 Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance
 Nginx
Nginx
 How to use nginx and docker to implement a simple load balancing
How to use nginx and docker to implement a simple load balancing
How to use nginx and docker to implement a simple load balancing
Test steps:
1. Build an nginx server in the server and start it
2. Pull the official image of nginx from the source in docker, docker pull nginx, keep it for later use
3. Create two new folders in the local directory. The new folders I created here are in /mydata/test1 and /mydata/test2/
4. Create a new index.html in a test folder to mark, output this is nginx1 in the first html, output this is nginx2 in the second html,
5. Run two nginx servers through docker container, and map the static directories to the directories we just created
[root@catchtouch test2]# docker run --name nginx-test -d -p 8080:80 -v /mydata/test1:/usr/share/nginx/html nginx #第一个,将8080端口映射到容器中的80端口 [root@catchtouch test2]# docker run --name nginx-test1 -d -p 8081:80 -v /mydata/test2:/usr/share/nginx/html nginx #第二个,将容器中的8081端口映射到容器中的80端口
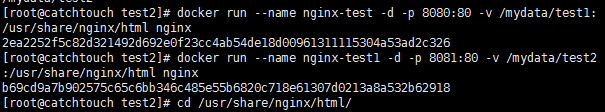
6. Modify the nginx configuration file in the host
In http Add the following code in {}
upstream myweb { #myproject为自定义名字
#ip_hash; #开启则代表用ip地址的形式来分配,可解决sesson问题
server 127.0.0.1:8080 weight=1; #weight越大,权重越高,被分配的几率越大
server 127.0.0.1:8081 weight=1; #我全部在本机,因此用了本地的ip,只要相应换成对应的ip或者域名即可
}7. Enter the conf.d directory and modify default.conf (there is no such file in conf.d and can be created. The file name is arbitrary and the suffix must be .conf)
location / {
#如果服务器要获取客户端真实ip,可以用下三句设置主机头和客户端真实地址
#proxy_set_header host $host;
#proxy_set_header x-real-ip $remote_addr;
#proxy_set_header x-forwarded-for $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index index.html index.htm;
proxy_pass http://myweb; #myweb为之前在nginx.conf中upstream后定义的名字
}8. Exit after saving and restart the server: systemctl restart nginx
9. Enter the current domain name through the browser and refresh the page. Sometimes nginx1 is output, sometimes nginx2 is output, and the configuration is successful
The above is the detailed content of How to use nginx and docker to implement a simple load balancing. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1657
1657
 14
14
 1415
1415
 52
52
 1309
1309
 25
25
 1257
1257
 29
29
 1229
1229
 24
24
 How to exit the container by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:15 PM
How to exit the container by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:15 PM
Four ways to exit Docker container: Use Ctrl D in the container terminal Enter exit command in the container terminal Use docker stop <container_name> Command Use docker kill <container_name> command in the host terminal (force exit)
 How to copy files in docker to outside
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
How to copy files in docker to outside
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
Methods for copying files to external hosts in Docker: Use the docker cp command: Execute docker cp [Options] <Container Path> <Host Path>. Using data volumes: Create a directory on the host, and use the -v parameter to mount the directory into the container when creating the container to achieve bidirectional file synchronization.
 How to restart docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:06 PM
How to restart docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:06 PM
How to restart the Docker container: get the container ID (docker ps); stop the container (docker stop <container_id>); start the container (docker start <container_id>); verify that the restart is successful (docker ps). Other methods: Docker Compose (docker-compose restart) or Docker API (see Docker documentation).
 How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
You can query the Docker container name by following the steps: List all containers (docker ps). Filter the container list (using the grep command). Gets the container name (located in the "NAMES" column).
 How to start containers by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
How to start containers by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Docker container startup steps: Pull the container image: Run "docker pull [mirror name]". Create a container: Use "docker create [options] [mirror name] [commands and parameters]". Start the container: Execute "docker start [Container name or ID]". Check container status: Verify that the container is running with "docker ps".
 How to start mysql by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
How to start mysql by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
The process of starting MySQL in Docker consists of the following steps: Pull the MySQL image to create and start the container, set the root user password, and map the port verification connection Create the database and the user grants all permissions to the database
 How to update the image of docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
How to update the image of docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
The steps to update a Docker image are as follows: Pull the latest image tag New image Delete the old image for a specific tag (optional) Restart the container (if needed)
 How to view logs from docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:24 PM
How to view logs from docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:24 PM
The methods to view Docker logs include: using the docker logs command, for example: docker logs CONTAINER_NAME Use the docker exec command to run /bin/sh and view the log file, for example: docker exec -it CONTAINER_NAME /bin/sh ; cat /var/log/CONTAINER_NAME.log Use the docker-compose logs command of Docker Compose, for example: docker-compose -f docker-com



