How to implement scheduled tasks in Java Spring
java implements scheduled tasks
In the library that comes with Jdk, there are two ways to implement scheduled tasks, one is Timer, the other is ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor.
Timer TimerTask
Creating a Timer creates a thread, which can be used to schedule TimerTask tasks
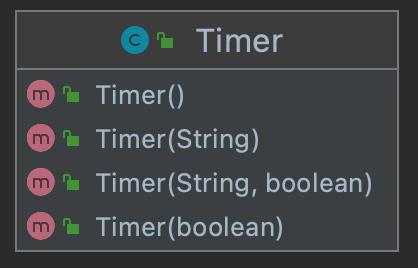
Timer has four construction methods, which can specify the name of the Timer thread and whether to set it as a daemon thread. The default name is Timer-number , which is not a daemon thread by default.
There are three main methods:
cancel(): Terminate task scheduling, cancel all currently scheduled tasks, and running tasks will not be affected
purge(): Remove all canceled tasks from the task queue
schedule: Start scheduling tasks, providing several overloaded methods :
schedule(TimerTask task, long delay) Delayed execution, which means delay will be executed once after tasktask
schedule(TimerTask task, Date time)`Execute at the specified time, and execute `task once at `time` time
#schedule(TimerTask task, long delay, long period)`Delay cycle execution, after ` `task
schedule(TimerTask task, Date firstTime, long period)` is executed periodically after the specified time `firstTime` and is executed once every `period` milliseconds after the specified time `firstTime` is reached.
Example
public class TimerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Timer timer = new Timer("aa");
Task task = new Task();
timer.schedule(task,new Date(),1000);
}
}
class Task extends TimerTask{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(new Date());
}
}Output:
Thu Jul 07 14:50:02 CST 2022
Thu Jul 07 14:50:03 CST 2022
Thu Jul 07 14:50:04 CST 2022
Thu Jul 07 14:50:05 CST 2022
…………
Disadvantages
Timer is single-threaded and does not throw exceptions. If an exception occurs in a scheduled task, the entire thread will stop, causing the scheduled task to terminate.
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor
Due to the defects of Timer, it is not recommended to use Timer. It is recommended to use ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor.
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor is a replacement for Timer. It was introduced in JDK1.5 and inherits ThreadPoolExecutor. It is a scheduled task class based on thread pool design. .
Main scheduling method:

scheduleExecute scheduling only once, (task, delay time, delay time unit)
scheduleAtFixedRateScheduling at a fixed frequency. If the execution time is too long, the next scheduling will be delayed, (task, delay time of the first execution, period, time unit)
scheduleWithFixedDelay Delay scheduling, after a task is executed, a delay time is added to execute the next task, (task, delay time of the first execution, interval time, time unit)
Example
public class TimerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
ScheduledExecutorService scheduledExecutorService = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(10);
scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(
() -> System.out.println(new Date()),
1,3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}Spring scheduled tasks
Spring scheduled tasks are mainly implemented by @Scheduled annotations, corn, fixedDelay, fixedDelayString, fixedRate, fixedRateString The five parameters are required Specifying one of them, passing two or three will throw an exception
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Repeatable(Schedules.class)
public @interface Scheduled {
String CRON_DISABLED = ScheduledTaskRegistrar.CRON_DISABLED;
// cron表达式
String cron() default "";
// 时区
String zone() default "";
// 从上一次调用结束到下一次调用之间的固定时间
long fixedDelay() default -1;
// 和fixedDelay意思相同,只是使用字符传格式,支持占位符。例如:fixedDelayString = "${time.fixedDelay}"
String fixedDelayString() default "";
// 两次调用之间固定的毫秒数(不需要等待上次任务完成)
long fixedRate() default -1;
// 同上,支持占位符
String fixedRateString() default "";
// 第一次执行任务前延迟的毫秒数
long initialDelay() default -1;
// 同上,支持占位符
String initialDelayString() default "";
}Example
@Component
@EnableScheduling
public class ScheduledTask {
@Scheduled(fixedDelay = 1000)
public void task(){
System.out.println("aaa");
}
}Principle
Project startupScheduledAnnotationBeanPostProcessorpostProcessAfterInitialization () Method scans methods with @Scheduled annotations:
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
if (bean instanceof AopInfrastructureBean || bean instanceof TaskScheduler ||
bean instanceof ScheduledExecutorService) {
// Ignore AOP infrastructure such as scoped proxies.
return bean;
}
Class<?> targetClass = AopProxyUtils.ultimateTargetClass(bean);
if (!this.nonAnnotatedClasses.contains(targetClass) &&
AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(targetClass, Arrays.asList(Scheduled.class, Schedules.class))) {
Map<Method, Set<Scheduled>> annotatedMethods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(targetClass,
(MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<Set<Scheduled>>) method -> {
Set<Scheduled> scheduledMethods = AnnotatedElementUtils.getMergedRepeatableAnnotations(
method, Scheduled.class, Schedules.class);
return (!scheduledMethods.isEmpty() ? scheduledMethods : null);
});
if (annotatedMethods.isEmpty()) {
this.nonAnnotatedClasses.add(targetClass);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No @Scheduled annotations found on bean class: " + targetClass);
}
}
else {
// Non-empty set of methods
annotatedMethods.forEach((method, scheduledMethods) ->
// 调用processScheduled方法将定时任务的方法存放到任务队列中
scheduledMethods.forEach(scheduled -> processScheduled(scheduled, method, bean)));
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(annotatedMethods.size() + " @Scheduled methods processed on bean '" + beanName +
"': " + annotatedMethods);
}
}
}
return bean;
} protected void processScheduled(Scheduled scheduled, Method method, Object bean) {
try {
// 创建任务线程
Runnable runnable = createRunnable(bean, method);
// 解析到定时任务方式的标记,解析到正确的参数后会设置为TRUE,如果在解析到了其他的参数就会抛出异常
boolean processedSchedule = false;
String errorMessage =
"Exactly one of the 'cron', 'fixedDelay(String)', or 'fixedRate(String)' attributes is required";
Set<ScheduledTask> tasks = new LinkedHashSet<>(4);
// Determine initial delay 解析第一次的延迟(解析initialDelay参数)
long initialDelay = scheduled.initialDelay();
String initialDelayString = scheduled.initialDelayString();
if (StringUtils.hasText(initialDelayString)) {
// initialDelay不能小于0
Assert.isTrue(initialDelay < 0, "Specify 'initialDelay' or 'initialDelayString', not both");
if (this.embeddedValueResolver != null) {
initialDelayString = this.embeddedValueResolver.resolveStringValue(initialDelayString);
}
if (StringUtils.hasLength(initialDelayString)) {
try {
initialDelay = parseDelayAsLong(initialDelayString);
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Invalid initialDelayString value \"" + initialDelayString + "\" - cannot parse into long");
}
}
}
// Check cron expression 解析cron表达式
String cron = scheduled.cron();
if (StringUtils.hasText(cron)) {
// 解析时区
String zone = scheduled.zone();
if (this.embeddedValueResolver != null) {
cron = this.embeddedValueResolver.resolveStringValue(cron);
zone = this.embeddedValueResolver.resolveStringValue(zone);
}
if (StringUtils.hasLength(cron)) {
Assert.isTrue(initialDelay == -1, "'initialDelay' not supported for cron triggers");
processedSchedule = true;
if (!Scheduled.CRON_DISABLED.equals(cron)) {
TimeZone timeZone;
if (StringUtils.hasText(zone)) {
timeZone = StringUtils.parseTimeZoneString(zone);
}
else {
timeZone = TimeZone.getDefault();
}
tasks.add(this.registrar.scheduleCronTask(new CronTask(runnable, new CronTrigger(cron, timeZone))));
}
}
}
// 第一次延迟参数小于0,默认为0
// At this point we don't need to differentiate between initial delay set or not anymore
if (initialDelay < 0) {
initialDelay = 0;
}
// Check fixed delay 解析fixedDelay参数
long fixedDelay = scheduled.fixedDelay();
if (fixedDelay >= 0) {
Assert.isTrue(!processedSchedule, errorMessage);
processedSchedule = true;
tasks.add(this.registrar.scheduleFixedDelayTask(new FixedDelayTask(runnable, fixedDelay, initialDelay)));
}
String fixedDelayString = scheduled.fixedDelayString();
if (StringUtils.hasText(fixedDelayString)) {
if (this.embeddedValueResolver != null) {
fixedDelayString = this.embeddedValueResolver.resolveStringValue(fixedDelayString);
}
if (StringUtils.hasLength(fixedDelayString)) {
Assert.isTrue(!processedSchedule, errorMessage);
processedSchedule = true;
try {
fixedDelay = parseDelayAsLong(fixedDelayString);
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Invalid fixedDelayString value \"" + fixedDelayString + "\" - cannot parse into long");
}
tasks.add(this.registrar.scheduleFixedDelayTask(new FixedDelayTask(runnable, fixedDelay, initialDelay)));
}
}
// Check fixed rate 解析fixedRate参数
long fixedRate = scheduled.fixedRate();
if (fixedRate >= 0) {
Assert.isTrue(!processedSchedule, errorMessage);
processedSchedule = true;
tasks.add(this.registrar.scheduleFixedRateTask(new FixedRateTask(runnable, fixedRate, initialDelay)));
}
String fixedRateString = scheduled.fixedRateString();
if (StringUtils.hasText(fixedRateString)) {
if (this.embeddedValueResolver != null) {
fixedRateString = this.embeddedValueResolver.resolveStringValue(fixedRateString);
}
if (StringUtils.hasLength(fixedRateString)) {
Assert.isTrue(!processedSchedule, errorMessage);
processedSchedule = true;
try {
fixedRate = parseDelayAsLong(fixedRateString);
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Invalid fixedRateString value \"" + fixedRateString + "\" - cannot parse into long");
}
tasks.add(this.registrar.scheduleFixedRateTask(new FixedRateTask(runnable, fixedRate, initialDelay)));
}
}
// Check whether we had any attribute set
// 如果五个参数一个也没解析到,抛出异常
Assert.isTrue(processedSchedule, errorMessage);
// Finally register the scheduled tasks
// 并发控制将任务队列存入注册任务列表
synchronized (this.scheduledTasks) {
Set<ScheduledTask> regTasks = this.scheduledTasks.computeIfAbsent(bean, key -> new LinkedHashSet<>(4));
regTasks.addAll(tasks);
}
}
catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Encountered invalid @Scheduled method '" + method.getName() + "': " + ex.getMessage());
}
}After the task is parsed and added to the task queue, it is handed over to the ScheduledTaskRegistrar class ##scheduleTasksMethod to add (register) scheduled tasks to the environment
protected void scheduleTasks() {
if (this.taskScheduler == null) {
//获取ScheduledExecutorService对象,实际上都是使用ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor执行定时任务调度
this.localExecutor = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor();
this.taskScheduler = new ConcurrentTaskScheduler(this.localExecutor);
}
if (this.triggerTasks != null) {
for (TriggerTask task : this.triggerTasks) {
addScheduledTask(scheduleTriggerTask(task));
}
}
if (this.cronTasks != null) {
for (CronTask task : this.cronTasks) {
addScheduledTask(scheduleCronTask(task));
}
}
if (this.fixedRateTasks != null) {
for (IntervalTask task : this.fixedRateTasks) {
addScheduledTask(scheduleFixedRateTask(task));
}
}
if (this.fixedDelayTasks != null) {
for (IntervalTask task : this.fixedDelayTasks) {
addScheduledTask(scheduleFixedDelayTask(task));
}
}
}
private void addScheduledTask(@Nullable ScheduledTask task) {
if (task != null) {
this.scheduledTasks.add(task);
}
}The above is the detailed content of How to implement scheduled tasks in Java Spring. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1657
1657
 14
14
 1415
1415
 52
52
 1309
1309
 25
25
 1257
1257
 29
29
 1229
1229
 24
24
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP is a scripting language widely used on the server side, especially suitable for web development. 1.PHP can embed HTML, process HTTP requests and responses, and supports a variety of databases. 2.PHP is used to generate dynamic web content, process form data, access databases, etc., with strong community support and open source resources. 3. PHP is an interpreted language, and the execution process includes lexical analysis, grammatical analysis, compilation and execution. 4.PHP can be combined with MySQL for advanced applications such as user registration systems. 5. When debugging PHP, you can use functions such as error_reporting() and var_dump(). 6. Optimize PHP code to use caching mechanisms, optimize database queries and use built-in functions. 7
 PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and the choice should be based on project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, with simple syntax and high execution efficiency. 2. Python is suitable for data science and machine learning, with concise syntax and rich libraries.
 PHP vs. Other Languages: A Comparison
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP vs. Other Languages: A Comparison
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP is suitable for web development, especially in rapid development and processing dynamic content, but is not good at data science and enterprise-level applications. Compared with Python, PHP has more advantages in web development, but is not as good as Python in the field of data science; compared with Java, PHP performs worse in enterprise-level applications, but is more flexible in web development; compared with JavaScript, PHP is more concise in back-end development, but is not as good as JavaScript in front-end development.
 PHP vs. Python: Core Features and Functionality
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP vs. Python: Core Features and Functionality
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages and are suitable for different scenarios. 1.PHP is suitable for web development and provides built-in web servers and rich function libraries. 2. Python is suitable for data science and machine learning, with concise syntax and a powerful standard library. When choosing, it should be decided based on project requirements.
 Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Capsules are three-dimensional geometric figures, composed of a cylinder and a hemisphere at both ends. The volume of the capsule can be calculated by adding the volume of the cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere at both ends. This tutorial will discuss how to calculate the volume of a given capsule in Java using different methods. Capsule volume formula The formula for capsule volume is as follows: Capsule volume = Cylindrical volume Volume Two hemisphere volume in, r: The radius of the hemisphere. h: The height of the cylinder (excluding the hemisphere). Example 1 enter Radius = 5 units Height = 10 units Output Volume = 1570.8 cubic units explain Calculate volume using formula: Volume = π × r2 × h (4
 PHP's Impact: Web Development and Beyond
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:10 AM
PHP's Impact: Web Development and Beyond
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:10 AM
PHPhassignificantlyimpactedwebdevelopmentandextendsbeyondit.1)ItpowersmajorplatformslikeWordPressandexcelsindatabaseinteractions.2)PHP'sadaptabilityallowsittoscaleforlargeapplicationsusingframeworkslikeLaravel.3)Beyondweb,PHPisusedincommand-linescrip
 PHP: The Foundation of Many Websites
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP: The Foundation of Many Websites
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
The reasons why PHP is the preferred technology stack for many websites include its ease of use, strong community support, and widespread use. 1) Easy to learn and use, suitable for beginners. 2) Have a huge developer community and rich resources. 3) Widely used in WordPress, Drupal and other platforms. 4) Integrate tightly with web servers to simplify development deployment.




