redis study notes-string principle
String is the most basic data type of Redis. Not only all keys are string types, but the elements composed of several other data types are also characters. string. Note that the length of the string cannot exceed 512M.
First of all, who stipulated that it cannot exceed 512 M? Or why not exceed 512M?
// 源码定义(检查字符串长度)
static int checkStringLength(redisClient *c, long long size) {
if (size > 512*1024*1024) {
addReplyError(c,"string exceeds maximum allowed size (512MB)");
return REDIS_ERR;
}
return REDIS_OK;
}Fixed by source code check and cannot exceed 512 M.
Let’s take a look at the redis string structure:
struct sdshdr{
// 记录 buf 数组中已使用字节的数量
// 等于 SDS 所保存字符串的长度
int len;
// 记录 buf 数组中未使用字节的数量
int free;
// 字节数组,用于保存字符串
char buf[];
}It can be directly seen that int is 32 bits, so the maximum 4G strings can be supported, but this is not the case.
In order to find out why it cannot exceed 512 M, I found an official answer:
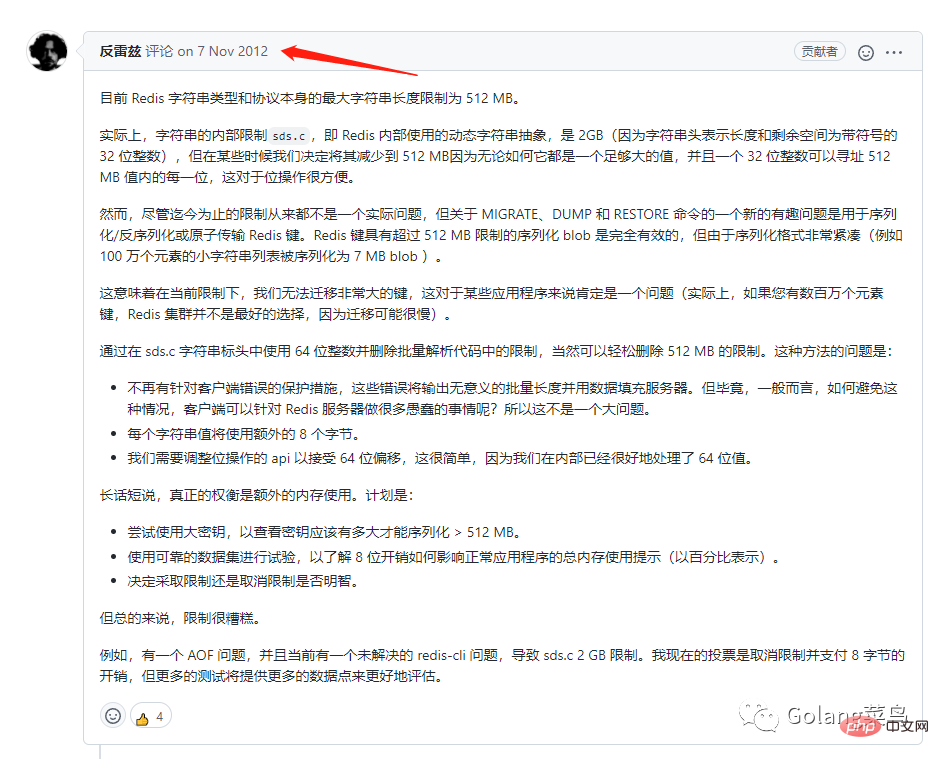
# #Then I discovered that the redis information I had read was out of date!
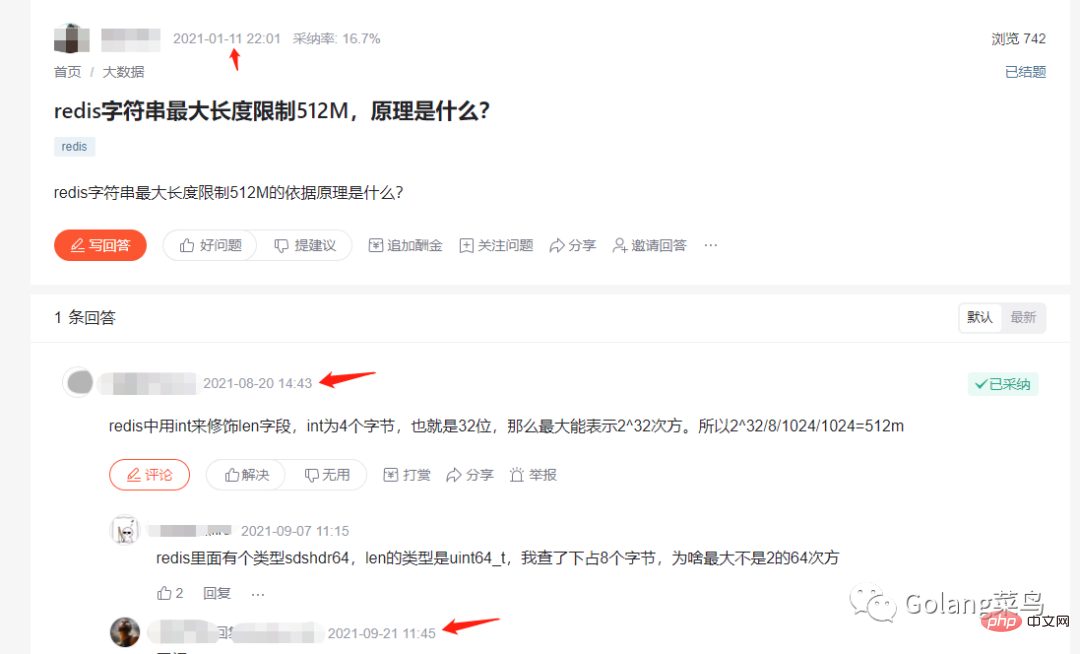
Look, someone else has also been tricked. The versions discussed in this discussion are all before 3.2.
话不多说,继续学习 redis5.0 版本的资料。不过之前学习了的也没事,我们可以一起来看下 redis 的字符串是怎么优化的。
用如下结构来存储长度小于32的短字符串:
struct __attribute__((__packed__)) sdshdr5 {
unsigned char flags; /* 低3位存储类型,高5位存储长度*/
char buf[]; /* 柔性数组,存放实际内容*/
}sdshdr5 结构中,flags占1个字节,其低3位(bit)表示type,高5位(bit)表示长度,能表示的长度区间为0~31(25-1), flags后面就是字符串的内容。
而对于长度大于31的字符串,这个结构就不够用了,所以对于不同长度的字符串,有不同的处理方式:
#define SDS_TYPE_5 0
#define SDS_TYPE_8 1
#define SDS_TYPE_16 2
#define SDS_TYPE_32 3
#define SDS_TYPE_64 4
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr8 {
uint8_t len; /* used */
uint8_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr16 {
uint16_t len; /* used */
uint16_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr32 {
uint32_t len; /* used */
uint32_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};
struct __attribute__ ((__packed__)) sdshdr64 {
uint64_t len; /* used */
uint64_t alloc; /* excluding the header and null terminator */
unsigned char flags; /* 3 lsb of type, 5 unused bits */
char buf[];
};可以看到,这4种结构的成员变量类似,唯一的区别是len和alloc的类型不同。
结构体中4个字段的具体含义分别如下:
1)len:表示buf中已占用字节数。
2)alloc:表示buf中已分配字节数,不同于free,记录的是为buf分配的总长度。
3)flags:标识当前结构体的类型,低3位用作标识位,高5位预留。
4) buf: flexible array, the data space that actually stores strings.
The process of creating a string:
Redis creates SDS through the sdsnewlen function. In the function, the appropriate type will be selected based on the length of the string. After initializing the corresponding statistical value, a pointer to the content of the string will be returned, and different types will be selected based on the length of the string.
For sdshdr5 type, when creating an empty string, it will be cast to sdshdr8. The reason may be that after creating an empty string, its content may be frequently updated and cause expansion, so it is directly created as sdshdr8 when created.
Splicing strings:
sdscatsds is a method exposed to the upper layer, and it ultimately calls sdscatlen. Since the expansion of SDS may be involved, sdsMakeRoomFor is called in sdscatlen to check the capacity of the spliced string s. If expansion is not required, s is returned directly; if expansion is required, the expanded new string s is returned. The length values such as len and curlen in the function do not contain terminators. When splicing, memcpy is used to splice the two strings together and the relevant lengths are specified, so this process ensures binary security. A terminator needs to be added at the end.
String expansion
If the remaining free length available in sds is greater than the length of the new content addlen, directly add Just append to the end of the flexible array buf, no expansion is required.
If the remaining free length available in sds is less than or equal to the length of the newly added content addlen, then discuss it on a case-by-case basis: if the total length after adding is len addlen1MB, the capacity will be expanded according to the new length plus 1MB.
#Finally, reselect the storage type based on the new length and allocate space. If there is no need to change the type here, just expand the flexible array through realloc; otherwise, you need to re-open the memory and move the buf content of the original string to a new location.
#The string contains roughly these contents.
In version 5.0, there is no string limit of 512M. The processing methods of strings are different according to different types, which saves more memory;
The above is the detailed content of redis study notes-string principle. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
On CentOS systems, you can limit the execution time of Lua scripts by modifying Redis configuration files or using Redis commands to prevent malicious scripts from consuming too much resources. Method 1: Modify the Redis configuration file and locate the Redis configuration file: The Redis configuration file is usually located in /etc/redis/redis.conf. Edit configuration file: Open the configuration file using a text editor (such as vi or nano): sudovi/etc/redis/redis.conf Set the Lua script execution time limit: Add or modify the following lines in the configuration file to set the maximum execution time of the Lua script (unit: milliseconds)
 How to set the redis expiration policy
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
How to set the redis expiration policy
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
There are two types of Redis data expiration strategies: periodic deletion: periodic scan to delete the expired key, which can be set through expired-time-cap-remove-count and expired-time-cap-remove-delay parameters. Lazy Deletion: Check for deletion expired keys only when keys are read or written. They can be set through lazyfree-lazy-eviction, lazyfree-lazy-expire, lazyfree-lazy-user-del parameters.
 How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Use the Redis command line tool (redis-cli) to manage and operate Redis through the following steps: Connect to the server, specify the address and port. Send commands to the server using the command name and parameters. Use the HELP command to view help information for a specific command. Use the QUIT command to exit the command line tool.
 How to implement redis counter
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:21 PM
How to implement redis counter
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:21 PM
Redis counter is a mechanism that uses Redis key-value pair storage to implement counting operations, including the following steps: creating counter keys, increasing counts, decreasing counts, resetting counts, and obtaining counts. The advantages of Redis counters include fast speed, high concurrency, durability and simplicity and ease of use. It can be used in scenarios such as user access counting, real-time metric tracking, game scores and rankings, and order processing counting.
 How to optimize the performance of debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:48 AM
How to optimize the performance of debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:48 AM
In Debian systems, readdir system calls are used to read directory contents. If its performance is not good, try the following optimization strategy: Simplify the number of directory files: Split large directories into multiple small directories as much as possible, reducing the number of items processed per readdir call. Enable directory content caching: build a cache mechanism, update the cache regularly or when directory content changes, and reduce frequent calls to readdir. Memory caches (such as Memcached or Redis) or local caches (such as files or databases) can be considered. Adopt efficient data structure: If you implement directory traversal by yourself, select more efficient data structures (such as hash tables instead of linear search) to store and access directory information






