Collection of 13 essential Python knowledge suggestions

Python has ranked first in the programming language popularity index PYPL many times.
It is considered the simplest language ever created due to its code readability and simpler syntax.
The richness of various AI and machine learning libraries such as NumPy, Pandas, and TensorFlow is one of the core requirements of Python.
If you are a data scientist or a beginner in AI/machine learning, then Python is the right choice to start your journey.
This time, Xiao F will take you to explore some basic knowledge of Python programming, which is simple but very useful.
- Directory
- Data type
- Variable
- List
- Collection
- Dictionary
- Comments
- Basic functions
- Conditional statements
- Loop statements
- Function
- Exception handling
- String operation
- Regular expression
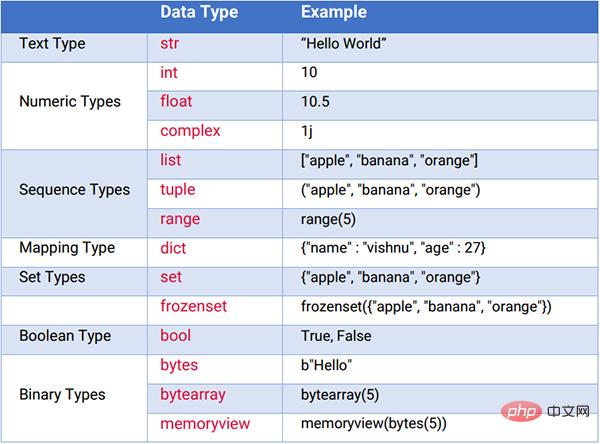
1. Data type
Data type is a data specification that can be stored in a variable. The interpreter allocates memory for variables based on their type.
The following are the various data types in Python.
#2. Variables
Variables are containers that store data values.
Variables can use short names (such as x and y) or more descriptive names (age, carname, total_volume).
Python variable naming rules:
- The variable name must start with a letter or underscore character
- The variable name cannot start with a number
- The variable name must only Can contain alphanumeric characters and underscores (A-z, 0-9, and _)
- Variable names are case-sensitive (age, Age, and AGE are three different variables)
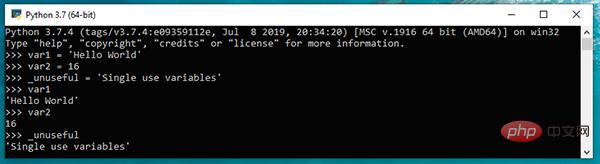
var1 = 'Hello World' var2 = 16 _unuseful = 'Single use variables'
The output is as follows.
3. List
A list (List) is an ordered and changeable collection that allows duplicate members.
It may not be homogeneous, we can create a list containing different data types such as integers, strings and objects.
>>> companies = ["apple","google","tcs","accenture"]
>>> print(companies)
['apple', 'google', 'tcs', 'accenture']
>>> companies.append("infosys")
>>> print(companies)
['apple', 'google', 'tcs', 'accenture', 'infosys']
>>> print(len(companies))
5
>>> print(companies[2])
tcs
>>> print(companies[-2])
accenture
>>> print(companies[1:])
['google', 'tcs', 'accenture', 'infosys']
>>> print(companies[:1])
['apple']
>>> print(companies[1:3])
['google', 'tcs']
>>> companies.remove("infosys")
>>> print(companies)
["apple","google","tcs","accenture"]
>>> companies.pop()
>>> print(companies)
["apple","google","tcs"]4. Set
Set is an unordered and unindexed collection with no duplicate members.
Useful for removing duplicate entries from a list. It also supports various mathematical operations such as union, intersection and difference.
>>> set1 = {1,2,3,7,8,9,3,8,1}
>>> print(set1)
{1, 2, 3, 7, 8, 9}
>>> set1.add(5)
>>> set1.remove(9)
>>> print(set1)
{1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 8}
>>> set2 = {1,2,6,4,2}
>>> print(set2)
{1, 2, 4, 6}
>>> print(set1.union(set2))# set1 | set2
{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8}
>>> print(set1.intersection(set2)) # set1 & set2
{1, 2}
>>> print(set1.difference(set2)) # set1 - set2
{8, 3, 5, 7}
>>> print(set2.difference(set1)) # set2 - set1
{4, 6}5. Dictionary
A dictionary is a variable collection of unordered items as key-value pairs.
Different from other data types, it saves data in a [key:value] pair format instead of storing individual data. This feature makes it the best data structure for mapping JSON responses.
>>> # example 1
>>> user = { 'username': 'Fan', 'age': 20, 'mail_id': 'codemaker2022@qq.com', 'phone': '18650886088' }
>>> print(user)
{'mail_id': 'codemaker2022@qq.com', 'age': 20, 'username': 'Fan', 'phone': '18650886088'}
>>> print(user['age'])
20
>>> for key in user.keys():
>>> print(key)
mail_id
age
username
phone
>>> for value in user.values():
>>>print(value)
codemaker2022@qq.com
20
Fan
18650886088
>>> for item in user.items():
>>>print(item)
('mail_id', 'codemaker2022@qq.com')
('age', 20)
('username', 'Fan')
('phone', '18650886088')
>>> # example 2
>>> user = {
>>> 'username': "Fan",
>>> 'social_media': [
>>> {
>>> 'name': "Linkedin",
>>> 'url': "https://www.linkedin.com/in/codemaker2022"
>>> },
>>> {
>>> 'name': "Github",
>>> 'url': "https://github.com/codemaker2022"
>>> },
>>> {
>>> 'name': "QQ",
>>> 'url': "https://codemaker2022.qq.com"
>>> }
>>> ],
>>> 'contact': [
>>> {
>>> 'mail': [
>>> "mail.Fan@sina.com",
>>> "codemaker2022@qq.com"
>>> ],
>>> 'phone': "18650886088"
>>> }
>>> ]
>>> }
>>> print(user)
{'username': 'Fan', 'social_media': [{'url': 'https://www.linkedin.com/in/codemaker2022', 'name': 'Linkedin'}, {'url': 'https://github.com/codemaker2022', 'name': 'Github'}, {'url': 'https://codemaker2022.qq.com', 'name': 'QQ'}], 'contact': [{'phone': '18650886088', 'mail': ['mail.Fan@sina.com', 'codemaker2022@qq.com']}]}
>>> print(user['social_media'][0]['url'])
https://www.linkedin.com/in/codemaker2022
>>> print(user['contact'])
[{'phone': '18650886088', 'mail': ['mail.Fan@sina.com', 'codemaker2022@qq.com']}]6. Comments
Single-line comments, starting with the pound character (#), followed by a message and ending at the end of the line.
# 定义用户年龄 age = 27 dob = '16/12/1994' # 定义用户生日
Multi-line comments, enclosed in special quotation marks ("""), you can put the message in multiple lines.
""" Python小常识 This is a multi line comment """
7. Basic functions
print The () function prints the provided message in the console. In addition, you can also provide file or buffer input as a parameter for printing on the screen.
print(object(s), sep=separator, end=end, file=file, flush=flush)
print("Hello World") # prints Hello World
print("Hello", "World")# prints Hello World?
x = ("AA", "BB", "CC")
print(x) # prints ('AA', 'BB', 'CC')
print("Hello", "World", sep="---") # prints Hello---WorldThe input() function is used to collect user input from the console.
It’s important to note here that input() will convert anything you enter into a string.
So if you provide age as an integer value, but the input() method converts it as The string is returned, and you need to manually convert it to an integer.
>>> name = input("Enter your name: ")
Enter your name: Codemaker
>>> print("Hello", name)
Hello Codemakerlen() can check the length of the object. If you enter a string, you can get the number of characters in the specified string.
>>> str1 = "Hello World"
>>> print("The length of the stringis ", len(str1))
The length of the stringis 11str() is used to convert other data types to string values.
>>> str(123) 123 >>> str(3.14) 3.14
int() is used to convert strings to integers.
>>> int("123")
123
>>> int(3.14)
38. Conditions Statements
Conditional statements are blocks of code used to change the flow of a program based on specific conditions. These statements are executed only when a specific condition is met.
In Python, we use if, if- else, loop (for, while) as a conditional statement to change the flow of the program based on certain conditions.
if-else statement.
>>> num = 5
>>> if (num > 0):
>>>print("Positive integer")
>>> else:
>>>print("Negative integer")elif statement.
>>> name = 'admin'
>>> if name == 'User1':
>>> print('Only read access')
>>> elif name == 'admin':
>>> print('Having read and write access')
>>> else:
>>> print('Invalid user')
Having read and write access9 , Loop statement
A loop is a conditional statement used to repeat certain statements (in its body) until a certain condition is met.
In Python, we usually use for and while Loop.
for loop.
>>> # loop through a list >>> companies = ["apple", "google", "tcs"] >>> for x in companies: >>> print(x) apple google tcs >>> # loop through string >>> for x in "TCS": >>>print(x) T C S
The range() function returns a sequence of numbers, which can be used as a for loop control.
It basically requires three parameters, where The second and third are optional. The parameters are the start value, stop value and step number. The step number is the incremental value of the loop variable for each iteration.
>>> # loop with range() function >>> for x in range(5): >>>print(x) 0 1 2 3 4 >>> for x in range(2, 5): >>>print(x) 2 3 4 >>> for x in range(2, 10, 3): >>>print(x) 2 5 8
We can also use else The keyword executes some statements at the end of the loop.
Provides the else statement at the end of the loop and the statements that need to be executed at the end of the loop.
>>> for x in range(5):
>>>print(x)
>>> else:
>>>print("finished")
0
1
2
3
4
finishedwhile loop.
>>> count = 0 >>> while (count < 5): >>>print(count) >>>count = count + 1 0 1 2 3 4
us You can use else at the end of a while loop, similar to a for loop, to execute some statements when the condition is false.
>>> count = 0
>>> while (count < 5):
>>>print(count)
>>>count = count + 1
>>> else:
>>>print("Count is greater than 4")
0
1
2
3
4
Count is greater than 410、函数
函数是用于执行任务的可重用代码块。在代码中实现模块化并使代码可重用,这是非常有用的。
>>> # This prints a passed string into this function
>>> def display(str):
>>>print(str)
>>>return
>>> display("Hello World")
Hello World11、异常处理
即使语句在语法上是正确的,它也可能在执行时发生错误。这些类型的错误称为异常。我们可以使用异常处理机制来避免此类问题。
在Python中,我们使用try,except和finally关键字在代码中实现异常处理。
>>> def divider(num1, num2):
>>> try:
>>> return num1 / num2
>>> except ZeroDivisionError as e:
>>> print('Error: Invalid argument: {}'.format(e))
>>> finally:
>>> print("finished")
>>>
>>> print(divider(2,1))
>>> print(divider(2,0))
finished
2.0
Error: Invalid argument: division by zero
finished
None12、字符串操作
字符串是用单引号或双引号(',")括起来的字符集合。
我们可以使用内置方法对字符串执行各种操作,如连接、切片、修剪、反转、大小写更改和格式化,如split()、lower()、upper()、endswith()、join()和ljust()、rjust()、format()。
>>> msg = 'Hello World'
>>> print(msg)
Hello World
>>> print(msg[1])
e
>>> print(msg[-1])
d
>>> print(msg[:1])
H
>>> print(msg[1:])
ello World
>>> print(msg[:-1])
Hello Worl
>>> print(msg[::-1])
dlroW olleH
>>> print(msg[1:5])
ello
>>> print(msg.upper())
HELLO WORLD
>>> print(msg.lower())
hello world
>>> print(msg.startswith('Hello'))
True
>>> print(msg.endswith('World'))
True
>>> print(', '.join(['Hello', 'World', '2022']))
Hello, World, 2022
>>> print(' '.join(['Hello', 'World', '2022']))
Hello World 2022
>>> print("Hello World 2022".split())
['Hello', 'World', '2022']
>>> print("Hello World 2022".rjust(25, '-'))
---------Hello World 2022
>>> print("Hello World 2022".ljust(25, '*'))
Hello World 2022*********
>>> print("Hello World 2022".center(25, '#'))
#####Hello World 2022####
>>> name = "Codemaker"
>>> print("Hello %s" % name)
Hello Codemaker
>>> print("Hello {}".format(name))
Hello Codemaker
>>> print("Hello {0}{1}".format(name, "2022"))
Hello Codemaker202213、正则表达式
- 导入regex模块,import re。
- re.compile()使用该函数创建一个Regex对象。
- 将搜索字符串传递给search()方法。
- 调用group()方法返回匹配的文本。
>>> import re
>>> phone_num_regex = re.compile(r'ddd-ddd-dddd')
>>> mob = phone_num_regex.search('My number is 996-190-7453.')
>>> print('Phone number found: {}'.format(mob.group()))
Phone number found: 996-190-7453
>>> phone_num_regex = re.compile(r'^d+$')
>>> is_valid = phone_num_regex.search('+919961907453.') is None
>>> print(is_valid)
True
>>> at_regex = re.compile(r'.at')
>>> strs = at_regex.findall('The cat in the hat sat on the mat.')
>>> print(strs)
['cat', 'hat', 'sat', 'mat']好了,本期的分享就到此结束了,有兴趣的小伙伴可以自行去实践学习。
The above is the detailed content of Collection of 13 essential Python knowledge suggestions. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP is mainly procedural programming, but also supports object-oriented programming (OOP); Python supports a variety of paradigms, including OOP, functional and procedural programming. PHP is suitable for web development, and Python is suitable for a variety of applications such as data analysis and machine learning.
 Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP is suitable for web development and rapid prototyping, and Python is suitable for data science and machine learning. 1.PHP is used for dynamic web development, with simple syntax and suitable for rapid development. 2. Python has concise syntax, is suitable for multiple fields, and has a strong library ecosystem.
 Why Use PHP? Advantages and Benefits Explained
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Why Use PHP? Advantages and Benefits Explained
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:16 AM
The core benefits of PHP include ease of learning, strong web development support, rich libraries and frameworks, high performance and scalability, cross-platform compatibility, and cost-effectiveness. 1) Easy to learn and use, suitable for beginners; 2) Good integration with web servers and supports multiple databases; 3) Have powerful frameworks such as Laravel; 4) High performance can be achieved through optimization; 5) Support multiple operating systems; 6) Open source to reduce development costs.
 PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP originated in 1994 and was developed by RasmusLerdorf. It was originally used to track website visitors and gradually evolved into a server-side scripting language and was widely used in web development. Python was developed by Guidovan Rossum in the late 1980s and was first released in 1991. It emphasizes code readability and simplicity, and is suitable for scientific computing, data analysis and other fields.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 PHP: An Introduction to the Server-Side Scripting Language
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:18 AM
PHP: An Introduction to the Server-Side Scripting Language
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:18 AM
PHP is a server-side scripting language used for dynamic web development and server-side applications. 1.PHP is an interpreted language that does not require compilation and is suitable for rapid development. 2. PHP code is embedded in HTML, making it easy to develop web pages. 3. PHP processes server-side logic, generates HTML output, and supports user interaction and data processing. 4. PHP can interact with the database, process form submission, and execute server-side tasks.
 How to run sublime code python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
How to run sublime code python
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:48 AM
To run Python code in Sublime Text, you need to install the Python plug-in first, then create a .py file and write the code, and finally press Ctrl B to run the code, and the output will be displayed in the console.
 The Continued Use of PHP: Reasons for Its Endurance
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:23 AM
The Continued Use of PHP: Reasons for Its Endurance
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:23 AM
What’s still popular is the ease of use, flexibility and a strong ecosystem. 1) Ease of use and simple syntax make it the first choice for beginners. 2) Closely integrated with web development, excellent interaction with HTTP requests and database. 3) The huge ecosystem provides a wealth of tools and libraries. 4) Active community and open source nature adapts them to new needs and technology trends.






