What are the three ways of redis clustering
Redis three clustering methods: master-slave replication, sentinel mode, and Cluster cluster.
Master-slave replication
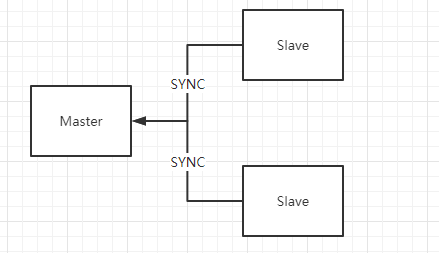
Basic principle
When a new slave server is created, the slave server will send a SYNC command to the master server. After receiving the SYNC command, the master server will execute a BGSAVE command. During the execution, all commands will be written into the buffer. When the BGSAVE command is executed, the generated RDB file will be sent to the slave server. The slave server will use this file. Load the data into the memory, and then the master server will send the buffer command to the slave server in the format of the Redis command protocol. After that, every time the master service executes a command, it will be synchronized to the slave server. Even if multiple slave servers send SYNC commands to the master server, the master server will only execute one BGSAVE command to process the next synchronization request. A master server can have multiple slave servers, and slave servers can also have slave servers, forming a graph-like structure. The replication function does not block the master server. Even if there are one or more synchronization requests, the master server can still process command requests. .
Persistence switch
When the master-slave replication mode is configured, the persistence function of the master server needs to be turned on. If the persistence function of the master server is turned off, once the master server is restarted, all slave servers will The data will be lost. Even if Sentinel mode is configured, if the main server automatically starts the process quickly, so that a new main server has not been elected in Sentinel mode, the startup of the main service will also cause data loss on the sub-server.
Configuration
To configure a master-slave replication mode, just use the Slaveof command, add it to the conf configuration file or execute the command in redis.
SLAVEOF host port
Sentinel Mode
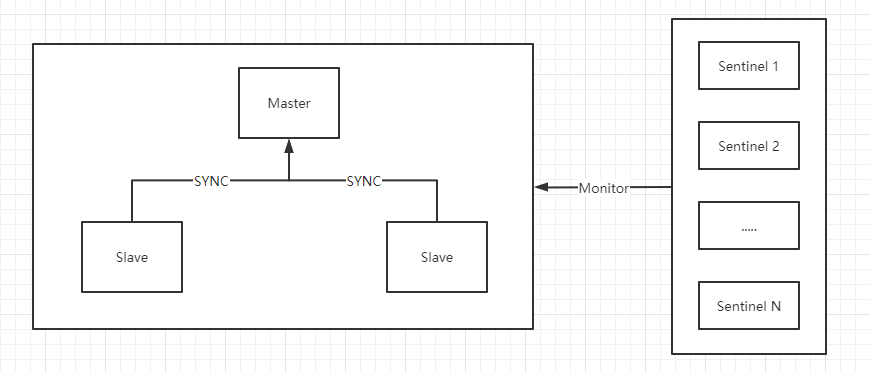
Basic Principle
The Sentinel system of Redis is used to manage multiple Redis and mainly performs the following three things:
Monitoring: Sentinel will continuously check the running status of the master and slave servers
Reminder: When a Redis server fails, notifications can be sent through API or other applications
Automatically Failover migration: When a master server fails to work properly, Sentinel will perform an automatic fault migration and elect a new master server from the slave server of the failed master server. The remaining slave servers will automatically connect and replicate the elected new master server. Server data.
The Sentinel system of Redis is a distributed system, and one or more Sentinel can be configured in the system.
Start
Use redis-sentinel to start
redis-sentinel sentinel.confy
You can also use redis-server to start
redis-server sentinel.conf --sentinelyy
Both of the above two methods can start sentinel, start Sentinel must specify a configuration file, otherwise it cannot be started:

Configuration
A sentinel.conf file requires at least one configuration:
sentinel monitor mymaster 127.0.0.1 6379 2
Monitoring A host with an alias named mymaster has an address of 127.0.0.1 and a port of 6379. To judge this master server as invalid requires the consent of at least 2 sentinels.
No matter how many sentinels are set up to agree to determine the failure of a master server, multiple Sentinels in the system are required to support fault migration. When only a few sentinels are running normally, fault migration cannot be performed.
Fault Migration
When a Sentinel finds that the main server is offline, it is called a subjective offline. Only multiple Sentinels find that the main service is offline and communicate with each other through commands to judge. When the main server goes offline, it is called objective offline. Only when the master server is objectively offline, the leader Sentinel will be elected. After the election, a new master server will be voted on to elect a slave server to be upgraded to the master server. And send the Slaveof no one command to the selected slave server to make it the master server. Through the publish and subscribe function, the new configuration is broadcast to other Sentinels for updates, and the Slaveof command is sent to the offline master server to let it Replicate the new master server. When all slave servers have started replicating the new master server, the leader Sentinel terminates this fault migration.
When a Redis instance is reconfigured, whether it is set as a master server, a slave server, or a slave server of another master server, Sentinel will send a message to the reconfigured instance. A
CONFIG REWRITEcommand to ensure that these configurations will be persisted to the hard disk.
Cluster
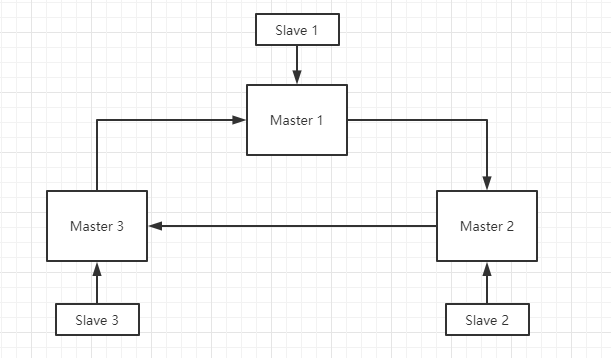
之前的主从复制,哨兵模式都难以再现扩容,而Redis cluster集群实现了对Redis的水平扩容,即启动N个Redis节点,每个节点又可以有自己的从服务器,将数据均匀分布的存储在这N个结点上,每个节点存储数据的1/N。Redis cluster集群就是一个可以在多个Redis节点之间进行数据共享的设施;Redis cluster集群采用的是无中心化配置,即节点A无法处理,会将请求转发只节点B进行处理。
键分布模型
Redis集群中的键空间被分割为16384个槽位。Redis采用CRC16算法对16384个槽位进行分配,每个主节点负责其中一部分。为了保证高可用,cluster模式也引入了主从复制模式,一个主节点对应一个或多个从节点,当主节点发生宕机时,可进行故障转移,将子节点升级为主节点。
配置cluster集群
Redis 集群由多个运行在集群模式(cluster mode)下的 Redis 实例组成, 实例的集群模式需要通过配置来开启,以下是一个包含了最少选项的集群配置文件示例:
port 7000 cluster-enabled yes cluster-config-file nodes.conf cluster-node-timeout 5000 appendonly yes
cluster-enabled:打开集群模式
cluster-config-file:节点配置文件名,无须人为修改, 它由 Redis 集群在启动时创建, 并在有需要时自动进行更新
cluster-node-timeout:节点失联时间,当超过此毫秒,集群将自动切换主从节点。
要让集群正常运作至少需要三个主节点,而每个主节点都应该正确配置一个或者多个从节点。
启动集群
使用redis-cli --cluster create命令将节点合并成一个集群
redis-cli --cluster create --cluster-replicas 1 127.0.0.1:7000 127.0.0.1:7001 127.0.0.1:7002 127.0.0.1:7003 127.0.0.1:7004 127.0.0.1:7005
--cluster-replicas 1 这个指的是从机的数量,表示我们希望为集群中的每个主节点创建一个从节点。
进入集群模式只需要使用redis-cli -c命令
redis-cli -c -p 7000
无中心话节点,所以进入任意一个端口号的主节点即可。
The above is the detailed content of What are the three ways of redis clustering. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1666
1666
 14
14
 1425
1425
 52
52
 1323
1323
 25
25
 1272
1272
 29
29
 1251
1251
 24
24
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
On CentOS systems, you can limit the execution time of Lua scripts by modifying Redis configuration files or using Redis commands to prevent malicious scripts from consuming too much resources. Method 1: Modify the Redis configuration file and locate the Redis configuration file: The Redis configuration file is usually located in /etc/redis/redis.conf. Edit configuration file: Open the configuration file using a text editor (such as vi or nano): sudovi/etc/redis/redis.conf Set the Lua script execution time limit: Add or modify the following lines in the configuration file to set the maximum execution time of the Lua script (unit: milliseconds)
 How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Use the Redis command line tool (redis-cli) to manage and operate Redis through the following steps: Connect to the server, specify the address and port. Send commands to the server using the command name and parameters. Use the HELP command to view help information for a specific command. Use the QUIT command to exit the command line tool.
 How to implement redis counter
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:21 PM
How to implement redis counter
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:21 PM
Redis counter is a mechanism that uses Redis key-value pair storage to implement counting operations, including the following steps: creating counter keys, increasing counts, decreasing counts, resetting counts, and obtaining counts. The advantages of Redis counters include fast speed, high concurrency, durability and simplicity and ease of use. It can be used in scenarios such as user access counting, real-time metric tracking, game scores and rankings, and order processing counting.
 How to set the redis expiration policy
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
How to set the redis expiration policy
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
There are two types of Redis data expiration strategies: periodic deletion: periodic scan to delete the expired key, which can be set through expired-time-cap-remove-count and expired-time-cap-remove-delay parameters. Lazy Deletion: Check for deletion expired keys only when keys are read or written. They can be set through lazyfree-lazy-eviction, lazyfree-lazy-expire, lazyfree-lazy-user-del parameters.
 How to optimize the performance of debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:48 AM
How to optimize the performance of debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:48 AM
In Debian systems, readdir system calls are used to read directory contents. If its performance is not good, try the following optimization strategy: Simplify the number of directory files: Split large directories into multiple small directories as much as possible, reducing the number of items processed per readdir call. Enable directory content caching: build a cache mechanism, update the cache regularly or when directory content changes, and reduce frequent calls to readdir. Memory caches (such as Memcached or Redis) or local caches (such as files or databases) can be considered. Adopt efficient data structure: If you implement directory traversal by yourself, select more efficient data structures (such as hash tables instead of linear search) to store and access directory information




