 Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance
 Nginx
Nginx
 How nginx implements load balancing of multiple geoserver services
How nginx implements load balancing of multiple geoserver services
How nginx implements load balancing of multiple geoserver services
Overview
In order to improve the access speed of the service, reduce the pressure on the geoserver service, and avoid problems with service nodes that affect the stability of service access, we usually solve the problem by deploying multiple geoservers, but deploying After installing multiple geoservers, we need a unified interface for use. nginx can meet such needs very well. This article talks about how to achieve load balancing of multiple geoserver services through nginx.
Implementation effect
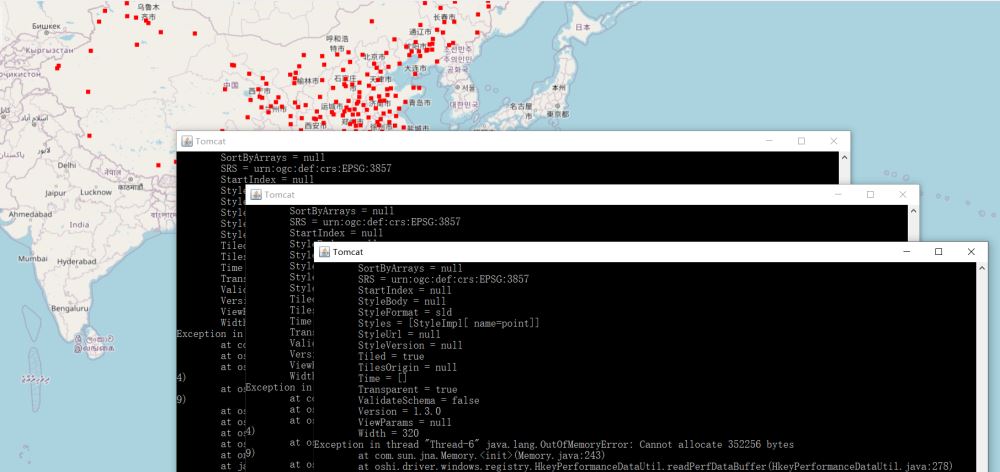
Implementation
1. Multiple geoserver deployment
In order to keep the geoserver service consistent, we first Configure a geoserver service. After configuring, copy the deployed Tomcat and clone multiple ones. This article copied two (three geoservers in total) for demonstration. Modify the Tomcat port so that the three ports do not conflict. After copying, respectively Start three Tomcats.
2. nginx configuration
Modify the nginx.conf file, the configuration information is as follows:
#user nobody;
worker_processes 1;
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
# 反向代理配置
upstream server_list{
# 这个是tomcat的访问路径
server localhost:8081;
server localhost:8082;
server localhost:8083;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' $http_origin;
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Credentials' 'true';
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Methods' 'GET, POST, OPTIONS';
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Headers' 'DNT,web-token,app-token,Authorization,Accept,Origin,Keep-Alive,User-Agent,X-Mx-ReqToken,X-Data-Type,X-Auth-Token,X-Requested-With,If-Modified-Since,Cache-Control,Content-Type,Range';
add_header 'Access-Control-Expose-Headers' 'Content-Length,Content-Range';
if ($request_method = 'OPTIONS') {
add_header 'Access-Control-Max-Age' 1728000;
add_header 'Content-Type' 'text/plain; charset=utf-8';
add_header 'Content-Length' 0;
return 204;
}
root html;
proxy_pass http://server_list;
index index.html index.htm;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
}
}After configuring nginx, start nginx.
3. Front-end call
According to the above configuration, the port of nginx is 80, so the address of geoserver is http://localhost/geoserver. The calling code in ol is as follows:
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>OpenLayers map preview</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="lib/ol/ol.css" rel="external nofollow" type="text/css">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="css/common.css" rel="external nofollow" >
<script src="../ol5/ol.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="map" class="map"></div>
<script>
const options = {
center: [52102781.07568731, 4456849.777083951],
zoom: 3,
minZoom: 0,
maxZoom: 18
}
const base = new ol.layer.Tile({
visible: true,
source: new ol.source.OSM()
});
const wms = new ol.layer.Tile({
source: new ol.source.TileWMS({
url: 'http://localhost/geoserver/mapbox/wms',
params: {'LAYERS': 'mapbox:city', 'TILED': true},
serverType: 'geoserver',
transition: 0
})
})
window.map = new ol.Map({
controls: ol.control.defaults({
attribution: false
}).extend([new ol.control.ScaleLine()]),
target: 'map',
layers: [base, wms],
view: new ol.View({
center: options.center,
zoom: options.zoom,
minZoom: options.minZoom,
maxZoom: options.maxZoom
})
});
</script>
</body>
</html>The above is the detailed content of How nginx implements load balancing of multiple geoserver services. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1653
1653
 14
14
 1413
1413
 52
52
 1306
1306
 25
25
 1251
1251
 29
29
 1224
1224
 24
24
 How to configure nginx in Windows
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:57 PM
How to configure nginx in Windows
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:57 PM
How to configure Nginx in Windows? Install Nginx and create a virtual host configuration. Modify the main configuration file and include the virtual host configuration. Start or reload Nginx. Test the configuration and view the website. Selectively enable SSL and configure SSL certificates. Selectively set the firewall to allow port 80 and 443 traffic.
 How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
You can query the Docker container name by following the steps: List all containers (docker ps). Filter the container list (using the grep command). Gets the container name (located in the "NAMES" column).
 How to start containers by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
How to start containers by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Docker container startup steps: Pull the container image: Run "docker pull [mirror name]". Create a container: Use "docker create [options] [mirror name] [commands and parameters]". Start the container: Execute "docker start [Container name or ID]". Check container status: Verify that the container is running with "docker ps".
 How to check whether nginx is started
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to check whether nginx is started
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to confirm whether Nginx is started: 1. Use the command line: systemctl status nginx (Linux/Unix), netstat -ano | findstr 80 (Windows); 2. Check whether port 80 is open; 3. Check the Nginx startup message in the system log; 4. Use third-party tools, such as Nagios, Zabbix, and Icinga.
 How to create containers for docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
How to create containers for docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
Create a container in Docker: 1. Pull the image: docker pull [mirror name] 2. Create a container: docker run [Options] [mirror name] [Command] 3. Start the container: docker start [Container name]
 How to check nginx version
Apr 14, 2025 am 11:57 AM
How to check nginx version
Apr 14, 2025 am 11:57 AM
The methods that can query the Nginx version are: use the nginx -v command; view the version directive in the nginx.conf file; open the Nginx error page and view the page title.
 How to configure cloud server domain name in nginx
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
How to configure cloud server domain name in nginx
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
How to configure an Nginx domain name on a cloud server: Create an A record pointing to the public IP address of the cloud server. Add virtual host blocks in the Nginx configuration file, specifying the listening port, domain name, and website root directory. Restart Nginx to apply the changes. Access the domain name test configuration. Other notes: Install the SSL certificate to enable HTTPS, ensure that the firewall allows port 80 traffic, and wait for DNS resolution to take effect.
 What to do if nginx server is hung
Apr 14, 2025 am 11:42 AM
What to do if nginx server is hung
Apr 14, 2025 am 11:42 AM
When the Nginx server goes down, you can perform the following troubleshooting steps: Check that the nginx process is running. View the error log for error messages. Check the syntax of nginx configuration. Make sure nginx has the permissions you need to access the file. Check file descriptor to open limits. Confirm that nginx is listening on the correct port. Add firewall rules to allow nginx traffic. Check reverse proxy settings, including backend server availability. For further assistance, please contact technical support.



