How to use nginx simulation for canary publishing
Canary Release/Grayscale Release
The focus of canary release is: trial and error. The origin of the canary release itself is a tragic story of the beautiful creatures of nature in the development of human industry. The canary uses its life to try and make mistakes for the safety of the miners. A small cost is used to exchange for overall security. In the practice of continuous deployment, the canary is traffic control. A very small amount of traffic, such as one percent or one tenth, is used to verify whether a certain version is normal. If it is abnormal, its function will be achieved at the lowest cost and the risk will be reduced. If it is normal, you can gradually increase the weight until it reaches 100%, and switch all traffic to the new version smoothly. Grayscale publishing is generally a similar concept. Gray is a transition between black and white. It is different from blue and green deployment, which is either blue or green. Grayscale release/canary release has a time period when both exist at the same time, but the corresponding traffic of the two is different. If canary release is different from grayscale release, the difference should be the purpose. The purpose of canary release is trial and error, while grayscale release is about stable release, while there is no problem in canary release. It is a smooth transition under the circumstances of grayscale publishing.
Simulating canary release
Next, we use nginx’s upstream to simply simulate the canary release scenario. The specific scenario is as follows. The main version is currently active. By adjusting the nginx settings and constantly adjusting the weight of the canary version, a smooth release is finally achieved.
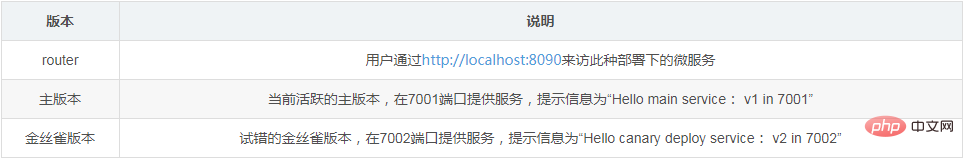
Preparation in advance
Start two services on the two ports 7001/7002 in advance to display different information. The demonstration is convenient. I used tornado to make an image. The different parameters passed when starting the docker container are used to display the differences in services.
docker run -d -p 7001:8080 liumiaocn/tornado:latest python /usr/local/bin/daemon.py "hello main service: v1 in 7001" docker run -d -p 7002:8080 liumiaocn/tornado:latest python /usr/local/bin/daemon.py "hello canary deploy service: v2 in 7002"
Execution log
[root@kong ~]# docker run -d -p 7001:8080 liumiaocn/tornado:latest python /usr/local/bin/daemon.py "hello main service: v1 in 7001" 28f42bbd21146c520b05ff2226514e62445b4cdd5d82f372b3791fdd47cd602a [root@kong ~]# docker run -d -p 7002:8080 liumiaocn/tornado:latest python /usr/local/bin/daemon.py "hello canary deploy service: v2 in 7002" b86c4b83048d782fadc3edbacc19b73af20dc87f5f4cf37cf348d17c45f0215d [root@kong ~]# curl http://192.168.163.117:7001 hello, service :hello main service: v1 in 7001 [root@kong ~]# curl http://192.168.163.117:7002 hello, service :hello canary deploy service: v2 in 7002 [root@kong ~]#
Start nginx
[root@kong ~]# docker run -p 9080:80 --name nginx-canary -d nginx 659f15c4d006df6fcd1fab1efe39e25a85c31f3cab1cda67838ddd282669195c [root@kong ~]# docker ps |grep nginx-canary 659f15c4d006 nginx "nginx -g 'daemon ..." 7 seconds ago up 7 seconds 0.0.0.0:9080->80/tcp nginx-canary [root@kong ~]#
nginx code segment
Prepare the following nginx code snippet and add it to /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf of nginx. The simulation method is very simple. Use down to indicate that the traffic is zero (weight cannot be set to zero in nginx). At the beginning, 100% of the traffic is sent to the main version.
http {
upstream nginx_canary {
server 192.168.163.117:7001 weight=100;
server 192.168.163.117:7002 down;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.liumiao.cn 192.168.163.117;
location / {
proxy_pass http://nginx_canary;
}
}How to modify default.conf
You can achieve the effect by installing vim in the container, you can also modify it locally and pass it in through docker cp, or directly sed Modifications are possible. If you install vim in a container, use the following method
[root@kong ~]# docker exec -it nginx-lb sh # apt-get update ...省略 # apt-get install vim ...省略
Before modification
# cat default.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log /var/log/nginx/host.access.log main;
location / {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
}
# proxy the php scripts to apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the php scripts to fastcgi server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param script_filename /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
#After modification
# cat default.conf
upstream nginx_canary {
server 192.168.163.117:7001 weight=100;
server 192.168.163.117:7002 down;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.liumiao.cn 192.168.163.117;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log /var/log/nginx/host.access.log main;
location / {
#root /usr/share/nginx/html;
#index index.html index.htm;
proxy_pass http://nginx_canary;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
}
# proxy the php scripts to apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the php scripts to fastcgi server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param script_filename /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
#Reload nginx settings
# nginx -s reload 2018/05/28 05:16:20 [notice] 319#319: signal process started #
Confirm the result
The output of all 10 calls is v1 in 7001
[root@kong ~]# cnt=0; while [ $cnt -lt 10 ]; do curl ; let cnt ; done
hello, service :hello main service: v1 in 7001
hello, service :hello main service: v1 in 7001
hello, service :hello main service: v1 in 7001
hello, service :hello main service: v1 in 7001
hello, service :hello main service: v1 in 7001
hello, service :hello main service: v1 in 7001
hello, service :hello main service: v1 in 7001
hello, service :hello main service: v1 in 7001
hello, service :hello main service : v1 in 7001
hello, service :hello main service: v1 in 7001
[root@kong ~]
Canary release: Canary version traffic Weight 10%
By adjusting the weight of default.conf and then executing nginx -s reload, adjust the weight of the canary version to 10%, and 10% of the traffic will execute the new service
How to modify default.conf
You only need to adjust the weight of the server in upstream as follows:
upstream nginx_canary {
server 192.168.163.117:7001 weight=10;
server 192.168.163.117:7002 weight=90;
}Reload nginx settings Determine
# nginx -s reload 2018/05/28 05:20:14 [notice] 330#330: signal process started #
Confirm the result
[root@kong ~]# cnt=0; while [ $cnt -lt 10 ]; do curl ; let cnt ; done
hello, service :hello canary deploy service: v2 in 7002
hello, service :hello canary deploy service: v2 in 7002
hello, service :hello canary deploy service: v2 in 7002
hello, service :hello canary deploy service: v2 in 7002
hello, service :hello main service: v1 in 7001
hello, service :hello canary deploy service: v2 in 7002
hello, service :hello canary deploy service: v2 in 7002
hello, service :hello canary deploy service: v2 in 7002
hello, service :hello canary deploy service: v2 in 7002
hello, service :hello canary deploy service : v2 in 7002
[root@kong ~]
#Canary release: Canary version traffic weight 50%
through adjustment The weight of default.conf, and then execute nginx -s reload, adjust the weight of the canary version to 50%, and 50% of the traffic will execute the new service
Method to modify default.conf
You only need to adjust the weight of the server in upstream as follows:
upstream nginx_canary {
server 192.168.163.117:7001 weight=50;
server 192.168.163.117:7002 weight=50;
}Reload nginx settings
# nginx -s reload 2018/05/28 05:22:26 [notice] 339#339: signal process started #
确认结果
[root@kong ~]# cnt=0; while [ $cnt -lt 10 ]; do curl ; let cnt++; done
hello, service :hello main service: v1 in 7001
hello, service :hello canary deploy service: v2 in 7002
hello, service :hello main service: v1 in 7001
hello, service :hello canary deploy service: v2 in 7002
hello, service :hello main service: v1 in 7001
hello, service :hello canary deploy service: v2 in 7002
hello, service :hello main service: v1 in 7001
hello, service :hello canary deploy service: v2 in 7002
hello, service :hello main service: v1 in 7001
hello, service :hello canary deploy service: v2 in 7002
[root@kong ~]#
金丝雀发布: 金丝雀版本流量权重90%
通过调整default.conf的weight,然后执行nginx -s reload的方式,调节金丝雀版本的权重为90%,流量的90%会执行新的服务
修改default.conf的方法
只需要将upstream中的server的权重做如下调整:
upstream nginx_canary {
server 192.168.163.117:7001 weight=10;
server 192.168.163.117:7002 weight=90;
}重新加载nginx设定
# nginx -s reload 2018/05/28 05:24:29 [notice] 346#346: signal process started #
确认结果
[root@kong ~]# cnt=0; while [ $cnt -lt 10 ]; do curl ; let cnt++; done
hello, service :hello canary deploy service: v2 in 7002
hello, service :hello canary deploy service: v2 in 7002
hello, service :hello canary deploy service: v2 in 7002
hello, service :hello canary deploy service: v2 in 7002
hello, service :hello main service: v1 in 7001
hello, service :hello canary deploy service: v2 in 7002
hello, service :hello canary deploy service: v2 in 7002
hello, service :hello canary deploy service: v2 in 7002
hello, service :hello canary deploy service: v2 in 7002
hello, service :hello canary deploy service: v2 in 7002
[root@kong ~]#
金丝雀发布: 金丝雀版本流量权重100%
通过调整default.conf的weight,然后执行nginx -s reload的方式,调节金丝雀版本的权重为100%,流量的100%会执行新的服务
修改default.conf的方法
只需要将upstream中的server的权重做如下调整:
upstream nginx_canary {
server 192.168.163.117:7001 down;
server 192.168.163.117:7002 weight=100;
}重新加载nginx设定
# nginx -s reload 2018/05/28 05:26:37 [notice] 353#353: signal process started
确认结果
[root@kong ~]# cnt=0; while [ $cnt -lt 10 ]; do curl ; let cnt++; done
hello, service :hello canary deploy service: v2 in 7002
hello, service :hello canary deploy service: v2 in 7002
hello, service :hello canary deploy service: v2 in 7002
hello, service :hello canary deploy service: v2 in 7002
hello, service :hello canary deploy service: v2 in 7002
hello, service :hello canary deploy service: v2 in 7002
hello, service :hello canary deploy service: v2 in 7002
hello, service :hello canary deploy service: v2 in 7002
hello, service :hello canary deploy service: v2 in 7002
hello, service :hello canary deploy service: v2 in 7002
[root@kong ~]#
The above is the detailed content of How to use nginx simulation for canary publishing. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to configure nginx in Windows
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:57 PM
How to configure nginx in Windows
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:57 PM
How to configure Nginx in Windows? Install Nginx and create a virtual host configuration. Modify the main configuration file and include the virtual host configuration. Start or reload Nginx. Test the configuration and view the website. Selectively enable SSL and configure SSL certificates. Selectively set the firewall to allow port 80 and 443 traffic.
 How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
You can query the Docker container name by following the steps: List all containers (docker ps). Filter the container list (using the grep command). Gets the container name (located in the "NAMES" column).
 How to start containers by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
How to start containers by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Docker container startup steps: Pull the container image: Run "docker pull [mirror name]". Create a container: Use "docker create [options] [mirror name] [commands and parameters]". Start the container: Execute "docker start [Container name or ID]". Check container status: Verify that the container is running with "docker ps".
 How to check whether nginx is started
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to check whether nginx is started
Apr 14, 2025 pm 01:03 PM
How to confirm whether Nginx is started: 1. Use the command line: systemctl status nginx (Linux/Unix), netstat -ano | findstr 80 (Windows); 2. Check whether port 80 is open; 3. Check the Nginx startup message in the system log; 4. Use third-party tools, such as Nagios, Zabbix, and Icinga.
 How to create containers for docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
How to create containers for docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
Create a container in Docker: 1. Pull the image: docker pull [mirror name] 2. Create a container: docker run [Options] [mirror name] [Command] 3. Start the container: docker start [Container name]
 How to check nginx version
Apr 14, 2025 am 11:57 AM
How to check nginx version
Apr 14, 2025 am 11:57 AM
The methods that can query the Nginx version are: use the nginx -v command; view the version directive in the nginx.conf file; open the Nginx error page and view the page title.
 How to configure cloud server domain name in nginx
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
How to configure cloud server domain name in nginx
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
How to configure an Nginx domain name on a cloud server: Create an A record pointing to the public IP address of the cloud server. Add virtual host blocks in the Nginx configuration file, specifying the listening port, domain name, and website root directory. Restart Nginx to apply the changes. Access the domain name test configuration. Other notes: Install the SSL certificate to enable HTTPS, ensure that the firewall allows port 80 traffic, and wait for DNS resolution to take effect.
 How to start nginx server
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
How to start nginx server
Apr 14, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Starting an Nginx server requires different steps according to different operating systems: Linux/Unix system: Install the Nginx package (for example, using apt-get or yum). Use systemctl to start an Nginx service (for example, sudo systemctl start nginx). Windows system: Download and install Windows binary files. Start Nginx using the nginx.exe executable (for example, nginx.exe -c conf\nginx.conf). No matter which operating system you use, you can access the server IP






