How to use complex data types in Python
1. Sequence:
Sequence is a base class type. Sequence extension types include: string, tuple and list
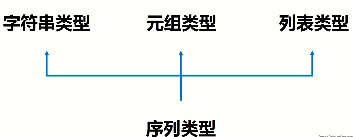
Sequences can be performed Operations include indexing, slicing, adding, multiplying, and checking members.
In addition, Python has built-in methods for determining the length of a sequence and determining the largest and smallest elements.
2. List: [a1, a2], variable data type
List: List is an extension of sequence type, very commonly used
1. Creation of a list
The list is a sequence type and can be modified at will after creation
Use square brackets [] or list() to create , use commas to separate the elements.
Each element type in the list can be different, and there is no length limit
hobby_list = [hobby, 'run', 'girl'] print(id(hobby_list)) # 4558605960 print(type(hobby_list)) # print(hobby_list) # ['read', 'run', 'girl']
If you want to initialize the length to 10 List
list_empty = [None]*10 print(list_empty) # [None, None, None, None, None, None, None, None, None, None]
Use the range() function to create a list:
hobby_list = list(range(5)) # [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
2. Composite list and multidimensional list
hobby_list = ['read', 'run',['girl_name', 18, 'shanghai'] ] print(hobby_list[2][1])# 取出girl的年龄 18
python creates a two-dimensional list and sets the required parameters Just write cols and rows
list_2d = [[0 for i in range(5)] for i in range(5)] list_2d[0].append(3) list_2d[0].append(5) list_2d[2].append(7) print(list_2d) # [[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 3, 5], [0, 0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 7], [0, 0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0, 0]]
The following example converts a 3X4 matrix list into a 4X3 list:
# 以下实例展示了3X4的矩阵列表:
matrix = [
[1, 2, 3, 4],
[5, 6, 7, 8],
[9, 10, 11, 12],
]
# 以下实例将3X4的矩阵列表转换为4X3列表:
transposed=[[row[i] for row in matrix] for i in range(4)]
print(transposed)
# [[1, 5, 9], [2, 6, 10], [3, 7, 11], [4, 8, 12]]
# 以下实例也可以使用以下方法来实现:
transposed = []
for i in range(4):
transposed.append([row[i] for row in matrix])
print(transposed)
# [[1, 5, 9], [2, 6, 10], [3, 7, 11], [4, 8, 12]]3. List index value
The index sequence number starts from 0 .
hobby_list = ['read', 'run', 'girl'] # 索引序号 0 1 2 print(hobby_list[1])# 取出第二个爱好 <code>run
4. List modification
You can modify or update the data items of the list. You can also use the append() method to add list items,
hobby_list = ['read', 'run', 'girl'] hobby_list[0] = 'write'
List method This makes the list easy to use as a stack. For a specific data structure like a stack, the last element inserted is the first to be removed (first in, last out).
Use the append() method to add an element to the top of the stack. Use the pop() method to remove the element at the top of the stack without specifying an index.
append: Add an element x at the end of the list ls
pop(): Move Remove an element in the list (the last element by default) and return the value of the element
For example:
stack = [3, 4, 5] stack.append(6) stack.append(7) print(stack) # [3, 4, 5, 6, 7] print(stack.pop()) # 7 print(stack) # [3, 4, 5, 6] print(stack.pop()) # 6 print(stack.pop()) # 5 print(stack) # [3, 4]
3. List comprehension
List comprehensions provide a simple way to create lists from sequences. Typically applications apply some operations to each element of a sequence and use the result as an element to generate a new list, or create a subsequence based on certain criteria.
Every list comprehension begins with for followed by an expression, and then zero or more for or if clauses.
The generated list is defined by the expressions in the context that follow the for and if statements. If you want the expression to derive a tuple, you must use parentheses.
1. List comprehension writing form:
[expression for variable in list]
[expression for Variable in list if condition]
Example:
print([i for i in range(10)] ) # [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
print([i ** 2 for i in range(10)]) # [0, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81]
print([0 for i in range(5)]) #[0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
name_list = ['nick', 'sean', 'jason', 'tank']
for n in [name if name == 'nick' else name + '_a' for name in name_list] :
print(n) # 'nick', 'sean_a', 'jason_a', 'tank_a'
li = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
print( [x ** 2 for x in li]) # [1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81]
print( [x ** 2 for x in li if x > 5]) # [36, 49, 64, 81]
print(dict([(x, x * 10) for x in li])) # {1: 10, 2: 20, 3: 30, 4: 40, 5: 50, 6: 60, 7: 70, 8: 80, 9: 90} #生成字典
vec1 = [2, 4, 6]
vec2 = [4, 3, -9]
sq = [vec2[i] + vec2[i] for i in range(len(vec))] # 实现列表相加
print(sq)
# [6, 7, -3]
testList = [1, 2, 3, 4]
def mul2(x):
return x * 2
print([mul2(i) for i in testList]) #使用复杂表达式或嵌套函数:
# [2, 4, 6, 8]2. The nested
statements of the list comprehension are nested relationships.
The second statement on the left is the outermost layer, go one level to the right, and the first statement on the left is the last level.
[x*y for x in range(1,5) if x > 2 for y in range(1,4) if y < 3]
His execution order is:
for x in range(1,5)
if x > 2
for y in range(1,4)
if y < 3
x*yExample
print( [ (x, y) for x in range(10) if x % 2 if x > 3 for y in range(10) if y > 7 if y != 8]) #生成元组 # [(5, 9), (7, 9), (9, 9)] print([x * y for x in [1, 2, 3] for y in [1, 2, 3]]) # [1, 2, 3, 2, 4, 6, 3, 6, 9]
4. Basic operations of lists
ls1 = ['python', 123]
ls2 = ['java', 456]
print(ls1 * 2); # ['python', 123, 'python', 123] 将列表复制n次。
print(ls1 + ls2); # ['python', 123, 'java', 456] 连接两个列表
name_list = ['nick', 'jason', 'tank', 'sean']
del name_list[2] # 删除索引2位置后的元素
print(name_list) # ['nick', 'jason', 'sean']
del name_list[2:4] # 从列表中删除切片 ,删除第i-j位置的元素
print(name_list) # ['nick', 'jason']
del name_list[:] #清空整个列表
print(name_list) # []
del a # 用 del 删除实体变量:
name_list = ['nick', 'jason', 'tank', 'sean']
print('tank sb' in name_list) # 成员运算:in; False
print('nick handsome' not in name_list) # 成员运算:in;True
name_list = ['nick', 'jason', 'tank', 'sean']
for name in name_list: # for循环
print(name)
a = ['Google', 'Baidu', 'Runoob', 'Taobao', 'QQ']
for i in range(len(a)): # 结合range()和len()函数以遍历一个序列的索引
print(i, a[i])
# 0 Google 1 Baidu 2 Runoob 3 Taobao 4 QQ
name_list = ['nick', 'jason', 'tank', 'sean']
print(name_list[0:3:2] ) # 切片 ['nick', 'tank']Example: There is the following list, and the list elements are Cannot hash type, remove duplicates, get a new list, and the new list must maintain the original order of the list
stu_info_list = [
{'name': 'nick', 'age': 19, 'sex': 'male'},
{'name': 'egon', 'age': 18, 'sex': 'male'},
{'name': 'tank', 'age': 20, 'sex': 'female'},
{'name': 'tank', 'age': 20, 'sex': 'female'},
{'name': 'egon', 'age': 18, 'sex': 'male'},
]
new_stu_info_list = []
for stu_info in stu_info_list:
if stu_info not in new_stu_info_list:
new_stu_info_list.append(stu_info)
for new_stu_info in new_stu_info_list:
print(new_stu_info)5. List related functions
name_list = ['nick', 'jason', 'tank', 'sean'] print(len(name_list)) # 4 列表元素个数:len; print(min(name_list)) # jason 返回序列s的最小元素; print(max(name_list)) # tank 返回序列s的最大元素 name_list = ['nick', 'jason', 'tank', 'sean'] name_list.insert(1, 'handsome') # insert(i,x):在列表的第i位置增加元素x print(name_list) # ['nick', 'handsome', 'jason', 'tank', 'sean'] name_list = ['nick', 'jason', 'tank', 'sean'] print(name_list.remove('nick')) # remove(x):将列表ls中出现的第一个元素x删除 ,None ; print(name_list) # ['jason', 'tank', 'sean'] name_list = ['nick', 'jason', 'tank', 'sean'] print(name_list.count('nick')) # 1 ;统计某个元素在列表中出现的次数 name_list = ['nick', 'jason', 'tank', 'sean'] print(name_list.index('nick')) # 0;返回元素所在列表中的索引 name_list = ['nick', 'jason', 'tank', 'sean'] name_list.clear() # 删除列表中所有元素 print(name_list) # [] name_list = ['nick', 'jason', 'tank', 'sean'] print(name_list.copy()) # 生成一个新列表,赋值原列表中所有元素 ['nick', 'jason', 'tank', 'sean'] name_list = ['nick', 'jason', 'tank', 'sean'] name_list2 = ['nick handsome'] name_list.extend(name_list2) # 在列表末尾一次性追加另一个序列中的多个值(用新列表扩展原来的列表) print(name_list) # ['nick', 'jason', 'tank', 'sean', 'nick handsome'] name_list = ['nick', 'jason', 'tank', 'sean'] name_list.reverse() # 将列表ls中的元素反转 print(name_list) # ['sean', 'tank', 'jason', 'nick'] name_list = ['nick', 'jason', 'tank', 'sean'] name_list.sort() # 排序,使用用sort列表的元素必须是同类型的 print(name_list) # ['jason', 'nick', 'sean', 'tank'] name_list.sort(reverse=True) # 倒序 print(name_list) # ['tank', 'sean', 'nick', 'jason']
6. Tuple (tuple): (a1 , a2)
1. Creation of tuples
Tuples are a list type and cannot be modified once created.
color = (0x001100, "blue", creature) # 使用小括号 () 或 tuple() 创建,元素间用逗号分隔。 print(type(color)) # creature = "cat", "dog", "tiger", "human" # 可以使用或不使用小括号。即元组由若干逗号分隔的值组成。 print(type(creature)) #
Note the difference from strings:
name_str = ('egon') # ()只是普通包含的意思 name_tuple = ('egon',) # 元组中只包含一个元素时,需要在元素后面添加逗号,否则括号会被当作字符串使用: print(type(name_str)) # print(type(name_tuple)) #
2. Tuple operations
Index value, slicing (ignoring the head) tail, step size), length len, member operations in and not in, loops, count, index, etc. are all the same as the list, but the value is not changed.
The element values in the tuple are not allowed to be modified, but we can connect and combine the tuples, as shown in the following example:
tup1 = (12, 34.56); tup2 = ('abc', 'xyz') # 以下修改元组元素操作是非法的。 # tup1[0] = 100 # 创建一个新的元组 tup3 = tup1 + tup2; print(tup3) # (12, 34.56, 'abc', 'xyz')
3, namedtuple (named tuple): An upgraded version of Python tuples
from collections import namedtuple User = namedtuple('User', 'name sex age') # 定义一个namedtuple类型User,并包含name,sex和age属性。 user = User(name='Runoob', sex='male', age=12) # 创建一个User对象 print(user.age) # 12
The above is the detailed content of How to use complex data types in Python. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1664
1664
 14
14
 1423
1423
 52
52
 1317
1317
 25
25
 1268
1268
 29
29
 1246
1246
 24
24
 PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP is mainly procedural programming, but also supports object-oriented programming (OOP); Python supports a variety of paradigms, including OOP, functional and procedural programming. PHP is suitable for web development, and Python is suitable for a variety of applications such as data analysis and machine learning.
 Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP is suitable for web development and rapid prototyping, and Python is suitable for data science and machine learning. 1.PHP is used for dynamic web development, with simple syntax and suitable for rapid development. 2. Python has concise syntax, is suitable for multiple fields, and has a strong library ecosystem.
 PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP originated in 1994 and was developed by RasmusLerdorf. It was originally used to track website visitors and gradually evolved into a server-side scripting language and was widely used in web development. Python was developed by Guidovan Rossum in the late 1980s and was first released in 1991. It emphasizes code readability and simplicity, and is suitable for scientific computing, data analysis and other fields.
 How to run sublime code python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
How to run sublime code python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
To run Python code in Sublime Text, you need to install the Python plug-in first, then create a .py file and write the code, and finally press Ctrl B to run the code, and the output will be displayed in the console.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 Golang vs. Python: Performance and Scalability
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Golang vs. Python: Performance and Scalability
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:18 AM
Golang is better than Python in terms of performance and scalability. 1) Golang's compilation-type characteristics and efficient concurrency model make it perform well in high concurrency scenarios. 2) Python, as an interpreted language, executes slowly, but can optimize performance through tools such as Cython.
 Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Writing code in Visual Studio Code (VSCode) is simple and easy to use. Just install VSCode, create a project, select a language, create a file, write code, save and run it. The advantages of VSCode include cross-platform, free and open source, powerful features, rich extensions, and lightweight and fast.
 How to run python with notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
How to run python with notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:33 PM
Running Python code in Notepad requires the Python executable and NppExec plug-in to be installed. After installing Python and adding PATH to it, configure the command "python" and the parameter "{CURRENT_DIRECTORY}{FILE_NAME}" in the NppExec plug-in to run Python code in Notepad through the shortcut key "F6".




