How to create an index for JSON fields in MySQL
Introduction to Multi-Valued Indexes
Starting from MySQL 8.0.17, InnoDB supports the creation of multi-valued indexes (Multi-Valued Indexes) , this index is a secondary index defined on the column of the JSON storage value array. There can be multiple index records for a single data record. The specific syntax definition for this type of index:
CAST(expression AS type ARRAY), for example, CAST(data->'$.zipcode' AS UNSIGNED ARRAY). Like ordinary indexes, they can also be viewed in EXPLAIN.
Create a multi-valued index
Like other indexes, a multi-valued index can be added when creating a table, or created through ALTER TABLE or CREATE INDEX.
JSON Object Field Index
Syntax
ALTER TABLE customers ADD INDEX idx_mv_custinfo_list( ( CAST( custinfo -> '$.key' AS UNSIGNED array ) ) );
Note: There are two layers of single brackets outside the CAST syntax! , if you write one less, an error will be reported!
Test Case
PS: The cases in the article refer to the cases in the official documents and are just for testing, so the naming and other aspects are not very standardized. They must be strict in the actual development process. Follow the development specifications of the company team and don’t be lazy!
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `customers`;
/*建表语句*/
CREATE TABLE customers (
id BIGINT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
modified DATETIME DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
custinfo JSON NOT NULL
);
/*插入写测试数据*/
INSERT INTO customers
VALUES
( NULL, NOW(), '{"key":94582,"value":"asdf"}' ),
( NULL, NOW(), '{"key":94568,"value":"gjgasdasdf"}' ),
( NULL, NOW(), '{"key":94477,"value":"ghasdfsdf"}' ),
( NULL, NOW(), '{"key":94536,"value":"hagsdfgdf"}' ),
( NULL, NOW(), '{"key":94507,"value":"wasfgjdf"}' );
/*添加多值索引*/
ALTER TABLE customers ADD INDEX idx_mv_custinfo_list( ( CAST( custinfo -> '$.key' AS UNSIGNED array)) );
/*测试 MEMBER OF 语法*/
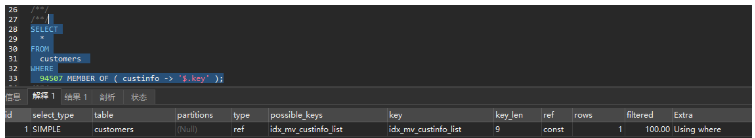
SELECT
*
FROM
customers
WHERE
94507 MEMBER OF ( custinfo -> '$.key' );
/*测试 JSON_CONTAINS 语法*/
SELECT
*
FROM
customers
WHERE
JSON_CONTAINS(
custinfo -> '$.key',
CAST( '[94582]' AS JSON ));
/*测试 JSON_OVERLAPS 语法*/
SELECT
*
FROM
customers
WHERE
JSON_OVERLAPS (
custinfo -> '$.key',
CAST( '[94477]' AS JSON ));Check the execution plan and find that the index can be used:
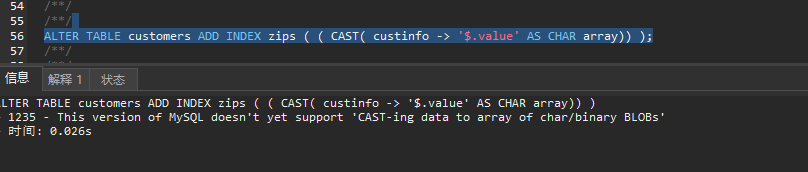
If you need to create a multi-value index for the character type, it must be the utf8mb4 character set And the sorting rule is utf8mb4_0900_as_cs, otherwise an error will be reported. This version does not support it:
If you want to create a multi-value index for a binary binary string, the sorting rule must be binary, otherwise an error will be reported and it is not supported.
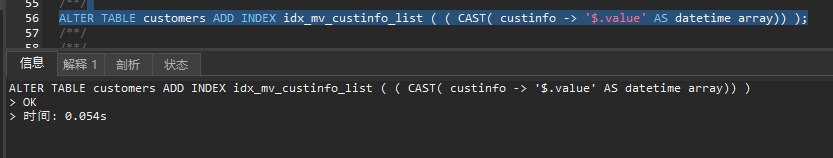
After modifying the sorting rules, the index can be added successfully:
JSON array object index
Syntax
ALTER TABLE customers ADD INDEX idx_mv_custinfo_list( ( CAST( custinfo -> '$[*].key' AS UNSIGNED array ) ) );
Note: There are two layers of single brackets outside the CAST syntax! If you write one less, an error will be reported!
Test case
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `customers`;
/*建表语句*/
CREATE TABLE customers (
id BIGINT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
modified DATETIME DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
custinfo JSON NOT NULL
);
/*插入写测试数据*/
INSERT INTO customers
VALUES
( NULL, NOW(), '[{"key":94582},{"key":94536}]'),
( NULL, NOW(), '[{"key":94568},{"key":94507},{"key":94582}]'),
( NULL, NOW(), '[{"key":94477},{"key":94507}]'),
( NULL, NOW(), '[{"key":94536}]'),
( NULL, NOW(), '[{"key":94507},{"key":94582}]');
/*添加多值索引*/
ALTER TABLE customers ADD INDEX idx_mv_custinfo_list( ( CAST( custinfo -> '$[*].key' AS UNSIGNED array)) );
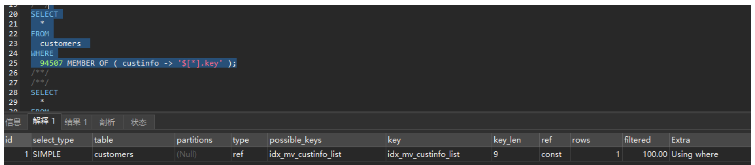
/*测试 MEMBER OF 语法*/
SELECT
*
FROM
customers
WHERE
94507 MEMBER OF ( custinfo -> '$[*].key' );
/*测试 JSON_CONTAINS 语法*/
SELECT
*
FROM
customers
WHERE
JSON_CONTAINS(
custinfo -> '$[*].key',
CAST( '[94582, 94507]' AS JSON ));
/*测试 JSON_OVERLAPS 语法*/
SELECT
*
FROM
customers
WHERE
JSON_OVERLAPS (
custinfo -> '$[*].key',
CAST( '[94477, 94582]' AS JSON ));View the execution plan and find that the index can be used:
Created in the combined index Multi-value index
Syntax
The syntax is similar to that of ordinary combined indexes. It also follows the leftmost matching principle:
ALTER TABLE customers ADD INDEX idx_age_custinfo$list_modified ( age, (CAST( custinfo -> '$[*].key' AS UNSIGNED ARRAY )), modified );
Note: You need to use parentheses outside the CAST syntax here. stand up!
Test case
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `customers`;
/*建表语句*/
CREATE TABLE customers (
id BIGINT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
age tinyint(4) not null,
modified DATETIME DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
custinfo JSON NOT NULL
);
/*插入写测试数据*/
INSERT INTO customers
VALUES
( NULL, 21, NOW(), '[{"key":94582},{"key":94536}]'),
( NULL, 22, NOW(), '[{"key":94568},{"key":94507},{"key":94582}]'),
( NULL, 23, NOW(), '[{"key":94477},{"key":94507}]'),
( NULL, 24, NOW(), '[{"key":94536}]'),
( NULL, 25, NOW(), '[{"key":94507},{"key":94582}]');
/*添加多值索引*/
alter table customers DROP INDEX idx_age_custinfo$list_modified ;
ALTER TABLE customers ADD INDEX idx_age_custinfo$list_modified ( age, (CAST( custinfo -> '$[*].key' AS UNSIGNED ARRAY )),modified );
ALTER TABLE customers ADD INDEX idx_age_custinfo$list_modified ((CAST( custinfo -> '$[*].key' AS UNSIGNED ARRAY )), age,modified );
ALTER TABLE customers ADD INDEX idx_age_custinfo$list_modified ( age,modified, (CAST( custinfo -> '$[*].key' AS UNSIGNED ARRAY )) );
/*测试 MEMBER OF 语法*/
SELECT
*
FROM
customers
WHERE
94536 MEMBER OF ( custinfo -> '$[*].key' ) and modified = '2021-08-05 10:36:34' and age = 21;View the execution plan and find that the index can be used:
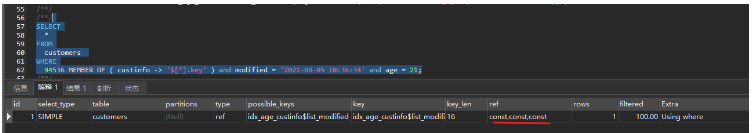
Limitations of multi-valued indexes
A multi-valued index is only allowed to contain the value of one attribute
This index currently only supports three Syntax
Currently, only three syntaxes: MEMBER OF, JSON_CONTAINS(), and JSON_OVERLAB() can use multi-value indexes.
The index value must be converted into an array
This index does not support table association
Cannot be combined with prefix index
Does not support online creation of multi-value indexes
Multi-valued indexes have clear requirements for character set type fields
This is just one of the small scenes. There are many similar scenes. The user can change it to anything, and the label can also be changed to any other attribute. As long as the thing has multiple attribute values, there is a many-to-many relationship. Then if there is no need for this attribute to be associated with other tables), you can use multi-valued indexes! Multi-valued indexes do not support table association, so it is not appropriate if you need to use this field for table association.
The above is the detailed content of How to create an index for JSON fields in MySQL. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1672
1672
 14
14
 1428
1428
 52
52
 1332
1332
 25
25
 1276
1276
 29
29
 1256
1256
 24
24
 Laravel Introduction Example
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
Laravel Introduction Example
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
Laravel is a PHP framework for easy building of web applications. It provides a range of powerful features including: Installation: Install the Laravel CLI globally with Composer and create applications in the project directory. Routing: Define the relationship between the URL and the handler in routes/web.php. View: Create a view in resources/views to render the application's interface. Database Integration: Provides out-of-the-box integration with databases such as MySQL and uses migration to create and modify tables. Model and Controller: The model represents the database entity and the controller processes HTTP requests.
 MySQL and phpMyAdmin: Core Features and Functions
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:12 AM
MySQL and phpMyAdmin: Core Features and Functions
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:12 AM
MySQL and phpMyAdmin are powerful database management tools. 1) MySQL is used to create databases and tables, and to execute DML and SQL queries. 2) phpMyAdmin provides an intuitive interface for database management, table structure management, data operations and user permission management.
 MySQL vs. Other Programming Languages: A Comparison
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:22 AM
MySQL vs. Other Programming Languages: A Comparison
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Compared with other programming languages, MySQL is mainly used to store and manage data, while other languages such as Python, Java, and C are used for logical processing and application development. MySQL is known for its high performance, scalability and cross-platform support, suitable for data management needs, while other languages have advantages in their respective fields such as data analytics, enterprise applications, and system programming.
 Laravel framework installation method
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
Laravel framework installation method
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
Article summary: This article provides detailed step-by-step instructions to guide readers on how to easily install the Laravel framework. Laravel is a powerful PHP framework that speeds up the development process of web applications. This tutorial covers the installation process from system requirements to configuring databases and setting up routing. By following these steps, readers can quickly and efficiently lay a solid foundation for their Laravel project.
 Explain the purpose of foreign keys in MySQL.
Apr 25, 2025 am 12:17 AM
Explain the purpose of foreign keys in MySQL.
Apr 25, 2025 am 12:17 AM
In MySQL, the function of foreign keys is to establish the relationship between tables and ensure the consistency and integrity of the data. Foreign keys maintain the effectiveness of data through reference integrity checks and cascading operations. Pay attention to performance optimization and avoid common errors when using them.
 Compare and contrast MySQL and MariaDB.
Apr 26, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Compare and contrast MySQL and MariaDB.
Apr 26, 2025 am 12:08 AM
The main difference between MySQL and MariaDB is performance, functionality and license: 1. MySQL is developed by Oracle, and MariaDB is its fork. 2. MariaDB may perform better in high load environments. 3.MariaDB provides more storage engines and functions. 4.MySQL adopts a dual license, and MariaDB is completely open source. The existing infrastructure, performance requirements, functional requirements and license costs should be taken into account when choosing.
 MySQL: The Database, phpMyAdmin: The Management Interface
Apr 29, 2025 am 12:44 AM
MySQL: The Database, phpMyAdmin: The Management Interface
Apr 29, 2025 am 12:44 AM
MySQL and phpMyAdmin can be effectively managed through the following steps: 1. Create and delete database: Just click in phpMyAdmin to complete. 2. Manage tables: You can create tables, modify structures, and add indexes. 3. Data operation: Supports inserting, updating, deleting data and executing SQL queries. 4. Import and export data: Supports SQL, CSV, XML and other formats. 5. Optimization and monitoring: Use the OPTIMIZETABLE command to optimize tables and use query analyzers and monitoring tools to solve performance problems.
 What software is better for yi framework? Recommended software for yi framework
Apr 18, 2025 pm 11:03 PM
What software is better for yi framework? Recommended software for yi framework
Apr 18, 2025 pm 11:03 PM
Abstract of the first paragraph of the article: When choosing software to develop Yi framework applications, multiple factors need to be considered. While native mobile application development tools such as XCode and Android Studio can provide strong control and flexibility, cross-platform frameworks such as React Native and Flutter are becoming increasingly popular with the benefits of being able to deploy to multiple platforms at once. For developers new to mobile development, low-code or no-code platforms such as AppSheet and Glide can quickly and easily build applications. Additionally, cloud service providers such as AWS Amplify and Firebase provide comprehensive tools




