What is the process of installing mysql under linux?
Preparation before installation
1. Check whether mysql has been installed and execute the command
[root@localhost /]# rpm -qa | grep mysql
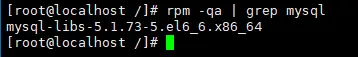
From the execution result, we can see that we have installed it mysql-libs-5.1.73-5.el6_6.x86_64, execute the delete command
[root@localhost /]# rpm -e --nodeps mysql-libs-5.1.73-5.el6_6.x86_64
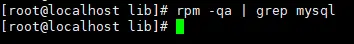
Execute the query command again to check whether it is deleted
[root@localhost /]# rpm -qa | grep mysql
2. Query all folders corresponding to Mysql
[root@localhost /]# whereis mysqlmysql: /usr/bin/mysql /usr/include/mysql[root@localhost lib]# find / -name mysql/data/mysql/data/mysql/mysql
Delete related directories or files
[root@localhost /]# rm -rf /usr/bin/mysql /usr/include/mysql /data/mysql /data/mysql/mysql
Verify whether the deletion is complete
[root@localhost /]# whereis mysql mysql:[root@localhost /]# find / -name mysql[root@localhost /]#
3. Check the mysql user group and whether the user exists, if not, create
[root@localhost /]# cat /etc/group | grep mysql[root@localhost /]# cat /etc/passwd |grep mysql[root@localhost /]# groupadd mysql[root@localhost /]# useradd -r -g mysql mysql[root@localhost /]#
4. Download the Mysql installation package for Linux from the official website
Download command:
[root@localhost /]# wget https://dev.mysql.com/get/Downloads/MySQL-5.7/mysql-5.7.24-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.gz
You can also go directly to mysql official website Select the corresponding version to download.
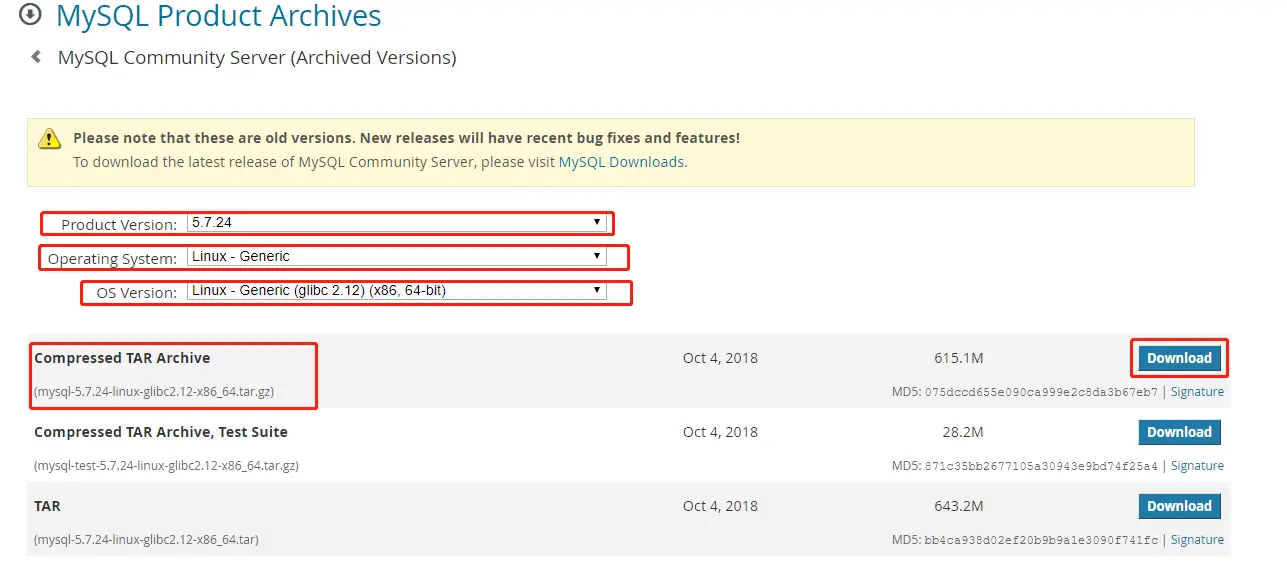
wget command is executed or in your upload directory: mysql-5.7.24-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.gzExecute the decompression command:
[root@localhost /]# tar xzvf mysql-5.7.24-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.gz [root@localhost /]# ls mysql-5.7.24-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64 mysql-5.7.24-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.gz
/usr/local/, and change the folder name to mysql.
IfThe execution command is as follows:mysql already exists under /usr/local/, please modify the existing mysql file to another name, otherwise the subsequent steps may not proceed correctly .
[root@localhost /]# mv mysql-5.7.24-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64 /usr/local/[root@localhost /]# cd /usr/local/[root@localhost /]# mv mysql-5.7.24-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64 mysql
mysql folder does not exist under /usr/local/, directly execute the following command, The above effects can also be achieved.
[root@localhost /]# mv mysql-5.7.24-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64 /usr/local/mysql
/usr/local/mysql directory
[root@localhost /]# mkdir /usr/local/mysql/data
[root@localhost /]# chown -R mysql:mysql /usr/local/mysql[root@localhost /]# chmod -R 755 /usr/local/mysql
Be sure to remember the password at the end of the initialization output log (temporary database administrator password)
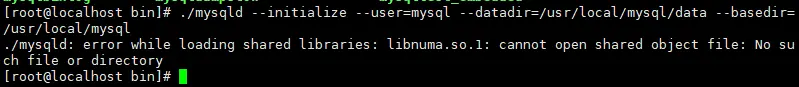
[root@localhost /]# cd /usr/local/mysql/bin[root@localhost bin]# ./mysqld --initialize --user=mysql --datadir=/usr/local/mysql/data --basedir=/usr/local/mysql
5. After running the initialization command successfully, the output log is as follows:Supplementary instructions:
In step 4, an error may occur:This error may occur: To solve the problem, first check whether the link library file is installed and use the command to verify.
After running the command, it is found that the link library file does not exist in the system.[root@localhost bin]# rpm -qa|grep libaio [root@localhost bin]#Copy after loginAfter the installation is successful, continue to run the database initialization command. At this time, the following error may occur:[root@localhost bin]# yum install libaio-devel.x86_64Copy after loginAfter executing the following command:
After the execution is correct, re-execute the initialization command in step 4. After it is correct, Go to step 5 again![root@localhost bin]# yum -y install numactlCopy after login
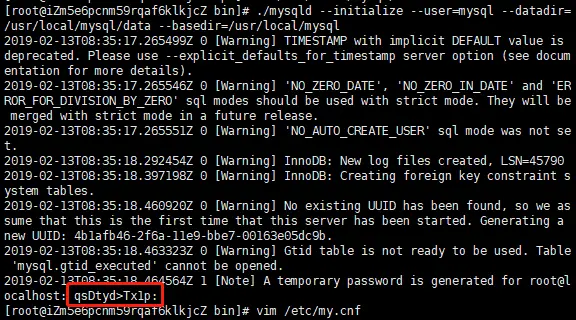
root@localhost:## The string after #, this string is the temporary login password of the mysql administrator. 6. Edit the configuration file my.cnf and add the configuration as follows
[root@localhost bin]# vi /etc/my.cnf[mysqld]datadir=/usr/local/mysql/data port=3306sql_mode=NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION,STRICT_TRANS_TABLESsymbolic-links=0max_connections=600innodb_file_per_table=1lower_case_table_names=1character_set_server=utf8
lower_case_table_names: whether it is case sensitive, 1 means the table name is lowercase when storing, and not case sensitive when operating; 0 means Case-sensitive; cannot be set dynamically. After modification, it must be restarted to take effect:
character_set_server: Set the default character set of the database. If not set, the default is latin1innodb_file_per_table: Whether to store the data of each table separately, 1 means Separate storage; 0 means to close the independent table space. You can check the difference in file structure by viewing the data directory;
7. Test starting the mysql server
[root@localhost /]# /usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server start
The following results are displayed, indicating that the database is installed and can Normal startup

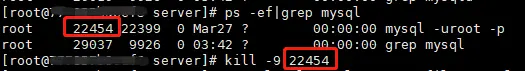
If the following prompt message appears
Starting MySQL... ERROR! The server quit without updating PID fileCopy after loginCheck whether there are mysql and mysqld services, if If exists, end the process and re-execute the startup command
#查询服务 ps -ef|grep mysql | grep -v grep ps -ef|grep mysqld | grep -v grep #结束进程 kill -9 PID #启动服务 /usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server startCopy after login8. Add a soft connection and restart the mysql service
[root@localhost /]# ln -s /usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server /etc/init.d/mysql [root@localhost /]# ln -s /usr/local/mysql/bin/mysql /usr/bin/mysql[root@localhost /]# service mysql restart
9. Log in mysql, change the password (the password is the temporary password generated in step 5)
[root@localhost /]# mysql -u root -pEnter password:mysql>set password for root@localhost = password('yourpass');
Note: When entering the password, there will be no display after Enter password. At this time, the input is actually successful. After entering the password, return directly Just take a car. Enter this command: mysql -u root -p Add your password, press Enter, and you can directly enter the database
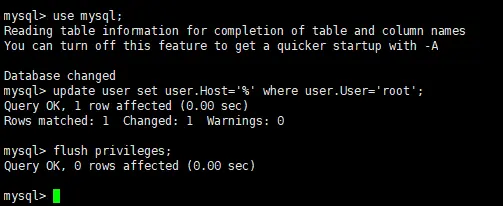
10、开放远程连接
mysql>use mysql; msyql>update user set user.Host='%' where user.User='root'; mysql>flush privileges;
11、设置开机自动启动
1、将服务文件拷贝到init.d下,并重命名为mysql[root@localhost /]# cp /usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server /etc/init.d/mysqld2、赋予可执行权限[root@localhost /]# chmod +x /etc/init.d/mysqld3、添加服务[root@localhost /]# chkconfig --add mysqld4、显示服务列表[root@localhost /]# chkconfig --list
什么是Linux系统
Linux是一种免费使用和自由传播的类UNIX操作系统,是一个基于POSIX的多用户、多任务、支持多线程和多CPU的操作系统,使用Linux能运行主要的Unix工具软件、应用程序和网络协议。
The above is the detailed content of What is the process of installing mysql under linux?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1664
1664
 14
14
 1423
1423
 52
52
 1318
1318
 25
25
 1269
1269
 29
29
 1248
1248
 24
24
 MySQL and phpMyAdmin: Core Features and Functions
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:12 AM
MySQL and phpMyAdmin: Core Features and Functions
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:12 AM
MySQL and phpMyAdmin are powerful database management tools. 1) MySQL is used to create databases and tables, and to execute DML and SQL queries. 2) phpMyAdmin provides an intuitive interface for database management, table structure management, data operations and user permission management.
 Explain the purpose of foreign keys in MySQL.
Apr 25, 2025 am 12:17 AM
Explain the purpose of foreign keys in MySQL.
Apr 25, 2025 am 12:17 AM
In MySQL, the function of foreign keys is to establish the relationship between tables and ensure the consistency and integrity of the data. Foreign keys maintain the effectiveness of data through reference integrity checks and cascading operations. Pay attention to performance optimization and avoid common errors when using them.
 Docker on Linux: Containerization for Linux Systems
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:03 AM
Docker on Linux: Containerization for Linux Systems
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:03 AM
Docker is important on Linux because Linux is its native platform that provides rich tools and community support. 1. Install Docker: Use sudoapt-getupdate and sudoapt-getinstalldocker-cedocker-ce-clicotainerd.io. 2. Create and manage containers: Use dockerrun commands, such as dockerrun-d--namemynginx-p80:80nginx. 3. Write Dockerfile: Optimize the image size and use multi-stage construction. 4. Optimization and debugging: Use dockerlogs and dockerex
 Compare and contrast MySQL and MariaDB.
Apr 26, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Compare and contrast MySQL and MariaDB.
Apr 26, 2025 am 12:08 AM
The main difference between MySQL and MariaDB is performance, functionality and license: 1. MySQL is developed by Oracle, and MariaDB is its fork. 2. MariaDB may perform better in high load environments. 3.MariaDB provides more storage engines and functions. 4.MySQL adopts a dual license, and MariaDB is completely open source. The existing infrastructure, performance requirements, functional requirements and license costs should be taken into account when choosing.
 SQL vs. MySQL: Clarifying the Relationship Between the Two
Apr 24, 2025 am 12:02 AM
SQL vs. MySQL: Clarifying the Relationship Between the Two
Apr 24, 2025 am 12:02 AM
SQL is a standard language for managing relational databases, while MySQL is a database management system that uses SQL. SQL defines ways to interact with a database, including CRUD operations, while MySQL implements the SQL standard and provides additional features such as stored procedures and triggers.
 How to understand DMA operations in C?
Apr 28, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
How to understand DMA operations in C?
Apr 28, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
DMA in C refers to DirectMemoryAccess, a direct memory access technology, allowing hardware devices to directly transmit data to memory without CPU intervention. 1) DMA operation is highly dependent on hardware devices and drivers, and the implementation method varies from system to system. 2) Direct access to memory may bring security risks, and the correctness and security of the code must be ensured. 3) DMA can improve performance, but improper use may lead to degradation of system performance. Through practice and learning, we can master the skills of using DMA and maximize its effectiveness in scenarios such as high-speed data transmission and real-time signal processing.
 MySQL: The Database, phpMyAdmin: The Management Interface
Apr 29, 2025 am 12:44 AM
MySQL: The Database, phpMyAdmin: The Management Interface
Apr 29, 2025 am 12:44 AM
MySQL and phpMyAdmin can be effectively managed through the following steps: 1. Create and delete database: Just click in phpMyAdmin to complete. 2. Manage tables: You can create tables, modify structures, and add indexes. 3. Data operation: Supports inserting, updating, deleting data and executing SQL queries. 4. Import and export data: Supports SQL, CSV, XML and other formats. 5. Optimization and monitoring: Use the OPTIMIZETABLE command to optimize tables and use query analyzers and monitoring tools to solve performance problems.
 macOS vs. Linux: Exploring the Differences and Similarities
Apr 25, 2025 am 12:03 AM
macOS vs. Linux: Exploring the Differences and Similarities
Apr 25, 2025 am 12:03 AM
macOSandLinuxbothofferuniquestrengths:macOSprovidesauser-friendlyexperiencewithexcellenthardwareintegration,whileLinuxexcelsinflexibilityandcommunitysupport.macOS,developedbyApple,isknownforitssleekinterfaceandecosystemintegration,whereasLinux,beingo