How to implement Redis cluster installation and configuration under Docker
1. Pull the mirrors from all machines
docker pull redis
2. Build the master-slave cluster
2.1. redis.cong file
2.1.1. Master node:
bind 0.0.0.0 protected-mode no //redis配置访问密码 requirepass 123456 //主节点密码 哨兵模式下主节点宕机从新恢复变成从节点 需要密码 masterauth 123456
2.1.2. Slave node:
bind 0.0.0.0 protected-mode no requirepass 123456 //主节点访问密码 masterauth 123456 //主节点信息 slaveof *.*.*.* 6379
2.2. Create a local mapping folder and put redis.conf in /usr/local/redis/ conf folder
# /usr/local/redis cd /usr/locar/redis mkdir conf mkdir data
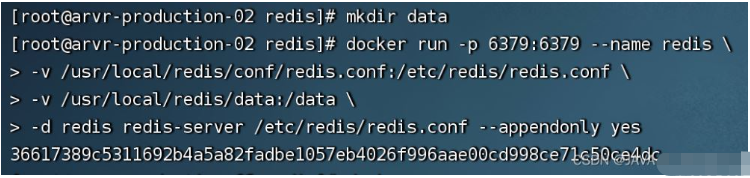
2.3. Start redis
docker run -p 6379:6379 --name redis \ -v /usr/local/redis/conf/redis.conf:/etc/redis/redis.conf \ -v /usr/local/redis/data:/data \ -d redis redis-server /etc/redis/redis.conf --appendonly yes
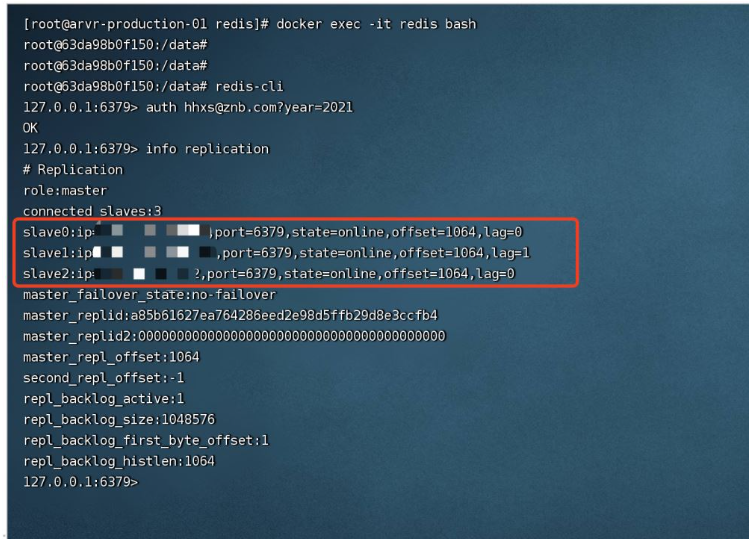
2.4. Verify whether the redis master-slave cluster installation is successful
### 在主节点查看 # 进入容器内部 docker exec -it redis bash # 进入redis redis-cli # 校验密码 auth 123456 # 查看集群信息 info replication

3. Turn on sentinel mode
3.1. Sentinel.conf configuration file
#### 根据需要修改一下内容 # 让sentinel服务后台运行(docker的话需要设置为no,非docker运行设置为yes, 因为docker有个-d属性就是让在后台运行的) daemonize no # 修改日志文件的路径 logfile "/data/sentinel.log" # 修改监控的主redis服务器 # 最后一个2表示,两台机器判定主被动下线后,就进行failover(故障转移) sentinel monitor mymaster *.*.*.*(公网ip) 6390 2 #超过5秒master还没有连接上,则认为master已经停止 sentinel down-after-milliseconds mymaster 5000 sentinel auth-pass mymaster 123456
3.2. Create a local mapping folder, And put sentinel.conf in the /usr/local/redis-sentinel/conf folder
# /usr/local/redis cd /usr/locar/redis-sentinel mkdir conf mkdir data
3.3. Start the redis-sentinel process
docker run -d --name sentinel -p 26379:26379 \ -v /usr/local/redis-sentinel/conf/sentinel.conf:/etc/sentinel.conf \ -v /usr/local/redis-sentinel/data:/data redis redis-sentinel /etc/sentinel.conf
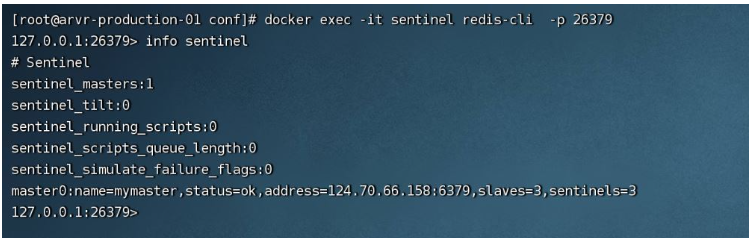
3.4. Enter the redis-sentinel container to view
# 进入sentinel节点 docker exec -it sentinel redis-cli -p 26379 # 查看sentinel信息 info sentinel
3.5. Service test
Close the master node
Execute multiple times "info replication" command to observe the changes in information after executing the 2.4 verification module built by the master-slave cluster
or monitor the log file of the sentinel configuration, you can see its occurrence in real time The change

The above is the detailed content of How to implement Redis cluster installation and configuration under Docker. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1665
1665
 14
14
 1423
1423
 52
52
 1321
1321
 25
25
 1269
1269
 29
29
 1249
1249
 24
24
 How to exit the container by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:15 PM
How to exit the container by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:15 PM
Four ways to exit Docker container: Use Ctrl D in the container terminal Enter exit command in the container terminal Use docker stop <container_name> Command Use docker kill <container_name> command in the host terminal (force exit)
 How to copy files in docker to outside
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
How to copy files in docker to outside
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
Methods for copying files to external hosts in Docker: Use the docker cp command: Execute docker cp [Options] <Container Path> <Host Path>. Using data volumes: Create a directory on the host, and use the -v parameter to mount the directory into the container when creating the container to achieve bidirectional file synchronization.
 How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
You can query the Docker container name by following the steps: List all containers (docker ps). Filter the container list (using the grep command). Gets the container name (located in the "NAMES" column).
 How to start containers by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
How to start containers by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Docker container startup steps: Pull the container image: Run "docker pull [mirror name]". Create a container: Use "docker create [options] [mirror name] [commands and parameters]". Start the container: Execute "docker start [Container name or ID]". Check container status: Verify that the container is running with "docker ps".
 How to restart docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:06 PM
How to restart docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:06 PM
How to restart the Docker container: get the container ID (docker ps); stop the container (docker stop <container_id>); start the container (docker start <container_id>); verify that the restart is successful (docker ps). Other methods: Docker Compose (docker-compose restart) or Docker API (see Docker documentation).
 How to start mysql by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
How to start mysql by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
The process of starting MySQL in Docker consists of the following steps: Pull the MySQL image to create and start the container, set the root user password, and map the port verification connection Create the database and the user grants all permissions to the database
 How to create containers for docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
How to create containers for docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
Create a container in Docker: 1. Pull the image: docker pull [mirror name] 2. Create a container: docker run [Options] [mirror name] [Command] 3. Start the container: docker start [Container name]
 How to view logs from docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:24 PM
How to view logs from docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:24 PM
The methods to view Docker logs include: using the docker logs command, for example: docker logs CONTAINER_NAME Use the docker exec command to run /bin/sh and view the log file, for example: docker exec -it CONTAINER_NAME /bin/sh ; cat /var/log/CONTAINER_NAME.log Use the docker-compose logs command of Docker Compose, for example: docker-compose -f docker-com




