filter the container list (using the grep command). Gets the container name (located in the "NAMES" column).
 How to start mysql by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
How to start mysql by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
The process of starting MySQL in Docker consists of the following steps: Pull the MySQL image to create and start the container, set the root user password, and map the port verification connection Create the database and the user grants all permissions to the database
 How to start containers by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
How to start containers by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Docker container startup steps: Pull the container image: Run "docker pull [mirror name]". Create a container: Use "docker create [options] [mirror name] [commands and parameters]". Start the container: Execute "docker start [Container name or ID]". Check container status: Verify that the container is running with "docker ps".
 How to update the image of docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
How to update the image of docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
The steps to update a Docker image are as follows: Pull the latest image tag New image Delete the old image for a specific tag (optional) Restart the container (if needed)
 How to view logs from docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:24 PM
How to view logs from docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:24 PM
The methods to view Docker logs include: using the docker logs command, for example: docker logs CONTAINER_NAME Use the docker exec command to run /bin/sh and view the log file, for example: docker exec -it CONTAINER_NAME /bin/sh ; cat /var/log/CONTAINER_NAME.log Use the docker-compose logs command of Docker Compose, for example: docker-compose -f docker-com






