How to configure redis master-slave under Docker
1. Pull the redis image
docker pull redis
2. Start 3 redis container services and use them respectively Go to ports 6379, 6380, 6381
docker run --name redis-6379 -p 6379:6379 -d redis docker run --name redis-6380 -p 6380:6379 -d redis docker run --name redis-6381 -p 6381:6379 -dredis
3. Check the container
[tcy@tcy1 ~]$ docker ps -a container id image command created status ports names a9fa77adc598 daocloud.io/library/redis "docker-entrypoint.s 2 hours ago up 2 hours 0.0.0.0:6381->6379/tcp redis-6381 6ee2f2f007e6 daocloud.io/library/redis "docker-entrypoint.s 2 hours ago up 2 hours 0.0.0.0:6380->6379/tcp redis-6380 ab54741166e1 daocloud.io/library/redis "docker-entrypoint.s 3 hours ago up 3 hours 0.0.0.0:6379->6379/tcp redis-6379
4. Test the container, success
docker exec -it ab54741166e1 redis-cli:进入容器 [root@tcy1 tcy]# docker exec -it ab54741166e1 redis-cli 127.0.0.1:6379> set b tcy ok 127.0.0.1:6379> get b "tcy" 127.0.0.1:6379> quit[root@tcy1 tcy]#
5. Start redis cluster configuration
5.1. Check the ip address of the container intranet
[root@tcy1 tcy]# docker inspect a9fa77adc598
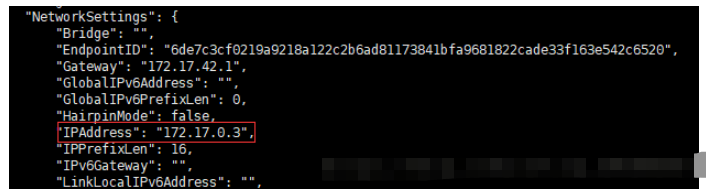
The intranet IP addresses of the three redis are:
redis-6379:172.17.0.1:6379 redis-6380:172.17.0.2:6379 redis-6381:172.17.0.3:6379
5.2. Enter the docker container and view the current redis Role (master or slave)
[root@tcy1 tcy]# docker exec -it ab54741166e1 /bin/bash root@ab54741166e1:/data# redis-cli 127.0.0.1:6379> info replication # replication role:master connected_slaves:0 master_replid:d43d1ae8cde6cb084220e18b926aba79e0bb2504 master_replid2:0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 master_repl_offset:0 second_repl_offset:-1 repl_backlog_active:0 repl_backlog_size:1048576 repl_backlog_first_byte_offset:0 repl_backlog_histlen:0 127.0.0.1:6379> quit root@ab54741166e1:/data# exit exit
Currently the three are in master status
5.3. Use the redis-cli command to modify the hosts of redis-6380 and redis-6381 to 172.17.0.1 :6379
[root@tcy1 tcy]# docker exec -it a9fa77adc598 /bin/bash //redis-6380 root@a9fa77adc598:/data# redis-cli 127.0.0.1:6379> slaveof 172.17.0.1 6379 ok 127.0.0.1:6379> quit root@a9fa77adc598:/data# exit exit [root@tcy1 tcy]# docker exec -it 6ee2f2f007e6 /bin/bash //redis-6381 root@6ee2f2f007e6:/data# redis-cli 127.0.0.1:6379> slaveof 172.17.0.1 6379 ok 127.0.0.1:6379> quit
5.4. Check whether redis-6379 already has 2 slaves, connected_slaves:2, yes
[root@tcy1 tcy]# docker exec -it ab54741166e1 /bin/bash root@ab54741166e1:/data# redis-cli 127.0.0.1:6379> info replication # replication role:master connected_slaves:2 slave0:ip=172.17.0.3,port=6379,state=online,offset=378,lag=1 slave1:ip=172.17.0.2,port=6379,state=online,offset=378,lag=0 master_replid:ce193b15cfd57f7dc3ccfbf2a4aef6156b131e6d master_replid2:0000000000000000000000000000000000000000 master_repl_offset:378 second_repl_offset:-1 repl_backlog_active:1 repl_backlog_size:1048576 repl_backlog_first_byte_offset:1 repl_backlog_histlen:378 127.0.0.1:6379> quit root@ab54741166e1:/data# exit exit
5.5. Configure sentinel sentinel
Enter three redis containers for configuration, and create the sentinel.conf file in the root directory of the container
The content of the file is: sentinel monitor mymaster 172.17.0.1 6379 1
[root@tcy1 tcy]# docker exec -it a9fa77adc598 /bin/bash root@a9fa77adc598:/data# cd / && touch sentinel.conf root@a9fa77adc598:/# vim /sentinel.conf
If it appears: bash: vim: command not found
Solution: 1. apt-get update 2. apt-get install vim
Finally, start the redis sentinel:
root@a9fa77adc598:/# redis-sentinel /sentinel.conf
342:x 24 jun 11:37:58.934 # oo0ooo0ooo0oo redis is starting oo0ooo0ooo0oo
342:x 24 jun 11:37:58.957 # redis version=4.0.10, bits=64, commit=00000000, modified=0, pid=342, just started
342:x 24 jun 11:37:58.958 # configuration loaded
342:x 24 jun 11:37:58.959 # you requested maxclients of 10000 requiring at least 10032 max file descriptors.
342:x 24 jun 11:37:58.959 # server can't set maximum open files to 10032 because of os error: operation not permitted.
342:x 24 jun 11:37:58.960 # current maximum open files is 4096. maxclients has been reduced to 4064 to compensate for low ulimit. if you need higher maxclients increase 'ulimit -n'.
_._
_.-``__ ''-._
_.-`` `. `_. ''-._ redis 4.0.10 (00000000/0) 64 bit
.-`` .-```. ```\/ _.,_ ''-._
( ' , .-` | `, ) running in sentinel mode
|`-._`-...-` __...-.``-._|'` _.-'| port: 26379
| `-._ `._ / _.-' | pid: 342
`-._ `-._ `-./ _.-' _.-'
|`-._`-._ `-.__.-' _.-'_.-'|
| `-._`-._ _.-'_.-' | http://redis.io
`-._ `-._`-.__.-'_.-' _.-'
|`-._`-._ `-.__.-' _.-'_.-'|
| `-._`-._ _.-'_.-' |
`-._ `-._`-.__.-'_.-' _.-'
`-._ `-.__.-' _.-'
`-._ _.-'
`-.__.-'
342:x 24 jun 11:37:59.068 # warning: the tcp backlog setting of 511 cannot be enforced because /proc/sys/net/core/somaxconn is set to the lower value of 128.
342:x 24 jun 11:37:59.089 # sentinel id is dfd5a5bfe1036b1df3395c4ba858329034fc5b7e
342:x 24 jun 11:37:59.091 # +monitor master mymaster 172.17.0.1 6379 quorum 1
342:x 24 jun 11:37:59.110 * +slave slave 172.17.0.3:6379 172.17.0.3 6379 @ mymaster 172.17.0.1 6379
342:x 24 jun 11:37:59.115 * +slave slave 172.17.0.2:6379 172.17.0.2 6379 @ mymaster 172.17.0.1 6379
342:x 24 jun 11:39:27.601 * +sentinel sentinel ba9b0d0539d8273edfcbd922fe138f50daa78bbb 172.17.0.2 26379 @ mymaster 172.17.0.1 6379
342:x 24 jun 11:41:59.144 * +sentinel sentinel f0510f8582b72c056531f219397ed8826683e665 172.17.0.1 26379 @ mymaster 172.17.0.1 6379Easy to observe, open multiple windows.

sentinel configuration is completed
5.6, test
Close master
[tcy@tcy1 ~]$ docker stop ab54741166e1 ab54741166e1
At this time, the remaining 2 The slave will automatically elect a new host. Here, 172.17.0.2 is elected as the host.
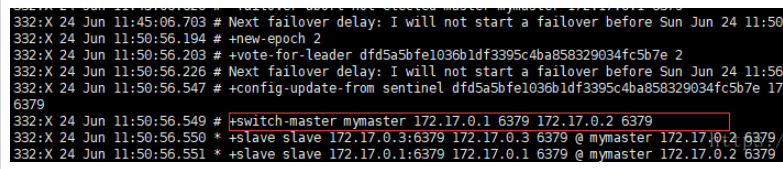
Check 172.17.0.2 and become the host.
[root@tcy1 /]# docker exec -it 6ee2f2f007e6 /bin/bash root@6ee2f2f007e6:/data# redis-cli 127.0.0.1:6379> info replication # replication role:master connected_slaves:1 slave0:ip=172.17.0.3,port=6379,state=online,offset=66906,lag=1 master_replid:5a7489c8181ddf0d73d418d30d6a4c8e039198ba master_replid2:ce193b15cfd57f7dc3ccfbf2a4aef6156b131e6d master_repl_offset:67041 second_repl_offset:65534 repl_backlog_active:1 repl_backlog_size:1048576 repl_backlog_first_byte_offset:85 repl_backlog_histlen:66957 127.0.0.1:6379>
The above is the detailed content of How to configure redis master-slave under Docker. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1664
1664
 14
14
 1422
1422
 52
52
 1316
1316
 25
25
 1267
1267
 29
29
 1239
1239
 24
24
 How to exit the container by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:15 PM
How to exit the container by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:15 PM
Four ways to exit Docker container: Use Ctrl D in the container terminal Enter exit command in the container terminal Use docker stop <container_name> Command Use docker kill <container_name> command in the host terminal (force exit)
 How to copy files in docker to outside
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
How to copy files in docker to outside
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
Methods for copying files to external hosts in Docker: Use the docker cp command: Execute docker cp [Options] <Container Path> <Host Path>. Using data volumes: Create a directory on the host, and use the -v parameter to mount the directory into the container when creating the container to achieve bidirectional file synchronization.
 How to start containers by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
How to start containers by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Docker container startup steps: Pull the container image: Run "docker pull [mirror name]". Create a container: Use "docker create [options] [mirror name] [commands and parameters]". Start the container: Execute "docker start [Container name or ID]". Check container status: Verify that the container is running with "docker ps".
 How to restart docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:06 PM
How to restart docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:06 PM
How to restart the Docker container: get the container ID (docker ps); stop the container (docker stop <container_id>); start the container (docker start <container_id>); verify that the restart is successful (docker ps). Other methods: Docker Compose (docker-compose restart) or Docker API (see Docker documentation).
 How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
You can query the Docker container name by following the steps: List all containers (docker ps). Filter the container list (using the grep command). Gets the container name (located in the "NAMES" column).
 How to start mysql by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
How to start mysql by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
The process of starting MySQL in Docker consists of the following steps: Pull the MySQL image to create and start the container, set the root user password, and map the port verification connection Create the database and the user grants all permissions to the database
 How to create containers for docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
How to create containers for docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
Create a container in Docker: 1. Pull the image: docker pull [mirror name] 2. Create a container: docker run [Options] [mirror name] [Command] 3. Start the container: docker start [Container name]
 How to view logs from docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:24 PM
How to view logs from docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:24 PM
The methods to view Docker logs include: using the docker logs command, for example: docker logs CONTAINER_NAME Use the docker exec command to run /bin/sh and view the log file, for example: docker exec -it CONTAINER_NAME /bin/sh ; cat /var/log/CONTAINER_NAME.log Use the docker-compose logs command of Docker Compose, for example: docker-compose -f docker-com




