How to configure user permissions for nginx, php-fpm and mysql

Normally, the servers we run web applications on include Linux distributions such as CentOS, Ubuntu, Debian, etc. At this time, the permission control of Nginx, PHP, MySQL and other applications necessary to form the service architecture is very important. Each service has different permission requirements for the code directory. The lack of certain permissions will cause the service to be unable to read, write or run. , which lowers the permission requirements and creates the risk of intrusion and modification.
1. Web server Nginx permissions
The running framework of PHP is usually combined with Nginx to form LNMP or combined with Apache to form LAMP architecture. Here, Nginx is used as an example to describe what is needed to run the Nginx service. permissions.
We know that Nginx itself cannot parse PHP syntax, so Nginx will directly parse and return results for static files (such as HTML, etc.), but for PHP files, Nginx will transfer them to the PHP interpreter php-fpm for processing. After processing, the response is returned to the client browser.
Therefore, we need to unify the permissions required for Nginx and PHP services in our code directory.
① If the root user is used uniformly, general guest accounts will not be able to access the application. If nginx is configured to run as root, there will be a great security risk. Once attacked, the root identity will be obtained to perform everything in the system. operate.
If the permissions of the code directory are uniformly set to rwxrwxrwx, there will be a hidden danger that users can directly modify the code directory through the browser.
So the best way is to classify them into a new user group and assign the user group the necessary permissions to run Nginx and PHP to achieve permission directory management for web applications. In many cases, teams will use the www user group to manage code directory permissions and uniformly manage user www.
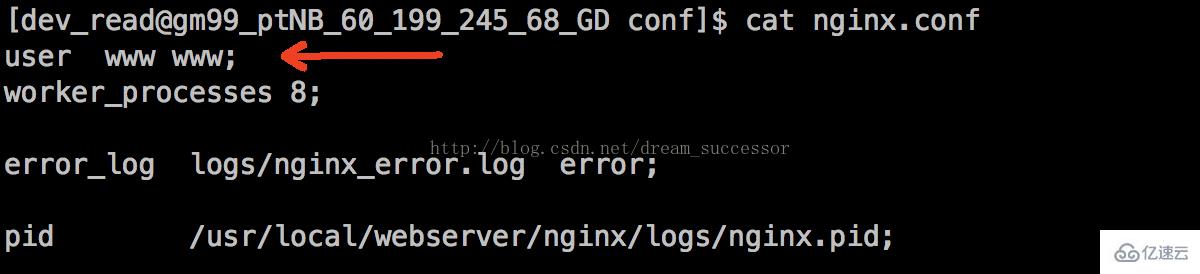
We can see the Nginx configuration file nginix.confThe running permissions divided in it are configured under the www user, so the Nginx child process is also executed by the www user, which can be passedps aux | grep nginx to view:
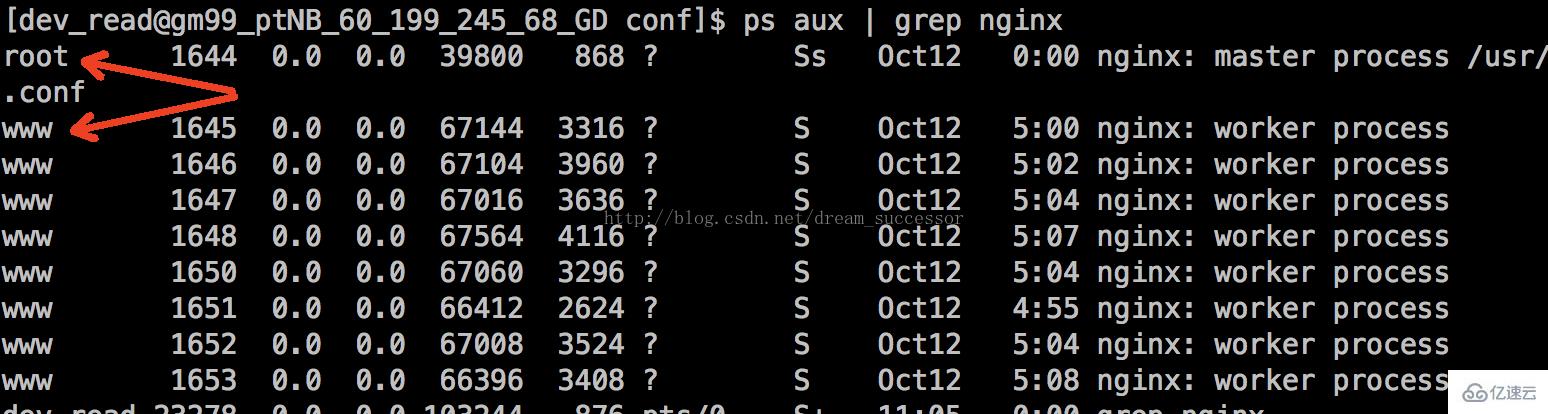
You can see that the main process of nginx is root, and the other sub-processes are all users of www
nginx.conf configuration:
2. PHP permission configuration
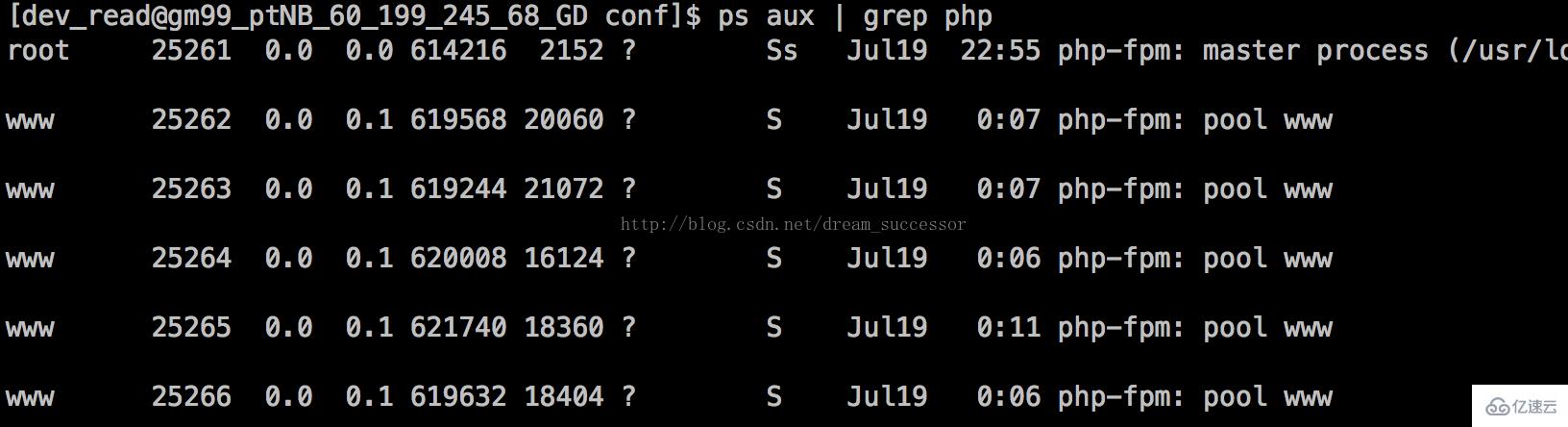
Same, php The running mode is also run by the main process root. The configuration in the child process pool (pool) is executed by the www user. The specific configuration is under etc\php-fpm.conf in the php root directory. Add two lines. :
user = www group = www
. You can also use ps aux | grep php to view the user identity used by the process:
3. Permission configuration of MySQL service
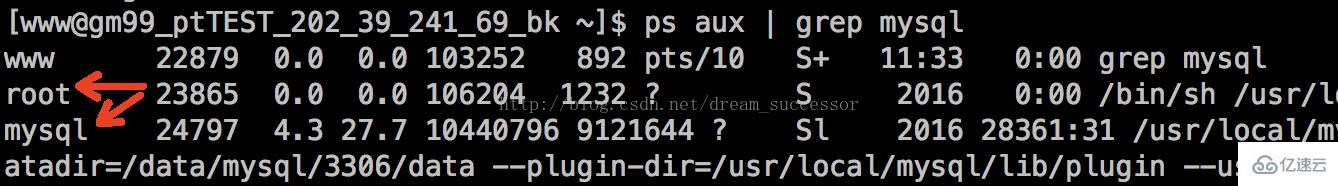
Through ps aux | grep mysql we can see that the MySQL service is running under the mysql user. The service only requires us to When the php code connects to mysql, just bring the user name and password of mysql. It does not need to be unified as www, because the data layer needs to be isolated from the business logic layer to ensure the security of the underlying data. The authorization of mysql is mainly to add new users and divide permissions in the mysql service, which is used to control different PHP businesses to connect with identities with different permission ranges to ensure data security.
4. Summary
nginx configuration:
user www www;
php-fpm:
user = www group = www
Directory:
drwxr-xr-x 就是755
The above is the detailed content of How to configure user permissions for nginx, php-fpm and mysql. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1662
1662
 14
14
 1418
1418
 52
52
 1311
1311
 25
25
 1261
1261
 29
29
 1234
1234
 24
24
 MySQL and phpMyAdmin: Core Features and Functions
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:12 AM
MySQL and phpMyAdmin: Core Features and Functions
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:12 AM
MySQL and phpMyAdmin are powerful database management tools. 1) MySQL is used to create databases and tables, and to execute DML and SQL queries. 2) phpMyAdmin provides an intuitive interface for database management, table structure management, data operations and user permission management.
 The Compatibility of IIS and PHP: A Deep Dive
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:01 AM
The Compatibility of IIS and PHP: A Deep Dive
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:01 AM
IIS and PHP are compatible and are implemented through FastCGI. 1.IIS forwards the .php file request to the FastCGI module through the configuration file. 2. The FastCGI module starts the PHP process to process requests to improve performance and stability. 3. In actual applications, you need to pay attention to configuration details, error debugging and performance optimization.
 Explain the purpose of foreign keys in MySQL.
Apr 25, 2025 am 12:17 AM
Explain the purpose of foreign keys in MySQL.
Apr 25, 2025 am 12:17 AM
In MySQL, the function of foreign keys is to establish the relationship between tables and ensure the consistency and integrity of the data. Foreign keys maintain the effectiveness of data through reference integrity checks and cascading operations. Pay attention to performance optimization and avoid common errors when using them.
 How to safely store JavaScript objects containing functions and regular expressions to a database and restore?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:09 PM
How to safely store JavaScript objects containing functions and regular expressions to a database and restore?
Apr 19, 2025 pm 11:09 PM
Safely handle functions and regular expressions in JSON In front-end development, JavaScript is often required...
 Compare and contrast MySQL and MariaDB.
Apr 26, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Compare and contrast MySQL and MariaDB.
Apr 26, 2025 am 12:08 AM
The main difference between MySQL and MariaDB is performance, functionality and license: 1. MySQL is developed by Oracle, and MariaDB is its fork. 2. MariaDB may perform better in high load environments. 3.MariaDB provides more storage engines and functions. 4.MySQL adopts a dual license, and MariaDB is completely open source. The existing infrastructure, performance requirements, functional requirements and license costs should be taken into account when choosing.
 SQL vs. MySQL: Clarifying the Relationship Between the Two
Apr 24, 2025 am 12:02 AM
SQL vs. MySQL: Clarifying the Relationship Between the Two
Apr 24, 2025 am 12:02 AM
SQL is a standard language for managing relational databases, while MySQL is a database management system that uses SQL. SQL defines ways to interact with a database, including CRUD operations, while MySQL implements the SQL standard and provides additional features such as stored procedures and triggers.
 Choosing Between MySQL and Oracle: A Decision Guide
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Choosing Between MySQL and Oracle: A Decision Guide
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Choosing MySQL or Oracle depends on project requirements: 1. MySQL is suitable for small and medium-sized applications and Internet projects because of its open source, free and ease of use; 2. Oracle is suitable for core business systems of large enterprises because of its powerful, stable and advanced functions, but at a high cost.
 NGINX and Apache: Understanding the Key Differences
Apr 26, 2025 am 12:01 AM
NGINX and Apache: Understanding the Key Differences
Apr 26, 2025 am 12:01 AM
NGINX and Apache each have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice should be based on specific needs. 1.NGINX is suitable for high concurrency scenarios because of its asynchronous non-blocking architecture. 2. Apache is suitable for low-concurrency scenarios that require complex configurations, because of its modular design.




