How to implement semi-sync replication in MySQL
1. Introduction to Semi-Synchronization
MASTERThe node does not return the result to the client immediately after executing the transaction submitted by the client, but waits for at least one The SLAVE node receives and writes it to the relay log before returning it to the client.Compared with asynchronous replication, semi-synchronization improves data security, but also causes a certain degree of delay. This delay is at least one TCP round trip time. Therefore, semi-synchronous replication is best used in low-latency networks.
MySQL has supported semi-synchronous replication since version 5.5. Semi-synchronous replication was improved in version 5.7.2; the original semi-synchronous strategy was AFTER_COMMIT and the improved strategy is The difference between AFTER_SYNC and the two is that the timing of the SLAVE node's ACK response to the MASTER is different.
2. Introduction to the two modes
AFTER_COMMIT Mode introduction
MASTER writes each transaction to the binary log and Flush and save, and send the transaction to SLAVE at the same time, then submit the transaction to the storage engine for processing and submission, and then wait for SLAVE to return confirmation information. After receiving the confirmation information, MASTER returns the result to the client, and then the current client can continue working.
AFTER_SYNC Mode introduction
MASTER writes each transaction to the binary log and flushes the disk to save it. At the same time, it sends the transaction to SLAVE, and then waits for SLAVE to return confirmation information. After receiving the confirmation information, the transaction is submitted to the storage engine for processing and submission, and the result is returned to the client, and then the current client can continue to work.
3. Comparison of the two methods
For the first AFTER_COMMIT method, the current client can only submit data to the storage engine after the server submits the data and receives the confirmation returned by SLAVE. , will receive the return result of the transaction. Before receiving confirmation information from SLAVE after the transaction is submitted, other clients can see the transaction information submitted by the current client at this moment.
If the SLAVE node does not receive the transaction passed by the MASTER node due to network and other reasons, and the MASTER node crashes at this moment. HA performs failover and the clients are connected to the SLAVE node. At this time, the transactions previously seen on the MASTER node are not seen on the SLAVE node, and transaction loss occurs.
For the second AFTER_SYNC method, when the transaction is confirmed by SLAVE and MASTER commits the transaction at the storage engine level, all clients can see the data changes caused by the transaction. Therefore, all clients see the same data on the MASTER at the same time.
When the MASTER node crashes, all transactions submitted on the MASTER are copied to SLAVE (saved in the relay log). The MASTER server crashed unexpectedly. At this moment, after HA fails over to SALVE, the data seen by the client is lossless because SLAVE is the latest.
Note, however, that in this case, MASTER cannot be directly restored to use because its binary log may contain uncommitted transactions. At this moment, when the binary log is restored and used for business needs, it may cause a conflict with SLAVE.
4. How to enable semi-synchronization
Method 1: Semi-synchronization exists in the form of a plug-in, and we can directly enable it online (this method is used this time)
Master node starts:
[root@GreatSQL][(none)]>INSTALL PLUGIN rpl_semi_sync_master SONAME 'semisync_master.so'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
Slave node starts:
[root@GreatSQL][(none)]>INSTALL PLUGIN rpl_semi_sync_slave SONAME 'semisync_slave.so'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
PS: Under normal circumstances, all nodes deploy the master and slave plug-ins simultaneously, so that it will be more convenient to handle during failover.
Method 2: Enable it in the my.cnf configuration
Both master and slave nodes are configured to open simultaneously:
plugin-load="rpl_semi_sync_master=semisync_master.so;rpl_sync_slave=semisync_slave.so" rpl_semi_sync_master_enabled=1 rpl_semi_sync_slave_enabled=1
5. Check the plug-in activation status
Method 1: Query plugin
Master node view:
[root@GreatSQL][test]>show plugins; | rpl_semi_sync_master | ACTIVE | REPLICATION | semisync_master.so | GPL |
Slave node view:
[root@GreatSQL][(none)]>show plugins; | rpl_semi_sync_slave | ACTIVE | REPLICATION | semisync_slave.so | GPL |
Method 2:Queryinformation_schema.pluginsMore comprehensive information
Master node information:
(Thu Feb 17 03:03:12 2022)[root@GreatSQL][(none)]>select * from information_schema.plugins where plugin_name like "%semi%"\G;
*************************** 1. row ***************************
PLUGIN_NAME: rpl_semi_sync_master
PLUGIN_VERSION: 1.0
PLUGIN_STATUS: ACTIVE
PLUGIN_TYPE: REPLICATION
PLUGIN_TYPE_VERSION: 4.0
PLUGIN_LIBRARY: semisync_master.so
PLUGIN_LIBRARY_VERSION: 1.10
PLUGIN_AUTHOR: Oracle Corporation
PLUGIN_DESCRIPTION: Semi-synchronous replication master
PLUGIN_LICENSE: GPL
LOAD_OPTION: ON
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
ERROR:
No query specified
# 从节点信息
(Thu Feb 17 16:05:19 2022)[root@GreatSQL][(none)]>select * from information_schema.plugins where plugin_name like "%semi%"\G;
*************************** 1. row ***************************
PLUGIN_NAME: rpl_semi_sync_slave
PLUGIN_VERSION: 1.0
PLUGIN_STATUS: ACTIVE
PLUGIN_TYPE: REPLICATION
PLUGIN_TYPE_VERSION: 4.0
PLUGIN_LIBRARY: semisync_slave.so
PLUGIN_LIBRARY_VERSION: 1.10
PLUGIN_AUTHOR: Oracle Corporation
PLUGIN_DESCRIPTION: Semi-synchronous replication slave
PLUGIN_LICENSE: GPL
LOAD_OPTION: ON
1 row in set (0.00 sec6. Turn on the semi-synchronization function
Because the above is online The plug-in is installed, so after the plug-in installation is completed, the service needs to be started
Enable semi-synchronous replication on the master node:
[root@GreatSQL][test]>SET GLOBAL rpl_semi_sync_master_enabled = on; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Enable semi-synchronous replication on the slave node :
t@GreatSQL][(none)]>SET GLOBAL rpl_semi_sync_slave_enabled = on; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
After the above settings are completed, restart the IO thread from the slave node
(Mon Feb 14 15:19:58 2022)[root@GreatSQL][(none)]> (Mon Feb 14 15:19:58 2022)[root@GreatSQL][(none)]>STOP SLAVE IO_THREAD; Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.01 sec) (Mon Feb 14 15:21:41 2022)[root@GreatSQL][(none)]>START SLAVE IO_THREAD; Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.01 sec)
7. Check whether semi-synchronization is running
Master node:
[root@GreatSQL][test]>show status like 'Rpl_semi_sync_master_status'; +-----------------------------+-------+ | Variable_name | Value | +-----------------------------+-------+ | Rpl_semi_sync_master_status | ON | +-----------------------------+-------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Slave node:
[root@GreatSQL][(none)]>show status like 'Rpl_semi_sync_slave_status'; +----------------------------+-------+ | Variable_name | Value | +----------------------------+-------+ | Rpl_semi_sync_slave_status | ON | +----------------------------+-------+ 1 row in set (0.01 sec)
Check the master node error.log, you can see that the slave node has enabled semi-synchronous replication
# 关键信息 Start semi-sync binlog_dump to slave (server_id: 3306) 2022-02-14T02:16:35.411061-05:00 13 [Note] [MY-010014] [Repl] While initializing dump thread for slave with UUID <652ade08-8b1c-11ec-9f62-00155dcff90a>, found a zombie dump thread with the same UUID. Master is killing the zombie dump thread(12). 2022-02-14T02:16:35.411236-05:00 13 [Note] [MY-010462] [Repl] Start binlog_dump to master_thread_id(13) slave_server(3306), pos(, 4) 2022-02-14T02:16:35.411263-05:00 13 [Note] [MY-011170] [Repl] Start asynchronous binlog_dump to slave (server_id: 3306), pos(, 4). 2022-02-14T02:16:35.411419-05:00 12 [Note] [MY-011171] [Repl] Stop asynchronous binlog_dump to slave (server_id: 3306). 2022-02-14T02:19:33.913084-05:00 9 [Note] [MY-011130] [Repl] Semi-sync replication initialized for transactions. 2022-02-14T02:19:33.913133-05:00 9 [Note] [MY-011142] [Repl] Semi-sync replication enabled on the master. 2022-02-14T02:19:33.913638-05:00 0 [Note] [MY-011166] [Repl] Starting ack receiver thread. 2022-02-14T02:21:46.899725-05:00 14 [Note] [MY-010014] [Repl] While initializing dump thread for slave with UUID <652ade08-8b1c-11ec-9f62-00155dcff90a>, found a zombie dump thread with the same UUID. Master is killing the zombie dump thread(13). 2022-02-14T02:21:46.899894-05:00 14 [Note] [MY-010462] [Repl] Start binlog_dump to master_thread_id(14) slave_server(3306), pos(, 4) 2022-02-14T02:21:46.899953-05:00 14 [Note] [MY-011170] [Repl] Start semi-sync binlog_dump to slave (server_id: 3306), pos(, 4).
or above, MySQL semi-synchronous replication is set up!
8. Semi-synchronous parameter information
Master node parameter information:
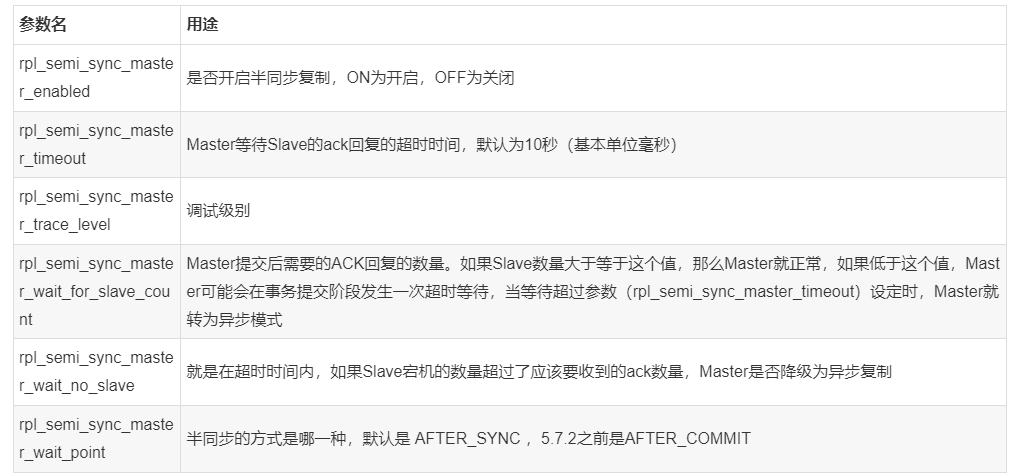
[root@GreatSQL][test]>show variables like '%Rpl%'; +-------------------------------------------+------------+ | Variable_name | Value | +-------------------------------------------+------------+ | rpl_read_size | 8192 | | rpl_semi_sync_master_enabled | ON | | rpl_semi_sync_master_timeout | 10000 | | rpl_semi_sync_master_trace_level | 32 | | rpl_semi_sync_master_wait_for_slave_count | 1 | | rpl_semi_sync_master_wait_no_slave | ON | | rpl_semi_sync_master_wait_point | AFTER_SYNC | | rpl_stop_slave_timeout | 31536000 | +-------------------------------------------+------------+ 8 rows in set (0.00 sec)
Brief description of some parameters:
Slave node parameter information:
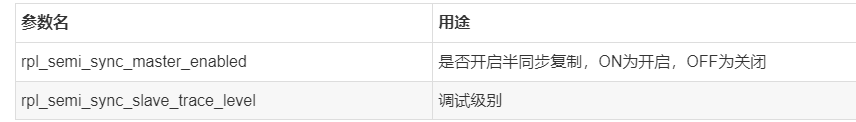
[root@GreatSQL][test]>show variables like '%Rpl%'; +---------------------------------+----------+ | Variable_name | Value | +---------------------------------+----------+ | rpl_read_size | 8192 | | rpl_semi_sync_slave_enabled | ON | | rpl_semi_sync_slave_trace_level | 32 | | rpl_stop_slave_timeout | 31536000 | +---------------------------------+----------+ 4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
Brief description of some parameters:
九、半同步状态信息
主节点查看:
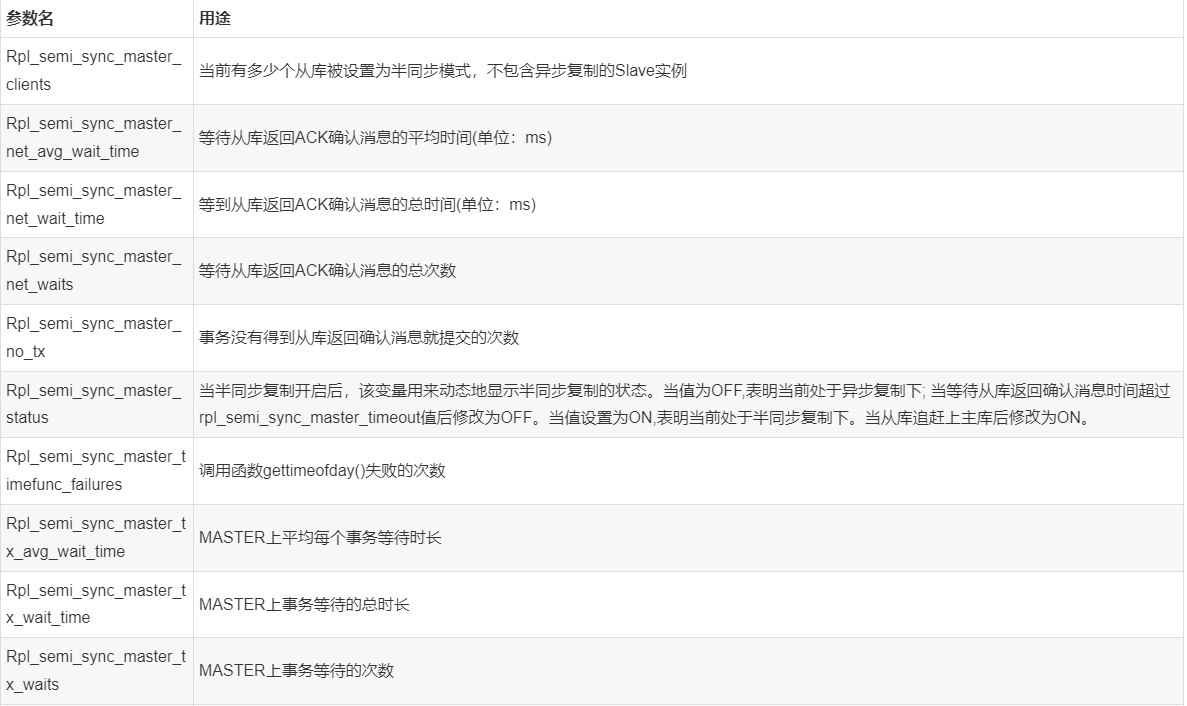
[root@GreatSQL][test]> show status like '%Rpl_semi%'; +--------------------------------------------+-------+ | Variable_name | Value | +--------------------------------------------+-------+ | Rpl_semi_sync_master_clients | 1 | | Rpl_semi_sync_master_net_avg_wait_time | 0 | | Rpl_semi_sync_master_net_wait_time | 0 | | Rpl_semi_sync_master_net_waits | 0 | | Rpl_semi_sync_master_no_times | 0 | | Rpl_semi_sync_master_no_tx | 0 | | Rpl_semi_sync_master_status | ON | | Rpl_semi_sync_master_timefunc_failures | 0 | | Rpl_semi_sync_master_tx_avg_wait_time | 0 | | Rpl_semi_sync_master_tx_wait_time | 0 | | Rpl_semi_sync_master_tx_waits | 0 | | Rpl_semi_sync_master_wait_pos_backtraverse | 0 | | Rpl_semi_sync_master_wait_sessions | 0 | | Rpl_semi_sync_master_yes_tx | 0 | +--------------------------------------------+-------+ 14 rows in set (0.00 sec)
部分参数用途简要说明:
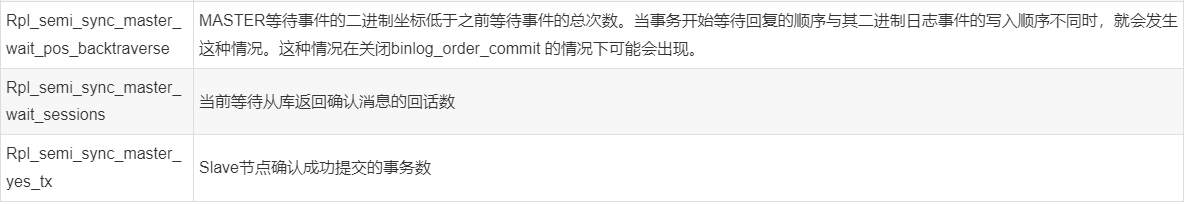
从节点转态信息:
show global status like '%semi%'; +----------------------------+-------+ | Variable_name | Value | +----------------------------+-------+ | Rpl_semi_sync_slave_status | ON | +----------------------------+-------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
参数简单说明:

十、测试一下半同步的同步情况
半同步是否会降级为异步复制?是会的。
当半同步复制发生超时时(由rpl_semi_sync_master_timeout参数控制,单位是毫秒,默认为10000,即10s),会暂时关闭半同步复制,转而使用异步复制。
当MASTER DUMP 线程发送完一个事务的所有事件之后,如果在rpl_semi_sync_master_timeout内,收到了从库的响应,则主从又重新恢复为半同步复制。
1.从节点暂时先关掉IO线程
[root@GreatSQL][(none)]>STOP SLAVE IO_THREAD; Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.02 sec)
2.主节点写入几条测试数据
[root@GreatSQL][test]>insert into ptype values(4,'4','4'),(5,'5','5'),(6,'6','6'); Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.02 sec)
3.等待10s后查看复制状态,半同步已经关掉了
[root@GreatSQL][test]>show status like 'Rpl_semi_sync_slave_status'; +----------------------------+-------+ | Variable_name | Value | +----------------------------+-------+ | Rpl_semi_sync_slave_status | OFF | +----------------------------+-------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
4.从节点开启IO线程
[root@GreatSQL][(none)]>START SLAVE IO_THREAD; Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.02 sec)
5.再次查看复制状态,半同步复制自动开启了
t@GreatSQL][test]>show status like 'Rpl_semi_sync_slave_status'; +----------------------------+-------+ | Variable_name | Value | +----------------------------+-------+ | Rpl_semi_sync_slave_status | ON | +----------------------------+-------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
The above is the detailed content of How to implement semi-sync replication in MySQL. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1664
1664
 14
14
 1423
1423
 52
52
 1317
1317
 25
25
 1268
1268
 29
29
 1242
1242
 24
24
 MySQL's Role: Databases in Web Applications
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
MySQL's Role: Databases in Web Applications
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
The main role of MySQL in web applications is to store and manage data. 1.MySQL efficiently processes user information, product catalogs, transaction records and other data. 2. Through SQL query, developers can extract information from the database to generate dynamic content. 3.MySQL works based on the client-server model to ensure acceptable query speed.
 Laravel Introduction Example
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
Laravel Introduction Example
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
Laravel is a PHP framework for easy building of web applications. It provides a range of powerful features including: Installation: Install the Laravel CLI globally with Composer and create applications in the project directory. Routing: Define the relationship between the URL and the handler in routes/web.php. View: Create a view in resources/views to render the application's interface. Database Integration: Provides out-of-the-box integration with databases such as MySQL and uses migration to create and modify tables. Model and Controller: The model represents the database entity and the controller processes HTTP requests.
 MySQL and phpMyAdmin: Core Features and Functions
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:12 AM
MySQL and phpMyAdmin: Core Features and Functions
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:12 AM
MySQL and phpMyAdmin are powerful database management tools. 1) MySQL is used to create databases and tables, and to execute DML and SQL queries. 2) phpMyAdmin provides an intuitive interface for database management, table structure management, data operations and user permission management.
 MySQL vs. Other Programming Languages: A Comparison
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:22 AM
MySQL vs. Other Programming Languages: A Comparison
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Compared with other programming languages, MySQL is mainly used to store and manage data, while other languages such as Python, Java, and C are used for logical processing and application development. MySQL is known for its high performance, scalability and cross-platform support, suitable for data management needs, while other languages have advantages in their respective fields such as data analytics, enterprise applications, and system programming.
 Solve database connection problem: a practical case of using minii/db library
Apr 18, 2025 am 07:09 AM
Solve database connection problem: a practical case of using minii/db library
Apr 18, 2025 am 07:09 AM
I encountered a tricky problem when developing a small application: the need to quickly integrate a lightweight database operation library. After trying multiple libraries, I found that they either have too much functionality or are not very compatible. Eventually, I found minii/db, a simplified version based on Yii2 that solved my problem perfectly.
 Laravel framework installation method
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
Laravel framework installation method
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
Article summary: This article provides detailed step-by-step instructions to guide readers on how to easily install the Laravel framework. Laravel is a powerful PHP framework that speeds up the development process of web applications. This tutorial covers the installation process from system requirements to configuring databases and setting up routing. By following these steps, readers can quickly and efficiently lay a solid foundation for their Laravel project.
 MySQL for Beginners: Getting Started with Database Management
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:10 AM
MySQL for Beginners: Getting Started with Database Management
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:10 AM
The basic operations of MySQL include creating databases, tables, and using SQL to perform CRUD operations on data. 1. Create a database: CREATEDATABASEmy_first_db; 2. Create a table: CREATETABLEbooks(idINTAUTO_INCREMENTPRIMARYKEY, titleVARCHAR(100)NOTNULL, authorVARCHAR(100)NOTNULL, published_yearINT); 3. Insert data: INSERTINTObooks(title, author, published_year)VA
 Solve MySQL mode problem: The experience of using the TheliaMySQLModesChecker module
Apr 18, 2025 am 08:42 AM
Solve MySQL mode problem: The experience of using the TheliaMySQLModesChecker module
Apr 18, 2025 am 08:42 AM
When developing an e-commerce website using Thelia, I encountered a tricky problem: MySQL mode is not set properly, causing some features to not function properly. After some exploration, I found a module called TheliaMySQLModesChecker, which is able to automatically fix the MySQL pattern required by Thelia, completely solving my troubles.




