How Springboot integrates Redis to achieve overselling problem
Oversold simple code
Write a simple and normal oversold logic code, and multiple users can operate the same piece of data at the same time to explore the problems that arise.
Store a piece of data information in Redis, request the corresponding interface, and obtain the product quantity information;
If the product quantity information is greater than 0, deduct 1 and re-store it in Redis;
Running code test problem .
/**
* Redis数据库操作,超卖问题模拟
* @author
*
*/
@RestController
public class RedisController {
// 引入String类型redis操作模板
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
// 测试数据设置接口
@RequestMapping("/setStock")
public String setStock() {
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("stock", "100");
return "ok";
}
// 模拟商品超卖代码
@RequestMapping("/deductStock")
public String deductStock() {
// 获取Redis数据库中的商品数量
Integer stock = Integer.parseInt(stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("stock"));
// 减库存
if(stock > 0) {
int realStock = stock -1;
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("stock", String.valueOf(realStock));
System.out.println("商品扣减成功,剩余商品:"+realStock);
}else {
System.out.println("库存不足.....");
}
return "end";
}
}Oversold problem
In the case of single server and single application
In single application mode, use jmeter for stress testing.
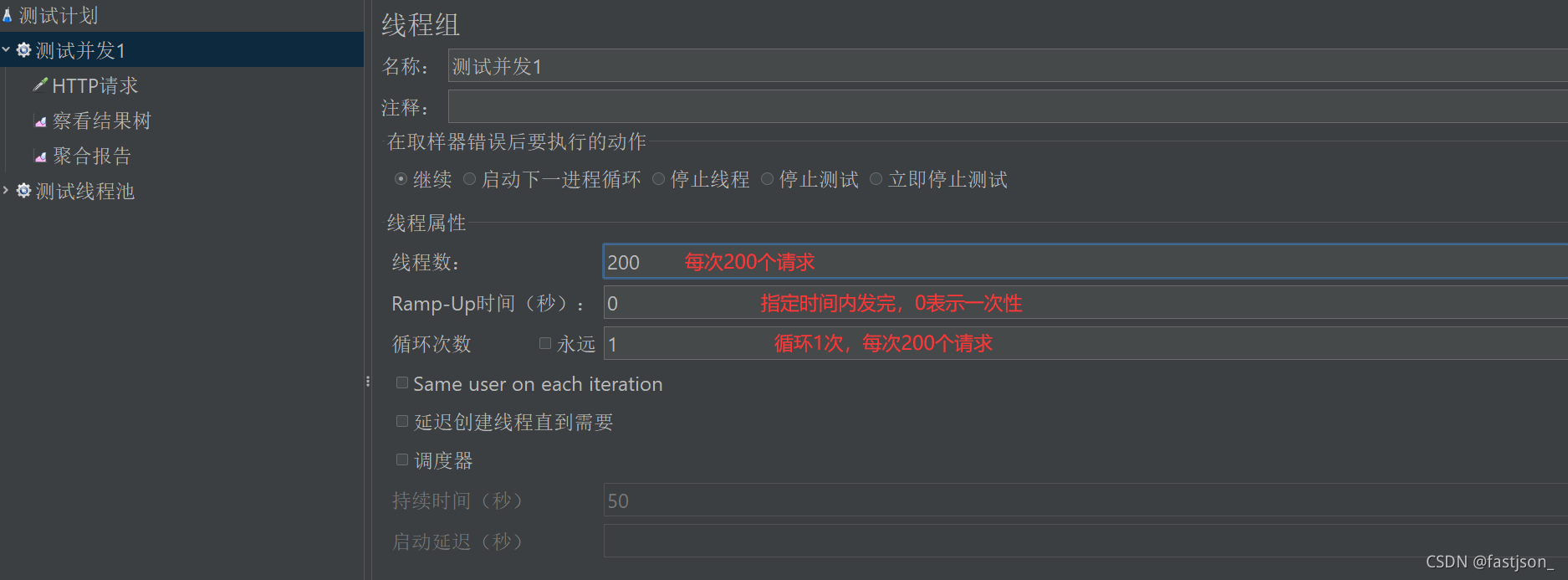
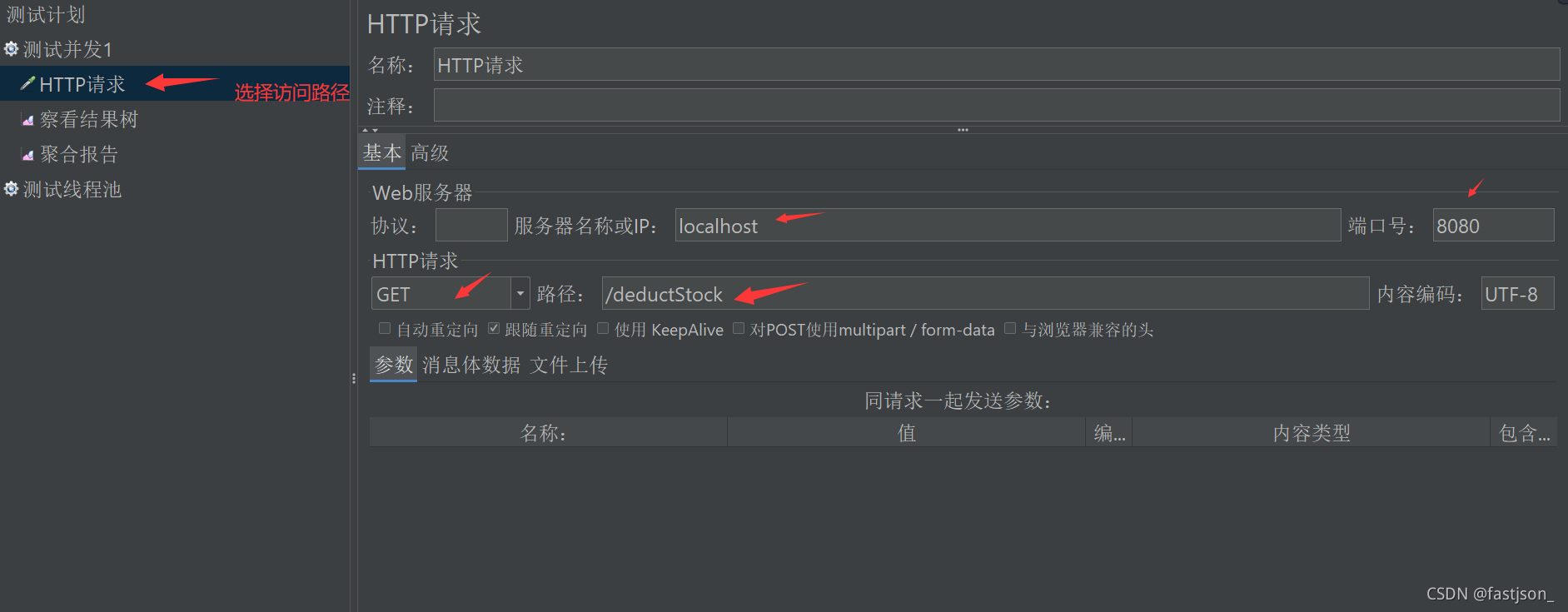
Test results:

Each request is equivalent to one thread, When several threads get the data at the same time, thread A gets the inventory as 84. At this time, thread B also enters the program and seizes the CPU, accessing the inventory as 84. In the end, both threads decrement the inventory by one, resulting in the final modification as 83. In fact, one more item was sold
Since the data processing is inconsistent between threads, can we use synchronized to lock the test?
Set up synchronized
Still test a single server first
// 模拟商品超卖代码,
// 设置synchronized同步锁
@RequestMapping("/deductStock1")
public String deductStock1() {
synchronized (this) {
// 获取Redis数据库中的商品数量
Integer stock = Integer.parseInt(stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("stock"));
// 减库存
if(stock > 0) {
int realStock = stock -1;
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("stock", String.valueOf(realStock));
System.out.println("商品扣减成功,剩余商品:"+realStock);
}else {
System.out.println("库存不足.....");
}
}
return "end";
}Quantity100
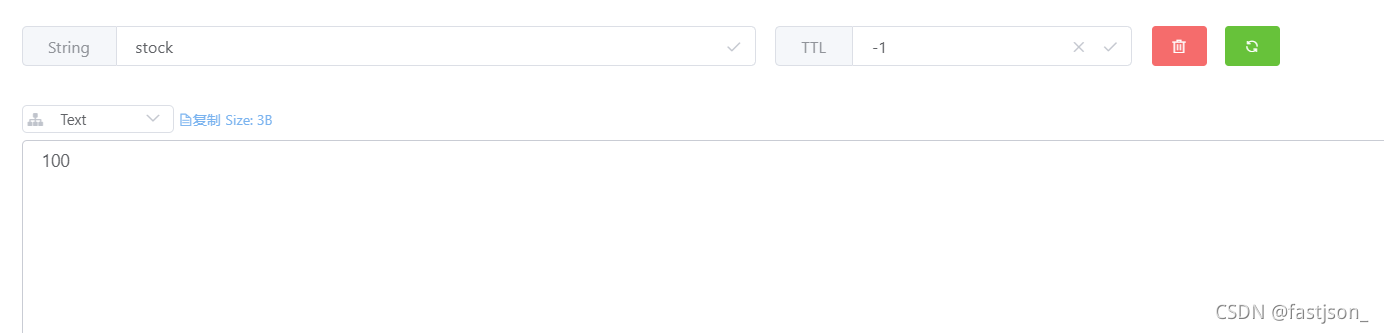
After re-testing, the log information obtained is as follows:

# In stand-alone mode, adding the synchronized keyword can indeed avoid the oversold phenomenon of products!
But in a distributed microservice, if a cluster is set up for the service, can synchronized still guarantee the correctness of the data?
Assuming that multiple requests are load balanced by the registration center, and the processing interface in each microservice is added with synchronized,
will still appear Similar oversold issues:
synchronizedOnlyJVMfor asingle serverLock, but the distribution is many different servers, causing two or more threads to jointly operate the product quantity information on different servers!
Redis implements distributed lock There is a command in Redis
setnx (set if not exists)
setnx key valueModify the processing interface and add keyIf the key does not exist, the setting can be successful; otherwise, the setting fails.
// 模拟商品超卖代码
@RequestMapping("/deductStock2")
public String deductStock2() {
// 创建一个key,保存至redis
String key = "lock";
// setnx
// 由于redis是一个单线程,执行命令采取“队列”形式排队!
// 优先进入队列的命令先执行,由于是setnx,第一个执行后,其他操作执行失败。
boolean result = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(key, "this is lock");
// 当不存在key时,可以设置成功,回执true;如果存在key,则无法设置,返回false
if (!result) {
// 前端监测,redis中存在,则不能让这个抢购操作执行,予以提示!
return "err";
}
// 获取Redis数据库中的商品数量
Integer stock = Integer.parseInt(stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("stock"));
// 减库存
if(stock > 0) {
int realStock = stock -1;
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("stock", String.valueOf(realStock));
System.out.println("商品扣减成功,剩余商品:"+realStock);
}else {
System.out.println("库存不足.....");
}
// 程序执行完成,则删除这个key
stringRedisTemplate.delete(key);
return "end";
}1. Request to enter the interface. If the key does not exist in redis, a new setnx will be created; if it exists, it will not It will be newly created and an error code will be returned at the same time, and the rush buying logic will not continue to be executed.This logic is much more reasonable than using2. After the creation is successful, execute the snap-up logic.
3. After the rush purchase logic is executed, delete the
keycorresponding tosetnxin the database. Enables other requests to be set up and acted upon.
syn alone before. However, if an exception occurs during the snap-up operation, this key cannot be used. delete. As a result, other processing requests have been unable to obtain key, and the program logic is deadlocked!
/**
* 模拟商品超卖代码 设置
*
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/deductStock3")
public String deductStock3() {
// 创建一个key,保存至redis
String key = "lock";
// setnx
// 由于redis是一个单线程,执行命令采取队列形式排队!优先进入队列的命令先执行,由于是setnx,第一个执行后,其他操作执行失败
boolean result = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(key, "this is lock");
// 当不存在key时,可以设置成功,回执true;如果存在key,则无法设置,返回false
if (!result) {
// 前端监测,redis中存在,则不能让这个抢购操作执行,予以提示!
return "err";
}
try {
// 获取Redis数据库中的商品数量
Integer stock = Integer.parseInt(stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("stock"));
// 减库存
if (stock > 0) {
int realStock = stock - 1;
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("stock", String.valueOf(realStock));
System.out.println("商品扣减成功,剩余商品:" + realStock);
} else {
System.out.println("库存不足.....");
}
} finally {
// 程序执行完成,则删除这个key
// 放置于finally中,保证即使上述逻辑出问题,也能del掉
stringRedisTemplate.delete(key);
}
return "end";
}downtime due to power outage, system crash, etc., the statements in finally that should be executed will not be successfully executed! ! It also appears that key always exists, resulting in deadlock!
setnx, and before the snap-up code logic is executed, increase the key time limit.
/**
* 模拟商品超卖代码 设置setnx保证分布式环境下,数据处理安全行问题;<br>
* 但如果某个代码段执行异常,导致key无法清理,出现死锁,添加try...finally;<br>
* 如果某个服务因某些问题导致释放key不能执行,导致死锁,此时解决思路为:增加key的有效时间;<br>
* 为了保证设置key的值和设置key的有效时间,两条命令构成同一条原子命令,将下列逻辑换成其他代码。
*
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/deductStock4")
public String deductStock4() {
// 创建一个key,保存至redis
String key = "lock";
// setnx
// 由于redis是一个单线程,执行命令采取队列形式排队!优先进入队列的命令先执行,由于是setnx,第一个执行后,其他操作执行失败
//boolean result = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(key, "this is lock");
//让设置key和设置key的有效时间都可以同时执行
boolean result = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(key, "this is lock", 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 当不存在key时,可以设置成功,回执true;如果存在key,则无法设置,返回false
if (!result) {
// 前端监测,redis中存在,则不能让这个抢购操作执行,予以提示!
return "err";
}
// 设置key有效时间
//stringRedisTemplate.expire(key, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
try {
// 获取Redis数据库中的商品数量
Integer stock = Integer.parseInt(stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("stock"));
// 减库存
if (stock > 0) {
int realStock = stock - 1;
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("stock", String.valueOf(realStock));
System.out.println("商品扣减成功,剩余商品:" + realStock);
} else {
System.out.println("库存不足.....");
}
} finally {
// 程序执行完成,则删除这个key
// 放置于finally中,保证即使上述逻辑出问题,也能del掉
stringRedisTemplate.delete(key);
}
return "end";
}If there is atimeout
problem in the processing logic.When the logic is executed and the time exceeds the set key validity time, what problems will occur at this time?
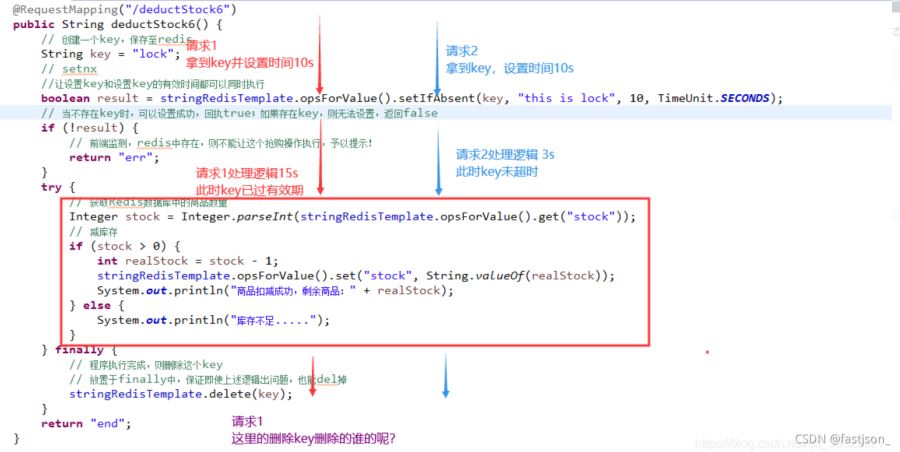
From the above figure we can clearly see the problem:If the execution time of a request exceeds the valid time of the key.
When a new request is executed, the key must be obtained and the time can be set;
The key saved in redis at this time is not the key of request 1, but set by other requests.
After the execution of request 1 is completed, the key is deleted here. What is deleted is the key set by other requests!
依然出现了key形同虚设的问题!如果失效一直存在,超卖问题依旧不会解决。
通过key设置值匹配的方式解决形同虚设问题
既然出现key形同虚设的现象,是否可以增加条件,当finally中需要执行删除操作时,获取数据判断值是否是该请求中对应的,如果是则删除,不是则不管!
修改上述代码如下所示:
/**
* 模拟商品超卖代码 <br>
* 解决`deductStock6`中,key形同虚设的问题。
*
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/deductStock5")
public String deductStock5() {
// 创建一个key,保存至redis
String key = "lock";
String lock_value = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
// setnx
//让设置key和设置key的有效时间都可以同时执行
boolean result = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(key, lock_value, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 当不存在key时,可以设置成功,回执true;如果存在key,则无法设置,返回false
if (!result) {
// 前端监测,redis中存在,则不能让这个抢购操作执行,予以提示!
return "err";
}
try {
// 获取Redis数据库中的商品数量
Integer stock = Integer.parseInt(stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("stock"));
// 减库存
if (stock > 0) {
int realStock = stock - 1;
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("stock", String.valueOf(realStock));
System.out.println("商品扣减成功,剩余商品:" + realStock);
} else {
System.out.println("库存不足.....");
}
} finally {
// 程序执行完成,则删除这个key
// 放置于finally中,保证即使上述逻辑出问题,也能del掉
// 判断redis中该数据是否是这个接口处理时的设置的,如果是则删除
if(lock_value.equalsIgnoreCase(stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key))) {
stringRedisTemplate.delete(key);
}
}
return "end";
}由于获得锁的线程必须执行完减库存逻辑才能释放锁,所以在此期间所有其他的线程都会由于没获得锁,而直接结束程序,导致有很多库存根本没有卖出去,所以这里应该可以优化,让没获得锁的线程等待,或者循环检查锁
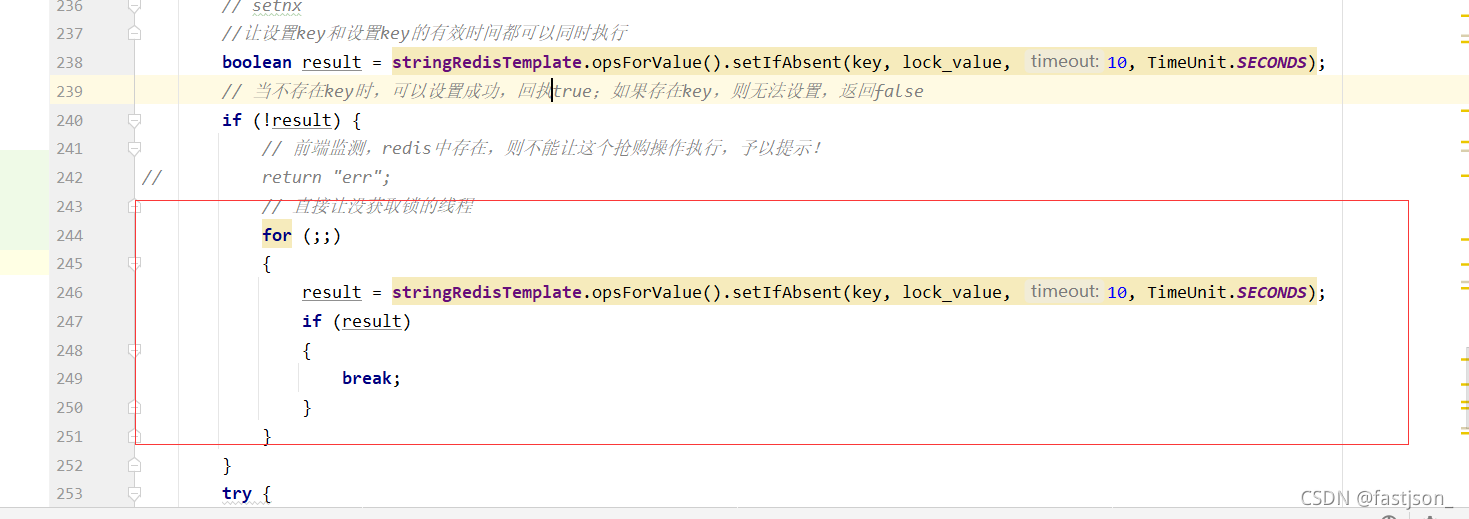
最终版
我们将锁封装到一个实体类中,然后加入两个方法,加锁和解锁
@Component
public class RedisLock {
private final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
private final long acquireTimeout = 10*1000; // 获取锁之前的超时时间(获取锁的等待重试时间)
private final int timeOut = 20; // 获取锁之后的超时时间(防止死锁)
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate; // 引入String类型redis操作模板
/**
* 获取分布式锁
* @return 锁标识
*/
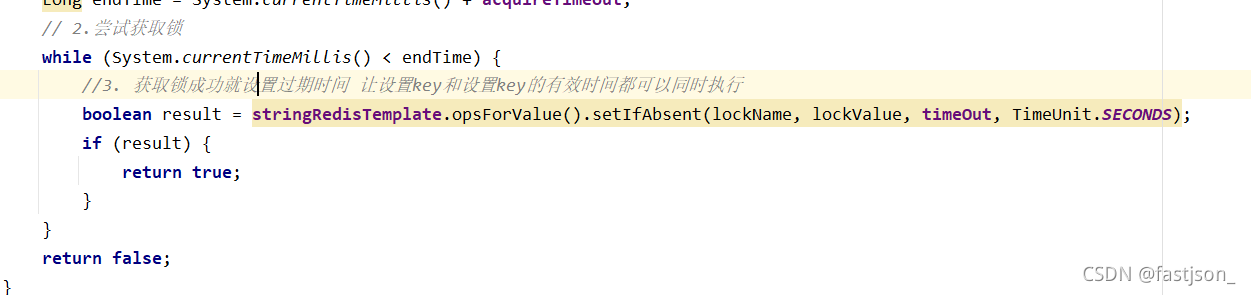
public boolean getRedisLock(String lockName,String lockValue) {
// 1.计算获取锁的时间
Long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis() + acquireTimeout;
// 2.尝试获取锁
while (System.currentTimeMillis() < endTime) {
//3. 获取锁成功就设置过期时间 让设置key和设置key的有效时间都可以同时执行
boolean result = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(lockName, lockValue, timeOut, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
if (result) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* 释放分布式锁
* @param lockName 锁名称
* @param lockValue 锁值
*/
public void unRedisLock(String lockName,String lockValue) {
if(lockValue.equalsIgnoreCase(stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(lockName))) {
stringRedisTemplate.delete(lockName);
}
}
}@RestController
public class RedisController {
// 引入String类型redis操作模板
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
@Autowired
private RedisLock redisLock;
@RequestMapping("/setStock")
public String setStock() {
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("stock", "100");
return "ok";
}
@RequestMapping("/deductStock")
public String deductStock() {
// 创建一个key,保存至redis
String key = "lock";
String lock_value = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
try {
boolean redisLock = this.redisLock.getRedisLock(key, lock_value);//获取锁
if (redisLock)
{
// 获取Redis数据库中的商品数量
Integer stock = Integer.parseInt(stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get("stock"));
// 减库存
if (stock > 0) {
int realStock = stock - 1;
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("stock", String.valueOf(realStock));
System.out.println("商品扣减成功,剩余商品:" + realStock);
} else {
System.out.println("库存不足.....");
}
}
} finally {
redisLock.unRedisLock(key,lock_value); //释放锁
}
return "end";
}
}可以看到失败的线程不会直接结束,而是会尝试重试,一直到重试结束时间,才会结束
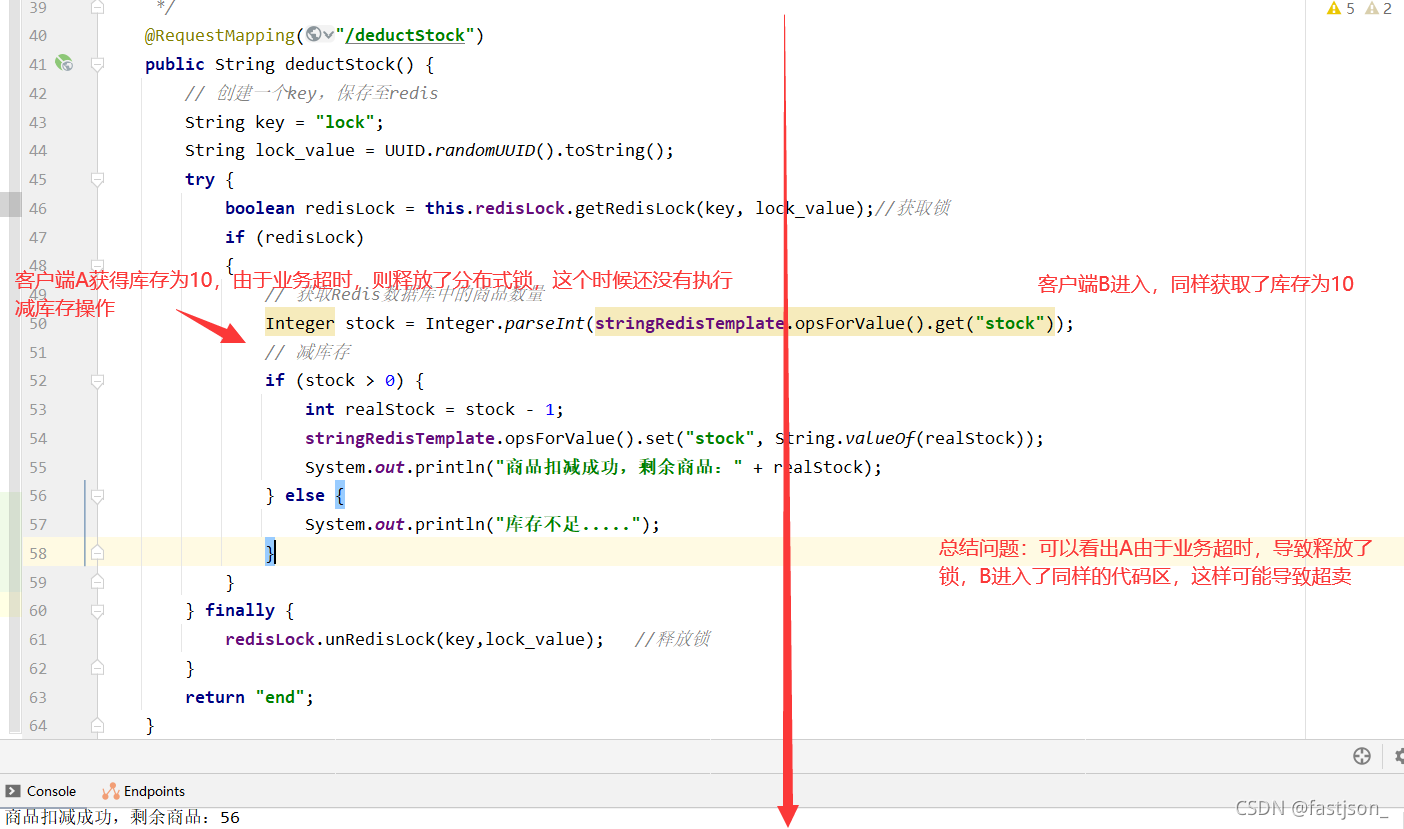
实际上这个最终版依然存在3个问题
1、在finally流程中,由于是先判断在处理。如果判断条件结束后,获取到的结果为true。但是在执行del操作前,此时jvm在执行GC操作(为了保证GC操作获取GC roots根完全,会暂停java程序),导致程序暂停。在GC操作完成并恢复后,执行del操作时,当前被加锁的key是否仍然存在?
2、问题如图所示
The above is the detailed content of How Springboot integrates Redis to achieve overselling problem. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1664
1664
 14
14
 1423
1423
 52
52
 1317
1317
 25
25
 1268
1268
 29
29
 1245
1245
 24
24
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
On CentOS systems, you can limit the execution time of Lua scripts by modifying Redis configuration files or using Redis commands to prevent malicious scripts from consuming too much resources. Method 1: Modify the Redis configuration file and locate the Redis configuration file: The Redis configuration file is usually located in /etc/redis/redis.conf. Edit configuration file: Open the configuration file using a text editor (such as vi or nano): sudovi/etc/redis/redis.conf Set the Lua script execution time limit: Add or modify the following lines in the configuration file to set the maximum execution time of the Lua script (unit: milliseconds)
 How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Use the Redis command line tool (redis-cli) to manage and operate Redis through the following steps: Connect to the server, specify the address and port. Send commands to the server using the command name and parameters. Use the HELP command to view help information for a specific command. Use the QUIT command to exit the command line tool.
 How to implement redis counter
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:21 PM
How to implement redis counter
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:21 PM
Redis counter is a mechanism that uses Redis key-value pair storage to implement counting operations, including the following steps: creating counter keys, increasing counts, decreasing counts, resetting counts, and obtaining counts. The advantages of Redis counters include fast speed, high concurrency, durability and simplicity and ease of use. It can be used in scenarios such as user access counting, real-time metric tracking, game scores and rankings, and order processing counting.
 How to set the redis expiration policy
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
How to set the redis expiration policy
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
There are two types of Redis data expiration strategies: periodic deletion: periodic scan to delete the expired key, which can be set through expired-time-cap-remove-count and expired-time-cap-remove-delay parameters. Lazy Deletion: Check for deletion expired keys only when keys are read or written. They can be set through lazyfree-lazy-eviction, lazyfree-lazy-expire, lazyfree-lazy-user-del parameters.
 How to optimize the performance of debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:48 AM
How to optimize the performance of debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:48 AM
In Debian systems, readdir system calls are used to read directory contents. If its performance is not good, try the following optimization strategy: Simplify the number of directory files: Split large directories into multiple small directories as much as possible, reducing the number of items processed per readdir call. Enable directory content caching: build a cache mechanism, update the cache regularly or when directory content changes, and reduce frequent calls to readdir. Memory caches (such as Memcached or Redis) or local caches (such as files or databases) can be considered. Adopt efficient data structure: If you implement directory traversal by yourself, select more efficient data structures (such as hash tables instead of linear search) to store and access directory information




