 Database
Database
 Redis
Redis
 Example analysis of Redis backup, disaster recovery and high availability practice
Example analysis of Redis backup, disaster recovery and high availability practice
Example analysis of Redis backup, disaster recovery and high availability practice
1. A brief introduction to Redis
Redis is a high-performance key-value non-relational database. Due to its high-performance characteristics, it supports high availability, persistence, and multiple A variety of data structures, clusters, etc. make it stand out and become a commonly used non-relational database.
In addition, Redis has many usage scenarios.
Session Cache
Redis cache session has a very good advantage, because Redis provides persistence, in application scenarios that need to maintain sessions for a long time, such as shopping cart scenarios. The scene can provide good long session support and provide users with a good shopping experience.
Full page caching
In WordPress, Pantheon provides a good plug-in wp-redis, which can load the pages you have browsed at the fastest speed.
Queue
Redis supports list and set operations, so it is very suitable for use as a message queue platform. We often use Reids’ queue function to limit purchases. For example, during holidays or promotion periods, some activities may be carried out to restrict users' purchasing behavior, limiting them to only a few purchases today or only once within a period of time. It is also more suitable for application.
Ranking
Redis implements the operation of incrementing or decrementing numbers in memory very well. Therefore, we use Redis in many ranking scenarios. For example, novel websites rank novels and recommend top-ranked novels to users based on the ranking.
Publish/Subscribe
Redis provides publish and subscribe functions. There are many scenarios for publish and subscribe. For example, we can use the publish and subscribe functions of Redis to create a script based on publish and subscribe script triggers. Up chat system.
In addition, there are many other scenarios in which Redis performs well.
2. Single point of failure problem in the use of Redis
Redis is used in various companies. Its multiple excellent features and rich application scenarios are the reason for its existence. . Then the problems and risks will come. Although Redis has rich application scenarios, some companies still use single-node deployment relatively conservatively when practicing Redis applications, which brings security risks to future maintenance.
I once dealt with a business interruption problem caused by a single point of failure in 2015. When Redis was first deployed, it used a single-node deployment rather than a distributed deployment, and did not consider disaster recovery issues.
At that time, we used the Redis server to control the user's purchase of discounted goods. However, due to unknown reasons, the server of the Redis node went down, resulting in us being unable to control the user's purchase behavior, resulting in the user being able to The behavior of purchasing discounted products multiple times within a period.
This kind of downtime accident can be said to have caused irreparable losses to the company. The security risk problem is very serious. As the person who operated and maintained the system at the time, it was necessary for me to repair this problem and improve the architecture. improvements on. Therefore, I started researching and learning about ways to solve Redis single point of failure in non-distributed applications.
3. Backup and disaster recovery of Redis applications in non-distributed scenarios
Redis master-slave replication should be very common now. Commonly used master-slave replication architectures include the following two architecture solutions.
Commonly used Redis master-slave replication
Option 1
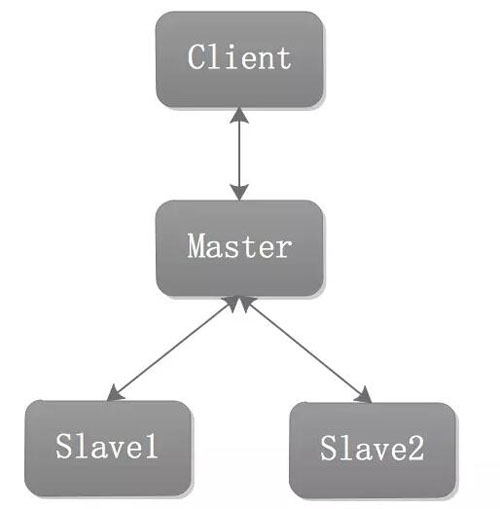
Under normal circumstances, This structure is the most common, with one master node and two slave nodes. When the client writes data, it writes to the Master node, and when reading, it reads from two Slaves. This achieves read expansion and reduces the read load on the Master node.
Option 2
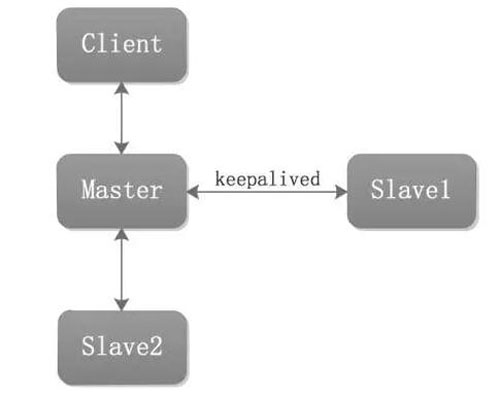
This architecture also has one Master and two Slaves. Master and Slave1 use keepalived to implement VIP migration in different ways. When the Client connects to the Master, it connects through VIP. This avoids the situation of IP change in Solution 1.
Advantages and disadvantages of Redis master-slave replication
Advantages
It realizes the backup of master data, once the master fails , the slave node can be promoted to the new master and continue to provide services in place of the old master
to achieve read expansion. The master-slave replication architecture is generally used to achieve read expansion. Master mainly implements the writing function, and Slave implements the reading function
Insufficiency
Architecture Solution 1
When the Master fails , the Client is disconnected from the Master and cannot implement the write function. At the same time, the Slave cannot copy from the Master.
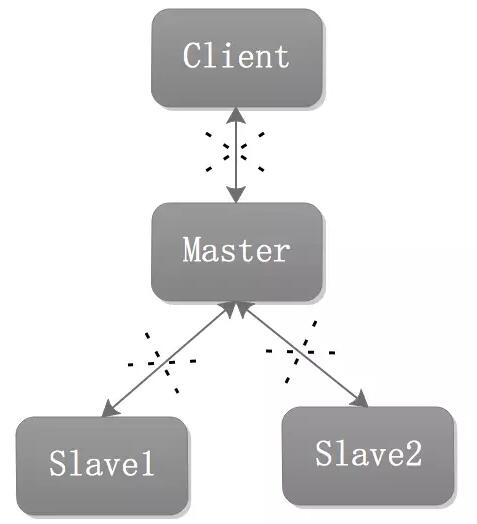
At this time, you need to go through the following operations (assuming that Slave1 is promoted to Master):
Execute the slaveof no one command on Slave1 to upgrade Slave1 is the new Master node.
Configure Slave1 to be writable. This is because in most cases, slave is configured as read-only.
Tell the client (that is, the program that connects to Redis) the connection address of the new Master node.
Configure Slave2 to copy data from the new Master.
Architecture Plan 2
When the master fails, the Client can connect to Slave1 for data operations, but Slave1 becomes a single point, there is a single point of failure (single point of failure) that often needs to be avoided.
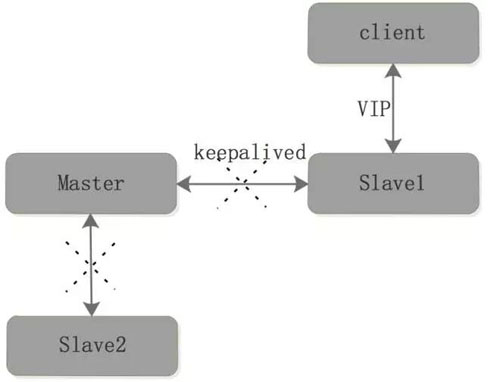
After that, you need to go through the following operations:
Execute the slaveof no one command on Slave1 to promote Slave1 as the new Master node
Configure Slave1 to be writable. This is because in most cases, the Slave configuration is read-only.
Configure Slave2 from the new Master. Data replication
It should be noted that all architectural solutions require manual intervention for failover. The need for manual intervention increases the workload of operation and maintenance, and also has a huge impact on the business. At this time, you can use Redis's high-availability solution - Sentinel
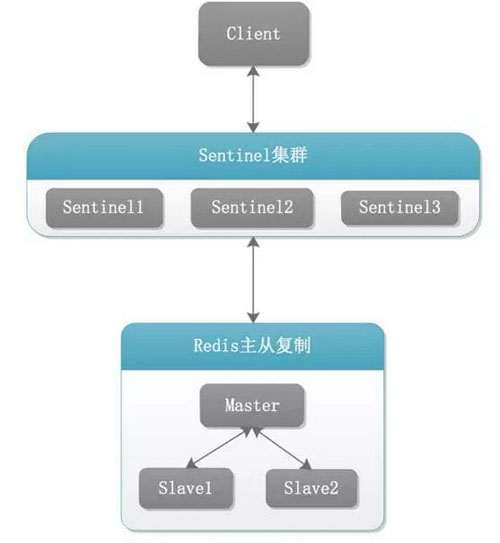
IV. Introduction to Redis Sentinel
Redis Sentinel provides a high-availability solution for Redis. From a practical perspective, using Redis Sentinel can create a Redis environment that prevents certain failures without human intervention.
Redis Sentinel adopts a distributed architecture and runs multiple processes for collaborative cooperation. Run multiple Sentinel processes to cooperate. When multiple Sentinels can no longer provide services to a given master, fault detection will be performed, which will reduce the possibility of false positives.
5. Redis Sentinel functions
The main functions of Redis Sentinel in the Redis high availability solution include the following functions:
Monitoring
Sentinel will constantly check whether the master and slave are running normally as expected
Notification
Through API, Sentinel can notify system administrators and programs The monitored Redis instance fails
Automatic failover
If the master does not run as expected, Sentinel can start the failover process, and one of the slaves will If it becomes the master, other slaves will be reconfigured to use the new master. Applications using the Redis service will also be notified to use the new address when connecting.
Configuration provider
Sentinel can be used as the authentication source for client service discovery: the client connects to Sentinel to obtain the Redis master address currently responsible for a given service. If a failover occurs, Sentinel will report the new address.
6. Redis Sentinel Architecture
##7. Redis Sentinel Implementation Principle
The Sentinel cluster monitors itself and Redis master-slave replication. When it is discovered that the Master node fails, the following steps will be followed:- 1) An election is held between Sentinels to elect a leader, and the elected leader will perform failover
- The Sentinel leader selects one from the Slave nodes as the new master node. Here is a rewrite of that sentence: To implement slave election, the following election methods need to be performed: a) The time to disconnect from the master
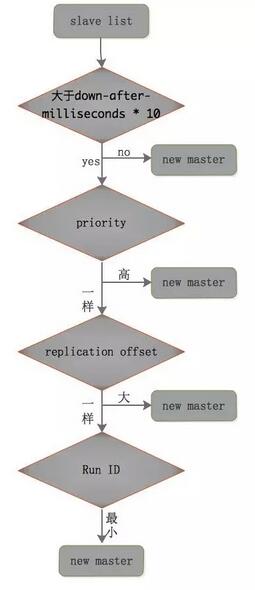
- 3) Sentinel leader will perform slaveof no one operation on the new master elected in the previous step and promote it to the master node
- 4) The Sentinel leader sends commands to other slaves to make the remaining slaves the slaves of the new master node
- 5) The Sentinel leader will let the original The master is downgraded to slave. When normal operation resumes, the Sentinel leader will send a command to replicate from the new master.
The above is the detailed content of Example analysis of Redis backup, disaster recovery and high availability practice. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
On CentOS systems, you can limit the execution time of Lua scripts by modifying Redis configuration files or using Redis commands to prevent malicious scripts from consuming too much resources. Method 1: Modify the Redis configuration file and locate the Redis configuration file: The Redis configuration file is usually located in /etc/redis/redis.conf. Edit configuration file: Open the configuration file using a text editor (such as vi or nano): sudovi/etc/redis/redis.conf Set the Lua script execution time limit: Add or modify the following lines in the configuration file to set the maximum execution time of the Lua script (unit: milliseconds)
 How to set the redis expiration policy
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
How to set the redis expiration policy
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
There are two types of Redis data expiration strategies: periodic deletion: periodic scan to delete the expired key, which can be set through expired-time-cap-remove-count and expired-time-cap-remove-delay parameters. Lazy Deletion: Check for deletion expired keys only when keys are read or written. They can be set through lazyfree-lazy-eviction, lazyfree-lazy-expire, lazyfree-lazy-user-del parameters.
 How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Use the Redis command line tool (redis-cli) to manage and operate Redis through the following steps: Connect to the server, specify the address and port. Send commands to the server using the command name and parameters. Use the HELP command to view help information for a specific command. Use the QUIT command to exit the command line tool.
 How to implement redis counter
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:21 PM
How to implement redis counter
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:21 PM
Redis counter is a mechanism that uses Redis key-value pair storage to implement counting operations, including the following steps: creating counter keys, increasing counts, decreasing counts, resetting counts, and obtaining counts. The advantages of Redis counters include fast speed, high concurrency, durability and simplicity and ease of use. It can be used in scenarios such as user access counting, real-time metric tracking, game scores and rankings, and order processing counting.
 How to optimize the performance of debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:48 AM
How to optimize the performance of debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:48 AM
In Debian systems, readdir system calls are used to read directory contents. If its performance is not good, try the following optimization strategy: Simplify the number of directory files: Split large directories into multiple small directories as much as possible, reducing the number of items processed per readdir call. Enable directory content caching: build a cache mechanism, update the cache regularly or when directory content changes, and reduce frequent calls to readdir. Memory caches (such as Memcached or Redis) or local caches (such as files or databases) can be considered. Adopt efficient data structure: If you implement directory traversal by yourself, select more efficient data structures (such as hash tables instead of linear search) to store and access directory information





