How to use SpringBoot + Redis to implement interface current limiting
Configuration
First we create a Spring Boot project, introduce Web and Redis dependencies, and consider that interface current limiting is generally marked through annotations, and annotations are parsed through AOP, so we also need Including AOP dependencies, the final dependencies are as follows:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>Then prepare a Redis instance in advance. After our project is configured, we can directly configure the basic information of Redis, as follows:
spring.redis.host=localhost spring.redis.port=6379 spring.redis.password=123
Current limiting annotation
Next we create a current limiting annotation. We divide the current limiting into two situations:
Global current limiting for the current interface , for example, the interface can be accessed 100 times in 1 minute.
Rate limit for a certain IP address, for example, an IP address can be accessed 100 times in 1 minute.
For these two situations, we create an enumeration class:
public enum LimitType {
/**
* 默认策略全局限流
*/
DEFAULT,
/**
* 根据请求者IP进行限流
*/
IP
}Next we create the current limiting annotation:
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface RateLimiter {
/**
* 限流key
*/
String key() default "rate_limit:";
/**
* 限流时间,单位秒
*/
int time() default 60;
/**
* 限流次数
*/
int count() default 100;
/**
* 限流类型
*/
LimitType limitType() default LimitType.DEFAULT;
}First A parameter current-limiting key. This is just a prefix. In the future, the complete key will be this prefix plus the complete path of the interface method, which together form the current-limiting key. This key will be stored in Redis.
The other three parameters are easy to understand, so I won’t say more.
Okay, if the interface needs to limit the flow in the future, just add the @RateLimiter annotation on that interface, and then configure the relevant parameters.
Customized RedisTemplate
In Spring Boot, we are actually more accustomed to using Spring Data Redis to operate Redis, but the default RedisTemplate has a small pitfall, that is, JdkSerializationRedisSerializer is used for serialization. I don’t know. Friends, have you ever noticed that the keys and values saved to Redis using this serialization tool will somehow have more prefixes, which may cause errors when you read them with commands.
For example, when storing, the key is name and the value is test, but when you operate on the command line, get name cannot get the data you want. The reason is that the data is stored After arriving in redis, there are some more characters in front of the name. At this time, we can only continue to use RedisTemplate to read them out.
When we use Redis for current limiting, we will use Lua scripts. When using Lua scripts, the situation mentioned above will occur, so we need to modify the serialization scheme of RedisTemplate.
Some friends may ask why not use StringRedisTemplate? StringRedisTemplate does not have the problems mentioned above, but the data types it can store are not rich enough, so it is not considered here.
Modify the RedisTemplate serialization scheme, the code is as follows:
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory);
// 使用Jackson2JsonRedisSerialize 替换默认序列化(默认采用的是JDK序列化)
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Object> jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<>(Object.class);
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
return redisTemplate;
}
}There is actually nothing to say about this. We use the default jackson serialization method in Spring Boot for both key and value. .
Lua script
In fact, I mentioned this in the previous vhr video. We can use Lua scripts to implement some atomic operations in Redis. If we want to call Lua scripts, we have Two different ideas:
Define the Lua script on the Redis server, and then calculate a hash value. In the Java code, use this hash value to lock which Lua to execute. script.
Define the Lua script directly in the Java code and then send it to the Redis server for execution.
Spring Data Redis also provides an interface for operating Lua scripts, which is quite convenient, so we will adopt the second solution here.
We create a new lua folder in the resources directory specifically to store lua scripts. The content of the script is as follows:
local key = KEYS[1]
local count = tonumber(ARGV[1])
local time = tonumber(ARGV[2])
local current = redis.call('get', key)
if current and tonumber(current) > count then
return tonumber(current)
end
current = redis.call('incr', key)
if tonumber(current) == 1 then
redis.call('expire', key, time)
end
return tonumber(current)This script is actually not difficult. You can probably tell what it is used for at a glance. KEYS and ARGV are both parameters passed in when calling. Tonumber is to convert a string into a number. redis.call is to execute specific redis instructions. The specific process is as follows:
First, obtain the incoming key and the current limit count and time.
Get the value corresponding to this key through get. This value is the number of times this interface can be accessed in the current time window.
If it is the first visit, the result obtained at this time is nil. Otherwise, the result obtained should be a number, so the next step is to judge if the result obtained is A number, and this number is greater than count, it means that the traffic limit has been exceeded, then the query results can be returned directly.
If the result obtained is nil, it means it is the first access. At this time, increase the current key by 1, and then set an expiration time.
Finally, just return the value that has been incremented by 1.
In fact, this Lua script is easy to understand.
Next we load this Lua script in a Bean, as follows:
@Bean
public DefaultRedisScript<Long> limitScript() {
DefaultRedisScript<Long> redisScript = new DefaultRedisScript<>();
redisScript.setScriptSource(new ResourceScriptSource(new ClassPathResource("lua/limit.lua")));
redisScript.setResultType(Long.class);
return redisScript;
}Okay, our Lua script is now ready.
Annotation analysis
Next we need to customize the aspect to parse this annotation. Let’s take a look at the definition of the aspect:
@Aspect
@Component
public class RateLimiterAspect {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RateLimiterAspect.class);
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate;
@Autowired
private RedisScript<Long> limitScript;
@Before("@annotation(rateLimiter)")
public void doBefore(JoinPoint point, RateLimiter rateLimiter) throws Throwable {
String key = rateLimiter.key();
int time = rateLimiter.time();
int count = rateLimiter.count();
String combineKey = getCombineKey(rateLimiter, point);
List<Object> keys = Collections.singletonList(combineKey);
try {
Long number = redisTemplate.execute(limitScript, keys, count, time);
if (number==null || number.intValue() > count) {
throw new ServiceException("访问过于频繁,请稍候再试");
}
log.info("限制请求'{}',当前请求'{}',缓存key'{}'", count, number.intValue(), key);
} catch (ServiceException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("服务器限流异常,请稍候再试");
}
}
public String getCombineKey(RateLimiter rateLimiter, JoinPoint point) {
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer(rateLimiter.key());
if (rateLimiter.limitType() == LimitType.IP) {
stringBuffer.append(IpUtils.getIpAddr(((ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes()).getRequest())).append("-");
}
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) point.getSignature();
Method method = signature.getMethod();
Class<?> targetClass = method.getDeclaringClass();
stringBuffer.append(targetClass.getName()).append("-").append(method.getName());
return stringBuffer.toString();
}
}This aspect is to intercept all additions The @RateLimiter annotated method is added, and the annotation is processed in the pre-notification.
首先获取到注解中的 key、time 以及 count 三个参数。
获取一个组合的 key,所谓的组合的 key,就是在注解的 key 属性基础上,再加上方法的完整路径,如果是 IP 模式的话,就再加上 IP 地址。以 IP 模式为例,最终生成的 key 类似这样:
rate_limit:127.0.0.1-org.javaboy.ratelimiter.controller.HelloController-hello(如果不是 IP 模式,那么生成的 key 中就不包含 IP 地址)。将生成的 key 放到集合中。
通过 redisTemplate.execute 方法取执行一个 Lua 脚本,第一个参数是脚本所封装的对象,第二个参数是 key,对应了脚本中的 KEYS,后面是可变长度的参数,对应了脚本中的 ARGV。
判断 Lua 脚本执行后的结果是否超过 count,若超过则视为过载,抛出异常处理即可。
接口测试
接下来我们就进行接口的一个简单测试,如下:
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
@RateLimiter(time = 5,count = 3,limitType = LimitType.IP)
public String hello() {
return "hello>>>"+new Date();
}
}每一个 IP 地址,在 5 秒内只能访问 3 次。
这个自己手动刷新浏览器都能测试出来。
全局异常处理
由于过载的时候是抛异常出来,所以我们还需要一个全局异常处理器,如下:
@RestControllerAdvice
public class GlobalException {
@ExceptionHandler(ServiceException.class)
public Map<String,Object> serviceException(ServiceException e) {
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("status", 500);
map.put("message", e.getMessage());
return map;
}
}我将这句话重写成如下: 这个 demo 很小,所以我没有定义实体类,而是直接使用 Map 来返回 JSON。 最后我们看看过载时的测试效果:
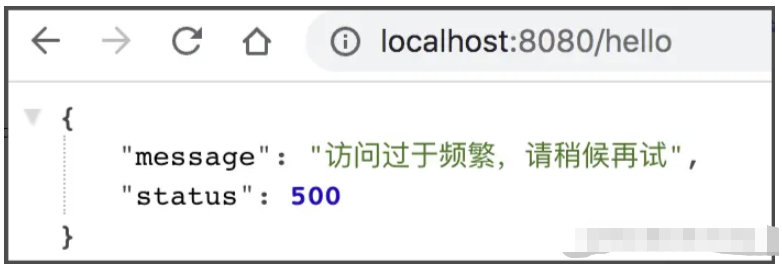
The above is the detailed content of How to use SpringBoot + Redis to implement interface current limiting. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1664
1664
 14
14
 1423
1423
 52
52
 1321
1321
 25
25
 1269
1269
 29
29
 1249
1249
 24
24
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
On CentOS systems, you can limit the execution time of Lua scripts by modifying Redis configuration files or using Redis commands to prevent malicious scripts from consuming too much resources. Method 1: Modify the Redis configuration file and locate the Redis configuration file: The Redis configuration file is usually located in /etc/redis/redis.conf. Edit configuration file: Open the configuration file using a text editor (such as vi or nano): sudovi/etc/redis/redis.conf Set the Lua script execution time limit: Add or modify the following lines in the configuration file to set the maximum execution time of the Lua script (unit: milliseconds)
 How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Use the Redis command line tool (redis-cli) to manage and operate Redis through the following steps: Connect to the server, specify the address and port. Send commands to the server using the command name and parameters. Use the HELP command to view help information for a specific command. Use the QUIT command to exit the command line tool.
 How to implement redis counter
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:21 PM
How to implement redis counter
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:21 PM
Redis counter is a mechanism that uses Redis key-value pair storage to implement counting operations, including the following steps: creating counter keys, increasing counts, decreasing counts, resetting counts, and obtaining counts. The advantages of Redis counters include fast speed, high concurrency, durability and simplicity and ease of use. It can be used in scenarios such as user access counting, real-time metric tracking, game scores and rankings, and order processing counting.
 How to set the redis expiration policy
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
How to set the redis expiration policy
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
There are two types of Redis data expiration strategies: periodic deletion: periodic scan to delete the expired key, which can be set through expired-time-cap-remove-count and expired-time-cap-remove-delay parameters. Lazy Deletion: Check for deletion expired keys only when keys are read or written. They can be set through lazyfree-lazy-eviction, lazyfree-lazy-expire, lazyfree-lazy-user-del parameters.
 How to optimize the performance of debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:48 AM
How to optimize the performance of debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:48 AM
In Debian systems, readdir system calls are used to read directory contents. If its performance is not good, try the following optimization strategy: Simplify the number of directory files: Split large directories into multiple small directories as much as possible, reducing the number of items processed per readdir call. Enable directory content caching: build a cache mechanism, update the cache regularly or when directory content changes, and reduce frequent calls to readdir. Memory caches (such as Memcached or Redis) or local caches (such as files or databases) can be considered. Adopt efficient data structure: If you implement directory traversal by yourself, select more efficient data structures (such as hash tables instead of linear search) to store and access directory information




