What is SPI mechanism in Java
1: Introduction to SPI mechanism
SPI The full name is Service Provider Interface, which is a JDK built-in dynamic loading implementation extension point Mechanism, through SPI technology we can dynamically obtain the implementation class of the interface without creating it ourselves. This is not a special technology, just a design concept.
2: SPI principle
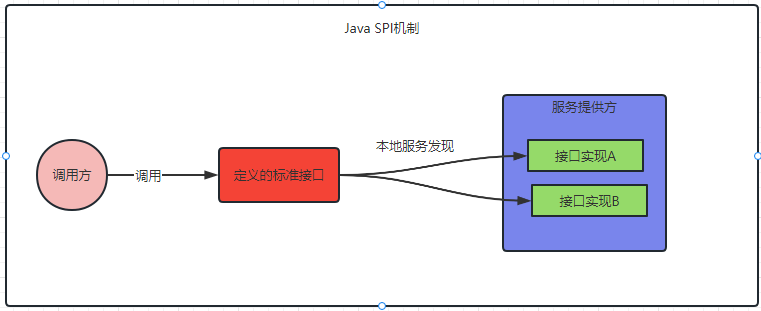
Java SPI is actually a dynamic loading mechanism implemented by a combination of interface-based programming + strategy mode + configuration files.
There are often many different implementation solutions for various abstractions in system design. In object-oriented design, it is generally recommended that modules be programmed based on interfaces, and implementation classes should not be hard-coded between modules. If a specific implementation class is referenced in the code, then the principle of pluggability is violated. In order to implement the replacement, the code needs to be modified. A service discovery mechanism is needed to enable module assembly without dynamically specifying it in the program.
Java SPI provides a mechanism to find service implementations related to a certain interface. In modular design, a mechanism similar to the IOC idea is widely used, that is, the assembly control of components is transferred outside the program. So the core idea of SPI is decoupling.
3: Usage Scenarios
The caller enables, extends, or replaces the framework’s implementation strategy according to actual usage needs
The following are some scenarios where this mechanism is used
JDBC driver, loading driver classes for different databases
Spring uses a lot of SPI, such as: the implementation of ServletContainerInitializer in the servlet3.0 specification, automatic Type Conversion SPI (Converter SPI, Formatter SPI), etc.
Dubbo also uses SPI extensively to implement framework extensions, but it encapsulates the native SPI provided by Java. Allow users to extend the implementation of the Filter interface
Tomcat loads the class that needs to be loaded under META-INF/services
Use the @SpringBootApplication annotation in the SpringBoot project , automatic configuration will start, and the startup configuration will scan the configuration class under META-INF/spring.factories
4: Source code demonstration
4.1 Application Call the ServiceLoader.load method
In the ServiceLoader.load method, first create a new ServiceLoader and instantiate the member variables in the class
private static final String PREFIX = "META-INF/services/";
private ServiceLoader(Class<S> svc, ClassLoader cl) {
service = Objects.requireNonNull(svc, "Service interface cannot be null");
loader = (cl == null) ? ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader() : cl;
acc = (System.getSecurityManager() != null) ? AccessController.getContext() : null;
reload();
}
/**
*
* 在调用该方法之后,迭代器方法的后续调用将延迟地从头开始查找和实例化提供程序,就像新创建的加载程序所做的 那样
*/
public void reload() {
providers.clear(); //清除此加载程序的提供程序缓存,以便重新加载所有提供程序。
lookupIterator = new LazyIterator(service, loader);
}
private class LazyIterator implements Iterator<S>{
Class<S> service;
ClassLoader loader;
Enumeration<URL> configs = null;
Iterator<String> pending = null;
String nextName = null;
private boolean hasNextService() {
if (nextName != null) {
return true;
}
if (configs == null) {
try {
//找到配置文件
String fullName = PREFIX + service.getName();
//加载配置文件中的内容
if (loader == null)
configs = ClassLoader.getSystemResources(fullName);
else
configs = loader.getResources(fullName);
} catch (IOException x) {
fail(service, "Error locating configuration files", x);
}
}
while ((pending == null) || !pending.hasNext()) {
if (!configs.hasMoreElements()) {
return false;
}
//解析配置文件
pending = parse(service, configs.nextElement());
}
//获取配置文件中内容
nextName = pending.next();
return true;
}
}
/**
*
* 通过反射 实例化配置文件中的具体实现类
*/
private S nextService() {
if (!hasNextService())
throw new NoSuchElementException();
String cn = nextName;
nextName = null;
Class<?> c = null;
try {
c = Class.forName(cn, false, loader);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException x) {
fail(service,
"Provider " + cn + " not found");
}
if (!service.isAssignableFrom(c)) {
fail(service,
"Provider " + cn + " not a subtype");
}
try {
S p = service.cast(c.newInstance());
providers.put(cn, p);
return p;
} catch (Throwable x) {
fail(service,
"Provider " + cn + " could not be instantiated",
x);
}
throw new Error(); // This cannot happen
}5: Practical combat
Step 1 Create the following class
public interface IService {
/**
* 获取价格
* @return
*/
String getPrice();
/**
* 获取规格信息
* @return
*/
String getSpecifications();
}public class GoodServiceImpl implements IService {
@Override
public String getPrice() {
return "2000.00元";
}
@Override
public String getSpecifications() {
return "200g/件";
}
}public class MedicalServiceImpl implements IService {
@Override
public String getPrice() {
return "3022.12元";
}
@Override
public String getSpecifications() {
return "30粒/盒";
}
}Step 2, create the /META-INF/services directory under src/main/resources/, and add a file named after the interface org.example.IService.txt. The content is the implementation class to be applied. The data I need to put in is as follows
org.example.GoodServiceImpl
org.example.MedicalServiceImpl
Step 3, use ServiceLoader to load the implementation specified in the configuration file.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final ServiceLoader<IService> serviceLoader = ServiceLoader.load(IService.class);
serviceLoader.forEach(service -> {
System.out.println(service.getPrice() + "=" + service.getSpecifications());
});
}
}Output:
2000.00 yuan=200g/piece
3022.12 yuan=30 capsules/box
6: Advantages and Disadvantages
6.1 Advantages
Decoupling separates the assembly control logic of the third-party service module from the caller's business code instead of coupling them together. The application can enable framework extension or replace the framework according to actual business conditions. components. Compared with the method of providing an interface jar package for third-party service modules to implement the interface, the SPI method allows the source framework to not need to care about the path of the interface implementation class
6.2 Disadvantages
-
Although ServiceLoader can be regarded as lazy loading, it can basically only be obtained through traversal, that is, all implementation classes of the interface are loaded and instantiated. If some implementation classes are loaded and instantiated but you don't need to use them, resources are wasted. The way to obtain a specific implementation class is too limited. It can only be obtained in the form of an iterator, and the corresponding implementation class cannot be obtained based on specific parameters.
Instances of multiple concurrent multi-threads using the ServiceLoader class are unsafe
The above is the detailed content of What is SPI mechanism in Java. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1659
1659
 14
14
 1415
1415
 52
52
 1310
1310
 25
25
 1258
1258
 29
29
 1232
1232
 24
24
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP is a scripting language widely used on the server side, especially suitable for web development. 1.PHP can embed HTML, process HTTP requests and responses, and supports a variety of databases. 2.PHP is used to generate dynamic web content, process form data, access databases, etc., with strong community support and open source resources. 3. PHP is an interpreted language, and the execution process includes lexical analysis, grammatical analysis, compilation and execution. 4.PHP can be combined with MySQL for advanced applications such as user registration systems. 5. When debugging PHP, you can use functions such as error_reporting() and var_dump(). 6. Optimize PHP code to use caching mechanisms, optimize database queries and use built-in functions. 7
 PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and the choice should be based on project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, with simple syntax and high execution efficiency. 2. Python is suitable for data science and machine learning, with concise syntax and rich libraries.
 PHP vs. Other Languages: A Comparison
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP vs. Other Languages: A Comparison
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP is suitable for web development, especially in rapid development and processing dynamic content, but is not good at data science and enterprise-level applications. Compared with Python, PHP has more advantages in web development, but is not as good as Python in the field of data science; compared with Java, PHP performs worse in enterprise-level applications, but is more flexible in web development; compared with JavaScript, PHP is more concise in back-end development, but is not as good as JavaScript in front-end development.
 PHP vs. Python: Core Features and Functionality
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP vs. Python: Core Features and Functionality
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages and are suitable for different scenarios. 1.PHP is suitable for web development and provides built-in web servers and rich function libraries. 2. Python is suitable for data science and machine learning, with concise syntax and a powerful standard library. When choosing, it should be decided based on project requirements.
 Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Capsules are three-dimensional geometric figures, composed of a cylinder and a hemisphere at both ends. The volume of the capsule can be calculated by adding the volume of the cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere at both ends. This tutorial will discuss how to calculate the volume of a given capsule in Java using different methods. Capsule volume formula The formula for capsule volume is as follows: Capsule volume = Cylindrical volume Volume Two hemisphere volume in, r: The radius of the hemisphere. h: The height of the cylinder (excluding the hemisphere). Example 1 enter Radius = 5 units Height = 10 units Output Volume = 1570.8 cubic units explain Calculate volume using formula: Volume = π × r2 × h (4
 PHP's Impact: Web Development and Beyond
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:10 AM
PHP's Impact: Web Development and Beyond
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:10 AM
PHPhassignificantlyimpactedwebdevelopmentandextendsbeyondit.1)ItpowersmajorplatformslikeWordPressandexcelsindatabaseinteractions.2)PHP'sadaptabilityallowsittoscaleforlargeapplicationsusingframeworkslikeLaravel.3)Beyondweb,PHPisusedincommand-linescrip
 PHP: The Foundation of Many Websites
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP: The Foundation of Many Websites
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
The reasons why PHP is the preferred technology stack for many websites include its ease of use, strong community support, and widespread use. 1) Easy to learn and use, suitable for beginners. 2) Have a huge developer community and rich resources. 3) Widely used in WordPress, Drupal and other platforms. 4) Integrate tightly with web servers to simplify development deployment.




