How to use MySQL's binlog, redo log and undo log

1. Binlog
Binlog is used to record information about write operations performed in the database. It excludes query operations and is saved on disk in binary format. . Binlog is the logical log of mysql and is recorded by the server layer. Mysql databases using any storage engine will record binlog logs.
Logical log: can be simply understood as a sql statement;
Physical log: The data in MySQL is stored in the data page. The physical log records changes on the data page; insert the code snippet here
The binlog is written by appending, and the size of each binlog file can be set through the max_binlog_size parameter. , when the file size reaches the given value, a new file will be generated to save the log.
binlog usage scenarios
Project In actual applications, there are two main usage scenarios for binlog, namely master-slave replication and data recovery.
Master-slave replication: Enable binlog on the Master side, and then send the binlog to each Slave side. The Slave side replays the binlog to achieve master-slave data consistency.
Data recovery: Recover data by using the mysqlbinlog tool.
MySQL master-slave synchronization principle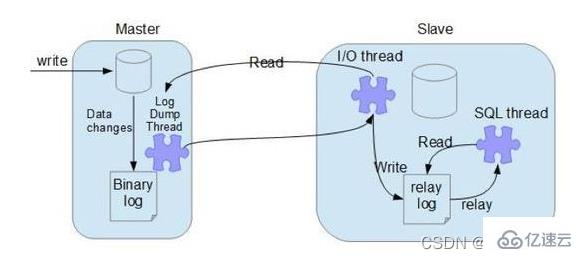
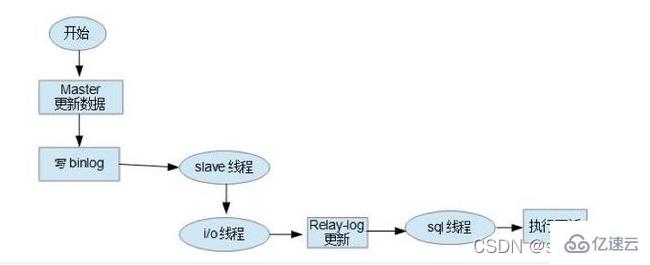
- ##Master node binlog dump thread
When the slave node connects to the master node, the master node will create a log dump thread to send the contents of the binlog. When reading operations in the binlog, this thread will lock the binlog on the master node. When the read is completed, the lock will be released even before launching to the slave node;
- Slave node I/O thread
When the start slave command is executed on the slave node, the slave node will create an I/O thread to connect to the master node and request the updated binlog in the master library. After the I/O thread receives the update from the master node binlog dump process, it saves it in the local relaylog;
- Slave node SQL thread
The SQL thread is responsible for reading the relaylog The content is parsed into specific operations and executed, ultimately ensuring the consistency of master-slave data;
MySQL database master-slave synchronization principle
binlog content As mentioned above, binlog is a logical log, which can be simply understood as a sql statement, but in fact it also contains the reverse logic of the executed sql statement. delete corresponds to delete itself and the reverse insert information; update contains information about the data rows before and after the corresponding update is executed; insert contains its own insert and corresponding delete information.
binlog format There are three binlog formats, namely statement, row and mixed. Before MySQL 5.7.7, statement was used by default, and after MySQL 5.7.7, row was used by default. The format of the log can be modified through binlog-format in the my.ini configuration file.
(1) Statement: Statement-based replication (SBR) based on SQL statements. Each SQL statement that modifies data will be recorded in the binlog.
- Advantages: No need to specifically record changes in a certain row, saving space, reducing IO, and improving performance;
- Disadvantages: When executing sysdate( ) or sleep() and other operations, it may lead to inconsistency between master and slave data;
- Advantages: The details of each row record modification are recorded in great detail, so there will be no situation where the data cannot be copied correctly;
- Disadvantages : Since the details of each record modification will be recorded in great detail, a large amount of log content will be generated. Assume that there is an update statement and many records are modified. Each modified record will be recorded in the binlog. In particular, for the alter table operation, due to changes in the table structure, each row of records will change, resulting in a sudden increase in log volume;
In particular, as mentioned above, the new version (after MySQL 5.7.7) uses the row format by default. The row here has also been optimized accordingly. When encountering the alter table operation, the statement format is used for recording. The rest Operations still use row format.
binlog flushing timing
For the InnoDB storage engine, the binlog will only be recorded when the transaction is submitted. At this time, the record is still in the memory, and MySQL passes sync_binlog controls the flushing timing of binlog. The value range is 0-N:0: It is not forced to flush to the disk, and the system will decide when to write to the disk;
1: The binlog must be written after each submission. Write to the disk;
N: Every N transactions, the binlog will be written to the disk;
As can be seen from the above , the safest setting for sync_binlog is 1, which is also the default value for MySQL versions after 5.7.7. However, setting a larger value can improve database performance. Therefore, in actual situations, you can also increase the value appropriately and sacrifice a certain degree of consistency to obtain better performance.
Physical file size of binlog
You can control the size of binlog by configuring the max_binlog_size parameter, which is located in the my.ini configuration file. The system will create a new file to continue to store logs when the size of the log exceeds the capacity limit of the binlog file. What should I do when a transaction is relatively large, or when there are more and more logs, and the physical space it occupies is too large? MySQL provides an automatic deletion mechanism, which can be solved by configuring the expire_logs_days parameter in the my.ini configuration file. The unit is days. When this parameter is 0, it means it will never be deleted; when it is N, it means it will be automatically deleted after the Nth day.
2. redo log
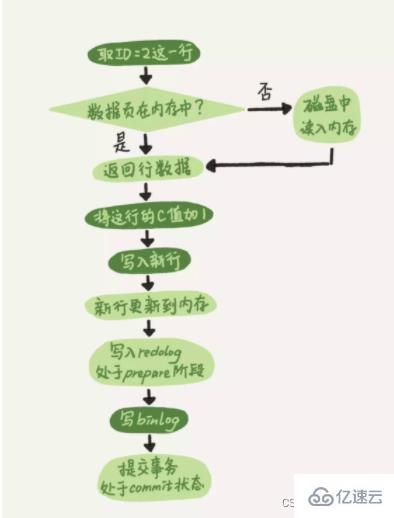
redolog is the proprietary log system of the InnoDB engine. It is mainly used to achieve transaction durability and crash-safe functions. Redolog is a physical log, which records the specific modifications on the data page after the SQL statement is executed.
We all know that when MySQL is running, data will be loaded from disk into memory. When a SQL statement is executed to modify the data, the modified content is actually only temporarily saved in the memory. If the power is cut off or other circumstances occur at this time, these modifications will be lost. Therefore, after modifying the data, MySQL will look for opportunities to flush these memory records back to the disk. But there is a performance problem, mainly in two aspects:
InnoDB interacts with the disk in data units of pages, and a transaction may only modify a few bytes on a page. , if a complete data page is flushed back to the disk, it will waste resources;
A transaction may involve multiple data pages. These data pages are only logically continuous but not physically continuous. Use random IO The performance is too poor;
Therefore, MySQL designed redolog to record the specific modifications made to the data page by the transaction, and then flush the redolog back to the disk. You may have doubts. Originally, I wanted to reduce io. Wouldn’t this add another io? The designers of InnoDB have taken these into consideration at the beginning of the design. Redo log files are usually small, and sequential I/O is used during disk flushing. Better performance compared to random I/O.
Basic concepts of redo log
Redolog consists of two parts, one is the log cache redo log buffer in the memory, and the other is the log file redo log file in the disk. Every time the data record is modified, these modifications will be written to the redo log buffer first, and then wait for the appropriate opportunity to flush the modifications in the memory back to the redo log file. This technology of writing logs first and then writing to disk is WAL (Write-Ahead Logging) technology. It should be noted that the redolog is flushed back to disk before the data page. Modifications to the clustered index, secondary index, and undo page all need to be recorded in the redolog.
In computer operating systems, buffer data in user space generally cannot be written directly to the disk, and must pass through the operating system kernel space buffer (OS Buffer). ). Therefore, writing the redo log buffer to the redo log file actually writes it to the OS Buffer first, and then flushes it to the redo log file through the system call fsync(). The process is as follows: 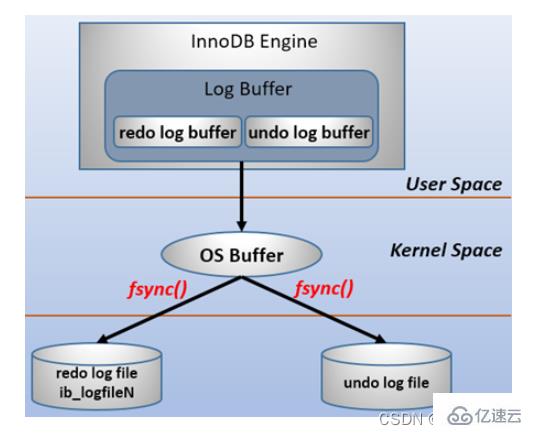
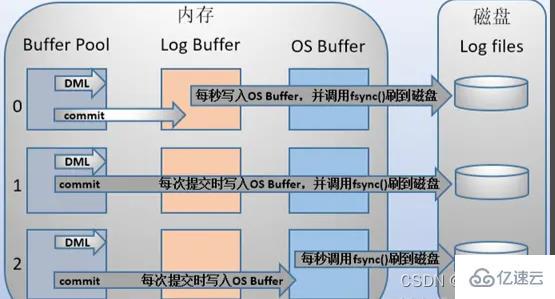
mysql support Three timings for writing redo log buffer to redo log file can be configured through the innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit parameter. The meaning of each parameter value is as follows:
| Parameter value | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 0 (delayed writing) | When the transaction is committed, the log in the redo log buffer will not be written to the os buffer, but every second Write to the os buffer and call fsync() to write to the redo log file. That is to say, when set to 0, data is written to the disk (approximately) every second. When the system crashes, 1 second of data will be lost. |
| 1 (real-time writing, real-time brushing) | Every time a transaction is submitted, the log in the redo log buffer will be written to the os buffer and fsync() will be called to flush to redo log file. This method will not lose any data even if the system crashes, but because each submission is written to the disk, the IO performance is poor. |
| 2 (real-time writing, delayed brushing) | Each submission is only written to the os buffer, and then fsync() is called every second to write the data in the os buffer The log is written to the redo log file. |
redo log recording format
Redolog adopts a fixed size and cyclic writing format. When the redolog is full, it will be written from the beginning again. Why is it designed like this?
The main purpose of redo log is to reduce the requirement for data page flushing. Redolog records the modifications on the data page, but when the data page is also flushed back to the disk, these records become useless. Therefore, when MySQL determines that the previous redolog has expired, the new data will overwrite the invalid data. So how to judge whether it should be covered? 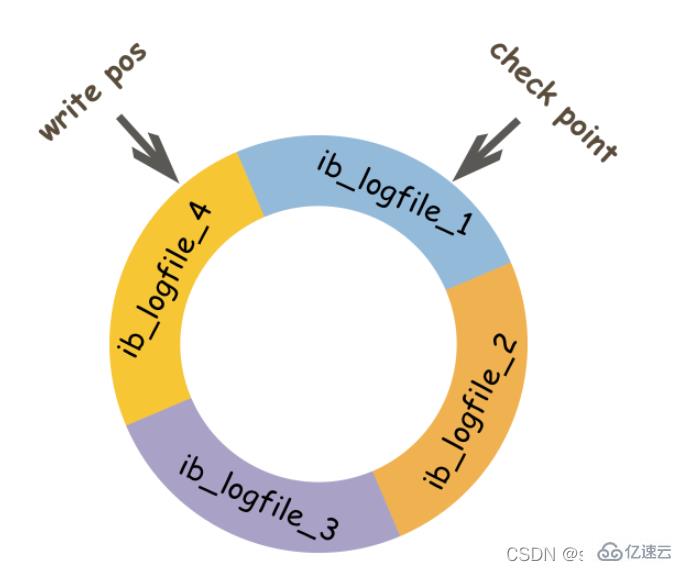
The above picture is a schematic diagram of redo log file. write pos represents the log sequence number LSN (log sequence number) currently recorded by redolog. When the data page has been flushed back to the disk, the LSN in the redo log file will be updated, indicating that the data before this LSN has been written to the disk. This LSN is the check point. The part between write pos and check point is the spare part of redolog, which is used to record new records; the part between check point and write pos is the modified part of the data page that redolog has recorded, but the data page has not been flushed back to the disk at this time. part. When the write pos catches up with the check point, it will first push the check point forward, vacate the position, and then record a new log.
When starting innodb, regardless of whether it was shut down normally or abnormally last time, recovery operations will always be performed. During recovery, the LSN in the data page will be checked first. If this LSN is smaller than the LSN in the redolog, that is, the write pos position, it means that the unfinished operations on the data page are recorded in the redolog, and then it will start from the nearest check point. , start synchronizing data.
Is it possible that the LSN in the data page is greater than the LSN in the redolog? The answer is of course possible. When this happens, the part beyond the redolog will not be redone, because this itself means that what has been done does not need to be redone.
The difference between redo log and binlog
| binlog | ||
|---|---|---|
| The size of the redo log is fixed. | Binlog can set the size of each binlog file through the configuration parameter max_binlog_size. | |
| The redo log is implemented by the InnoDB engine layer, and not all engines have it. | Binlog is implemented by the Server layer. All engines can use binlog logs | |
| redo log is recorded in a loop writing method. When writing to the end, it will return to the beginning and write the log in a loop. | binlog is recorded by appending. When the file size is larger than the given value, subsequent logs will be recorded to new files | |
| redo log is suitable for crash recovery (crash-safe) | binlog is suitable for master-slave replication and data recovery |
The above is the detailed content of How to use MySQL's binlog, redo log and undo log. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1662
1662
 14
14
 1419
1419
 52
52
 1311
1311
 25
25
 1262
1262
 29
29
 1235
1235
 24
24
 MySQL's Role: Databases in Web Applications
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
MySQL's Role: Databases in Web Applications
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
The main role of MySQL in web applications is to store and manage data. 1.MySQL efficiently processes user information, product catalogs, transaction records and other data. 2. Through SQL query, developers can extract information from the database to generate dynamic content. 3.MySQL works based on the client-server model to ensure acceptable query speed.
 Laravel Introduction Example
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
Laravel Introduction Example
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
Laravel is a PHP framework for easy building of web applications. It provides a range of powerful features including: Installation: Install the Laravel CLI globally with Composer and create applications in the project directory. Routing: Define the relationship between the URL and the handler in routes/web.php. View: Create a view in resources/views to render the application's interface. Database Integration: Provides out-of-the-box integration with databases such as MySQL and uses migration to create and modify tables. Model and Controller: The model represents the database entity and the controller processes HTTP requests.
 How to start mysql by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
How to start mysql by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
The process of starting MySQL in Docker consists of the following steps: Pull the MySQL image to create and start the container, set the root user password, and map the port verification connection Create the database and the user grants all permissions to the database
 MySQL and phpMyAdmin: Core Features and Functions
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:12 AM
MySQL and phpMyAdmin: Core Features and Functions
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:12 AM
MySQL and phpMyAdmin are powerful database management tools. 1) MySQL is used to create databases and tables, and to execute DML and SQL queries. 2) phpMyAdmin provides an intuitive interface for database management, table structure management, data operations and user permission management.
 Solve database connection problem: a practical case of using minii/db library
Apr 18, 2025 am 07:09 AM
Solve database connection problem: a practical case of using minii/db library
Apr 18, 2025 am 07:09 AM
I encountered a tricky problem when developing a small application: the need to quickly integrate a lightweight database operation library. After trying multiple libraries, I found that they either have too much functionality or are not very compatible. Eventually, I found minii/db, a simplified version based on Yii2 that solved my problem perfectly.
 Laravel framework installation method
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
Laravel framework installation method
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
Article summary: This article provides detailed step-by-step instructions to guide readers on how to easily install the Laravel framework. Laravel is a powerful PHP framework that speeds up the development process of web applications. This tutorial covers the installation process from system requirements to configuring databases and setting up routing. By following these steps, readers can quickly and efficiently lay a solid foundation for their Laravel project.
 MySQL vs. Other Programming Languages: A Comparison
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:22 AM
MySQL vs. Other Programming Languages: A Comparison
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Compared with other programming languages, MySQL is mainly used to store and manage data, while other languages such as Python, Java, and C are used for logical processing and application development. MySQL is known for its high performance, scalability and cross-platform support, suitable for data management needs, while other languages have advantages in their respective fields such as data analytics, enterprise applications, and system programming.
 MySQL for Beginners: Getting Started with Database Management
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:10 AM
MySQL for Beginners: Getting Started with Database Management
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:10 AM
The basic operations of MySQL include creating databases, tables, and using SQL to perform CRUD operations on data. 1. Create a database: CREATEDATABASEmy_first_db; 2. Create a table: CREATETABLEbooks(idINTAUTO_INCREMENTPRIMARYKEY, titleVARCHAR(100)NOTNULL, authorVARCHAR(100)NOTNULL, published_yearINT); 3. Insert data: INSERTINTObooks(title, author, published_year)VA