**截止文章发布chinese_calendar版本为1.8.0,大约在每年的11月份更新次年的节假日新版本
import datetime
from chinese_calendar import is_workday
def get_pervious_work_day(day: datetime):
"""获取上一个工作日"""
day = day - datetime.timedelta(days=1)
if is_workday(day):
return day
return get_pervious_work_day(day)测试周六日:
today = datetime.date.today().replace(day=20) date = get_pervious_work_day(today) print(date)
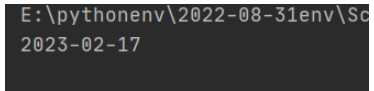
测试2023春节:
today = datetime.date.today().replace(day=28).replace(month=1) date = get_pervious_work_day(today) print(date)
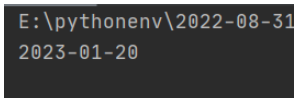
立即学习“Python免费学习笔记(深入)”;
测试2023劳动节:
today = datetime.date.today().replace(day=4).replace(month=5) date = get_pervious_work_day(today) print(date)
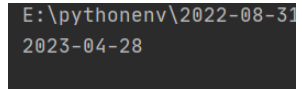
测试2023国庆节:
today = datetime.date.today().replace(day=7).replace(month=10) date = get_pervious_work_day(today) print(date)
刚开始想自己写,但是因为中国的节假日时间并不是固定的,因此需要自己持续并手动填写日期是否是法定节假日,比较麻烦,所以找到python有一个叫chinese_calendar的模块,该作者应该会持续更新
代码和思路其实都很简单
我的需求是计算某一日期开始,多少个工作日后这个日期是多少
下面的例子,是我用2021年9月10日到2022年9月10日这一年的时间范围内
要计算2021年9月10日之后30个工作日,是什么日期
import chinese_calendar
import datetime
def after_work_day():
year = 2021
month = 9
day = 10
# after_work_days是设置多少个工作日
after_work_days = 30
next_year = year + 1
range_time = datetime.datetime(next_year, month, day)
# 如果一年后的时间超过了模块规定的最长时间,那么直接取最新版的最大时间 截止目前(2022.11.30)最新版到2022年末,需要等国家出台了明年的放假安排之后可能才会更新
if range_time >= datetime.datetime(2022, 12, 31):
range_time = datetime.datetime(2022, 12, 31)
work_days = chinese_calendar.get_workdays(datetime.datetime(year, month, day), range_time)
count = 0
for work_day in work_days:
count += 1
if count > after_work_days:
print(work_day)
break
if __name__ == '__main__':
after_work_day()有一个需要注意的点就是二月份的天数,闰年和平年的天数不一样,根据需求考虑进去
以上就是python怎么利用chinese_calendar获取上一个工作日日期的详细内容,更多请关注php中文网其它相关文章!

python怎么学习?python怎么入门?python在哪学?python怎么学才快?不用担心,这里为大家提供了python速学教程(入门到精通),有需要的小伙伴保存下载就能学习啦!

Copyright 2014-2025 https://www.php.cn/ All Rights Reserved | php.cn | 湘ICP备2023035733号