How to install Redis in Centos7
1 Preliminary preparation
1.1 Download the redis installation package
You can also download other versions, I download the 5.0.8 version here.
1.2 Upload the installation package
Upload the downloaded installation package to the specified directory on the server, and then decompress it through tar -zxvf xxxx, such as:
Second check gcc
Installing redis requires a c environment, so offline installation requires downloading some dependent installation packages.
2.1 Download address: https://vault.centos.org/7.0.1406/os/x86_64/Packages/
cpp-4.8.2-16.el7.x86_64.rpm gcc-4.8.2-16.el7.x86_64.rpm glibc-2.17-55.el7.x86_64.rpm glibc-common-2.17-55.el7.x86_64.rpm glibc-devel-2.17-55.el7.x86_64.rpm glibc-headers-2.17-55.el7.x86_64.rpm glibc-static-2.17-55.el7.x86_64.rpm glibc-utils-2.17-55.el7.x86_64.rpm kernel-headers-3.10.0-123.el7.x86_64.rpm libmpc-1.0.1-3.el7.x86_64.rpm mpfr-3.1.1-4.el7.x86_64.rpm
Choose to download the above to meet the installation needs.
2.2 After the download is completed, upload it to the server and install it through rpm
rpm -Uvh *.rpm --nodeps --force
--nodeps When installing the package, the dependencies are not checked. For example, when installing B, B depends on C and cannot be installed. Use -- nodeps can be installed successfully
--force force installation
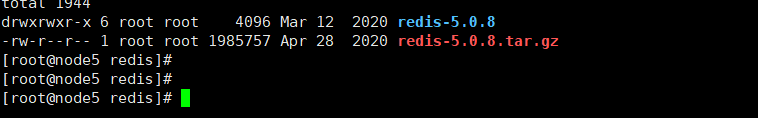
2.3 Check whether the installation is successful
rpm -q gcc
Three installation Redis
cd redis-5.0.8 Enter the decompressed directory
3.1 Compile redis
make
3.2 Install the compiled files to the directory
make PREFIX=/usr/local/redis install
Note: PREFIX is required At the same time, the redis directory will be automatically created for us, and the result will be installed in this directory
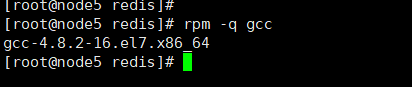
3.3 After the installation is completed, the following files will be generated in the /usr/local/bin/ folder
3.4 Configure redis.conf
cd Go to the installation package decompression directory and copy redis.conf to the directory where redis is installed
cd redis-5.0.8 mkdir /usr/local/redis/etc cp redis.conf /usr/local/redis/etc vim redis.conf
daemonize no is changed to daemonize yes
requirepass is changed to redis123 (This is a redis add password)
appendonly yes Comment open
3.5 Open service port
# 查看6379端口是否开启 firewall-cmd --query-port=6379/tcp # 开启6379端口 firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=6379/tcp
3.6 Redis startup
/usr/local/redis/bin/redis-server /usr/local/redis/etc/redis.conf
3.7 View process
ps -ef|grep redis
3.8 Client startup
# 没密码 ./redis-cli # 有密码 ./redis-cli -a redis123
3.9 Execute command on the server
redis-cli -h host -p port -a password
格式为 redis-cli –h IP地址 –p 端口 –a 密码
3.10 Redis shutdown
First way
# 查询进度PID ps -ef | grep -i redis # 关闭 kill -9 PID
Second Method
./bin/redis-cli shutdown
Four uninstall
4.1 First close the redis service
4.2 Then delete the redis-related files in the /usr/local/redis/bin/ directory
rm -rf /usr/local/redis/bin/redis*
The above is the detailed content of How to install Redis in Centos7. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1665
1665
 14
14
 1424
1424
 52
52
 1322
1322
 25
25
 1270
1270
 29
29
 1250
1250
 24
24
 Centos shutdown command line
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
Centos shutdown command line
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
The CentOS shutdown command is shutdown, and the syntax is shutdown [Options] Time [Information]. Options include: -h Stop the system immediately; -P Turn off the power after shutdown; -r restart; -t Waiting time. Times can be specified as immediate (now), minutes ( minutes), or a specific time (hh:mm). Added information can be displayed in system messages.
 Difference between centos and ubuntu
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:09 PM
Difference between centos and ubuntu
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:09 PM
The key differences between CentOS and Ubuntu are: origin (CentOS originates from Red Hat, for enterprises; Ubuntu originates from Debian, for individuals), package management (CentOS uses yum, focusing on stability; Ubuntu uses apt, for high update frequency), support cycle (CentOS provides 10 years of support, Ubuntu provides 5 years of LTS support), community support (CentOS focuses on stability, Ubuntu provides a wide range of tutorials and documents), uses (CentOS is biased towards servers, Ubuntu is suitable for servers and desktops), other differences include installation simplicity (CentOS is thin)
 Centos configuration IP address
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:06 PM
Centos configuration IP address
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:06 PM
Steps to configure IP address in CentOS: View the current network configuration: ip addr Edit the network configuration file: sudo vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 Change IP address: Edit IPADDR= Line changes the subnet mask and gateway (optional): Edit NETMASK= and GATEWAY= Lines Restart the network service: sudo systemctl restart network verification IP address: ip addr
 How to install mysql in centos7
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:30 PM
How to install mysql in centos7
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:30 PM
The key to installing MySQL elegantly is to add the official MySQL repository. The specific steps are as follows: Download the MySQL official GPG key to prevent phishing attacks. Add MySQL repository file: rpm -Uvh https://dev.mysql.com/get/mysql80-community-release-el7-3.noarch.rpm Update yum repository cache: yum update installation MySQL: yum install mysql-server startup MySQL service: systemctl start mysqld set up booting
 Centos stops maintenance 2024
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Centos stops maintenance 2024
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
CentOS will be shut down in 2024 because its upstream distribution, RHEL 8, has been shut down. This shutdown will affect the CentOS 8 system, preventing it from continuing to receive updates. Users should plan for migration, and recommended options include CentOS Stream, AlmaLinux, and Rocky Linux to keep the system safe and stable.
 How to check CentOS HDFS configuration
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
How to check CentOS HDFS configuration
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
Complete Guide to Checking HDFS Configuration in CentOS Systems This article will guide you how to effectively check the configuration and running status of HDFS on CentOS systems. The following steps will help you fully understand the setup and operation of HDFS. Verify Hadoop environment variable: First, make sure the Hadoop environment variable is set correctly. In the terminal, execute the following command to verify that Hadoop is installed and configured correctly: hadoopversion Check HDFS configuration file: The core configuration file of HDFS is located in the /etc/hadoop/conf/ directory, where core-site.xml and hdfs-site.xml are crucial. use
 How to use the Redis cache solution to efficiently realize the requirements of product ranking list?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
How to use the Redis cache solution to efficiently realize the requirements of product ranking list?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
How does the Redis caching solution realize the requirements of product ranking list? During the development process, we often need to deal with the requirements of rankings, such as displaying a...
 How to view firewall status in centos
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
How to view firewall status in centos
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
The state of the CentOS firewall can be viewed through the sudo firewall-cmd --state command, returning to running or not running. For more detailed information, you can use sudo firewall-cmd --list-all to view, including configured areas, services, ports, etc. If firewall-cmd does not solve the problem, you can use sudo iptables -L -n to view iptables rules. Be sure to make a backup before modifying the firewall configuration to ensure server security.




