Microservice principles and implementation in Go language
With the rapid development of the Internet and the continuous updating of technology, the microservice architecture model has been adopted by more and more enterprises, and the Go language, as a lightweight, high-concurrency, and high-performance language, has also It has attracted much attention for its excellent performance in microservice scenarios. This article will start from the principles of microservices and explore the application of Go language in microservices.
1. Principle of microservice architecture
Microservice architecture is a model that splits the system into small services that are deployed independently. Each service has its own responsibilities and data storage method. And cooperate with each other through lightweight communication methods to realize the functions of the overall system. This model has the following characteristics:
1. Loose coupling: Microservices are designed to be independent of each other. They do not share code and data, so the degree of coupling between them is very low. Low.
2. High scalability: Since each microservice can be deployed and upgraded independently, the microservice architecture is very easy to achieve horizontal expansion, thus meeting the needs of high-concurrency environments.
3. Strong fault tolerance: Each microservice is independent, and failures between them will not affect the operation of the entire system, thus improving the fault tolerance of the entire system.
4. Technology heterogeneity: Each microservice can be different in technology stack, so the entire system can use different technology stacks to implement different parts of the service to improve development efficiency.
5. Rapid delivery: Each microservice can be deployed independently, so system delivery becomes more flexible and faster.
2. Application of Go language in microservices
Go language is a compiled language with fast compilation speed, efficient memory management and concurrent processing capabilities. It is very suitable for microservices. Used in service scenarios. The following introduces the application of Go language in microservices.
1. Service registration and discovery
An important issue that needs to be solved in the microservice architecture is the registration and discovery of services, that is, how to enable services to register themselves and be discovered by other services. Commonly used service registration and discovery tools in Go language include consul and etcd. Both of these tools can easily solve service registration and discovery problems in microservices.
2. Lightweight communication method
The Go language provides lightweight RPC frameworks, such as gRPC and Micro, which can be used for remote calls between services. gRPC is a standard open source RPC framework that supports multiple languages and supports advanced features such as transport security and streams, encoding and decoding. Micro is a microservice framework that is specifically used to handle operations such as service registration, discovery, load balancing, and remote invocation.
3. High concurrency performance
Since the Go language naturally supports concurrency, it is more suitable for use in high-concurrency microservice scenarios. In the Go language, goroutine is a lightweight thread with very little startup and switching overhead, so it is very suitable for handling multiple concurrent requests. In addition, the channel provided by the Go language standard library can also be used for concurrent processing. It is a data structure that can safely transfer data between goroutines and is very suitable for message passing operations in microservices.
4. Easy to build and deploy
In the Go language, since the compilation and deployment of code is very simple, it is very convenient to quickly build and deploy microservices. The standard library of the Go language provides some packages for web development, such as net/http and html/template, which can be used to quickly build web applications. In addition, the Go language also supports multi-platform compilation, so Go programs can be run on different operating systems and hardware platforms.
3. Go language microservice practice
The best example of Go language microservice practice is Kubernetes used internally by Google. It is currently one of the most popular container orchestration tools. Ability to support automated deployment, scaling and updates. Kubernetes is written in Go language, which provides many abstract concepts based on microservices, such as Pod, Service, Deployment, ConfigMap, etc., which is very consistent with the design idea of microservice architecture.
In addition, Docker is also a widely used containerization tool that works with Kubernetes to achieve a more flexible and reliable microservice architecture.
4. Conclusion
This article introduces the basic principles of microservice architecture and the application of Go language in microservices. Given that the microservice architecture provides many building blocks that help build scalability, the Go language, as a high-performance, high-concurrency development language, is very suitable for use in microservice scenarios. Therefore, microservice architecture and Go language are very good choices for applications that need to achieve high scalability, high concurrency, and rapid iteration.
The above is the detailed content of Microservice principles and implementation in Go language. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1664
1664
 14
14
 1423
1423
 52
52
 1321
1321
 25
25
 1269
1269
 29
29
 1249
1249
 24
24
 PHP Frameworks and Microservices: Cloud Native Deployment and Containerization
Jun 04, 2024 pm 12:48 PM
PHP Frameworks and Microservices: Cloud Native Deployment and Containerization
Jun 04, 2024 pm 12:48 PM
Benefits of combining PHP framework with microservices: Scalability: Easily extend the application, add new features or handle more load. Flexibility: Microservices are deployed and maintained independently, making it easier to make changes and updates. High availability: The failure of one microservice does not affect other parts, ensuring higher availability. Practical case: Deploying microservices using Laravel and Kubernetes Steps: Create a Laravel project. Define microservice controllers. Create Dockerfile. Create a Kubernetes manifest. Deploy microservices. Test microservices.
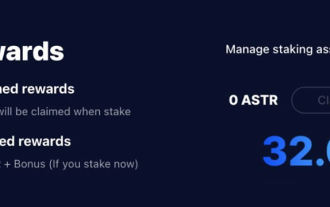 Astar staking principle, income dismantling, airdrop projects and strategies & operation nanny-level strategy
Jun 25, 2024 pm 07:09 PM
Astar staking principle, income dismantling, airdrop projects and strategies & operation nanny-level strategy
Jun 25, 2024 pm 07:09 PM
Table of Contents Astar Dapp Staking Principle Staking Revenue Dismantling of Potential Airdrop Projects: AlgemNeurolancheHealthreeAstar Degens DAOVeryLongSwap Staking Strategy & Operation "AstarDapp Staking" has been upgraded to the V3 version at the beginning of this year, and many adjustments have been made to the staking revenue rules. At present, the first staking cycle has ended, and the "voting" sub-cycle of the second staking cycle has just begun. To obtain the "extra reward" benefits, you need to grasp this critical stage (expected to last until June 26, with less than 5 days remaining). I will break down the Astar staking income in detail,
 How does the Java framework support horizontal scaling of microservices?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 04:34 PM
How does the Java framework support horizontal scaling of microservices?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 04:34 PM
The Java framework supports horizontal expansion of microservices. Specific methods include: Spring Cloud provides Ribbon and Feign for server-side and client-side load balancing. NetflixOSS provides Eureka and Zuul to implement service discovery, load balancing and failover. Kubernetes simplifies horizontal scaling with autoscaling, health checks, and automatic restarts.
 Java framework's microservice architecture data consistency guarantee
Jun 02, 2024 am 10:00 AM
Java framework's microservice architecture data consistency guarantee
Jun 02, 2024 am 10:00 AM
Data consistency guarantee in microservice architecture faces the challenges of distributed transactions, eventual consistency and lost updates. Strategies include: 1. Distributed transaction management, coordinating cross-service transactions; 2. Eventual consistency, allowing independent updates and synchronization through message queues; 3. Data version control, using optimistic locking to check for concurrent updates.
 What role does Spring Boot play in microservices architecture?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 02:34 PM
What role does Spring Boot play in microservices architecture?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 02:34 PM
SpringBoot plays a crucial role in simplifying development and deployment in microservice architecture: providing annotation-based automatic configuration and handling common configuration tasks, such as database connections. Support verification of API contracts through contract testing, reducing destructive changes between services. Has production-ready features such as metric collection, monitoring, and health checks to facilitate managing microservices in production environments.
 Create distributed systems using the Golang microservices framework
Jun 05, 2024 pm 06:36 PM
Create distributed systems using the Golang microservices framework
Jun 05, 2024 pm 06:36 PM
Create a distributed system using the Golang microservices framework: Install Golang, choose a microservices framework (such as Gin), create a Gin microservice, add endpoints to deploy the microservice, build and run the application, create an order and inventory microservice, use the endpoint to process orders and inventory Use messaging systems such as Kafka to connect microservices Use the sarama library to produce and consume order information
 Microservice architecture monitoring and alarming in Java framework
Jun 02, 2024 pm 12:39 PM
Microservice architecture monitoring and alarming in Java framework
Jun 02, 2024 pm 12:39 PM
Microservice architecture monitoring and alarming in the Java framework In the microservice architecture, monitoring and alarming are crucial to ensuring system health and reliable operation. This article will introduce how to use Java framework to implement monitoring and alarming of microservice architecture. Practical case: Use SpringBoot+Prometheus+Alertmanager1. Integrate Prometheus@ConfigurationpublicclassPrometheusConfig{@BeanpublicSpringBootMetricsCollectorspringBootMetric
 PHP framework and microservices: data consistency and transaction management
Jun 02, 2024 pm 04:59 PM
PHP framework and microservices: data consistency and transaction management
Jun 02, 2024 pm 04:59 PM
In PHP microservice architecture, data consistency and transaction management are crucial. The PHP framework provides mechanisms to implement these requirements: use transaction classes, such as DB::transaction in Laravel, to define transaction boundaries. Use an ORM framework, such as Doctrine, to provide atomic operations such as the lock() method to prevent concurrency errors. For distributed transactions, consider using a distributed transaction manager such as Saga or 2PC. For example, transactions are used in online store scenarios to ensure data consistency when adding to a shopping cart. Through these mechanisms, the PHP framework effectively manages transactions and data consistency, improving application robustness.




