How to perform AES encryption and decryption operations in Java
1. Background knowledge
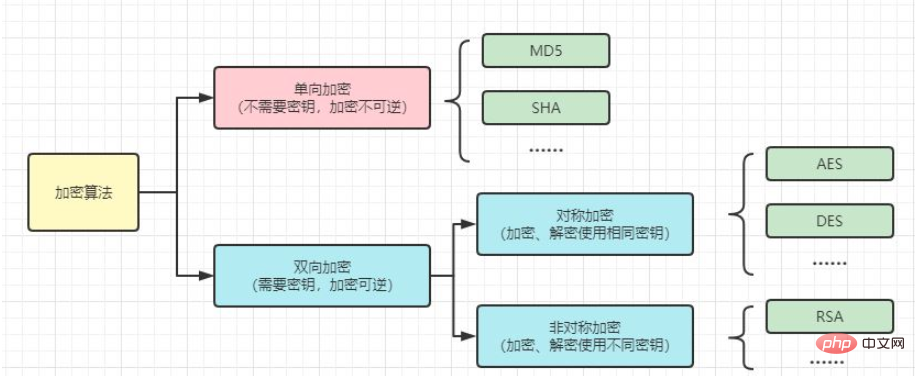
In cryptography, encryption algorithms are divided into one-way encryption and two-way encryption.
Symmetric encryption means that encryption and decryption use the same key, including AES encryption, DES encryption, etc.
Asymmetric encryption means that encryption and decryption use different keys, including RSA encryption, etc.
One-way encryption includes digest algorithms such as MD5 and SHA, which are irreversible.
Two-way encryption includes symmetric encryption and asymmetric encryption. Two-way encryption is reversible, and the key to the ciphertext exists.
2. Introduction to AES
AES: Advanced Encryption Standard is adopted by the U.S. federal government A block encryption standard that is currently the most popular
symmetric encryption algorithm.
is a new generation block encryption algorithm used to replace DES.
AES supports three key lengths: 128 bits, 192 bits, and 256 bits.
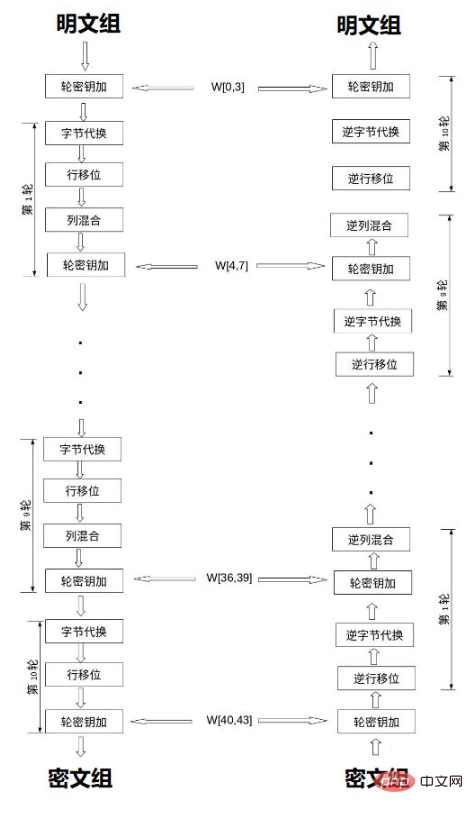
3. AES encryption process (AES processing unit: byte)
The encryption and decryption process of AES is the same as DES, both through Block encryption, group decryption. The so-called block encryption is to group the content to be encrypted and decrypted into groups according to 128 bits, group the keys into groups according to 128 bits, 192 bits, and 256 bits, and encrypt and decrypt the grouped plaintext and the corresponding grouped keys respectively.
Encryption: After the plaintext and key are grouped, for each group: plaintext group and key group processing-> round key addition-> 10 rounds of encryption-> ciphertext Group
Decryption: For each group: Ciphertext group-> Round key addition-> 10 rounds of decryption-> Plaintext group
Plaintext Grouping: Each group is equal in length, both 128 bits (16 bytes);
Key grouping: There are 128 bits, 192 bits, and 256 bits. The recommended number of encryption rounds They are 10, 12, and 14 respectively
Key group processing: Take the key grouping of 128 bits as an example (then the recommended number of encryption rounds is 10, and the operation is the same for the first 9 times, The tenth time is different) Similarly, the 128-bit key is also represented by a matrix in byte units. Through the key arrangement function, a sequence of 44 elements is formed W[0],W[1], … , W[43] (each element is 4 bytes); among them, W[0], W[1], W[2], W[3] are the original keys, and the remaining 40 elements are divided into 10 groups, each Group 4 elements (4*4=16 bytes), which are used for 10 rounds of encryption respectively.
The AES encryption algorithm involves 4 operations: Byte substitution (SubBytes), Row shift (ShiftRows), column Mix (MixColumns) and round keys plus (AddRoundKey).
The following figure shows the AES encryption and decryption process:
AddRoundKey (round key addition)— Each word in the matrix Each subkey is XORed with the round key; each subkey is generated by the key generation scheme.
SubBytes (byte replacement) - Through a non-linear replacement function, each byte is replaced with the corresponding byte using a lookup table.
ShiftRows (row shift) — Circularly shift each column in the matrix.
MixColumns (column confusion)— In order to fully mix the operations of each straight row in the matrix. This step uses a linear transformation to blend the four bytes of each column.
If the length of a piece of plaintext is 192 bits, and if it is split into one plaintext block every 128 bits, the second plaintext block will only have 64 bits, which is less than 128 bits. . What to do at this time? It is necessary to pad the plaintext block (Padding).
Padding involves the following three padding modes:
NoPadding: No padding is done, but the plain text must be An integer multiple of 16 bytes.PKCS5Padding(default): If the plaintext block is less than 16 bytes (128bit), add the corresponding number of characters at the end of the plaintext block, and each word The value of the section is equal to the number of missing characters.
For example, plain text: {1,2,3,4,5,a,b,c,d,e}, if 6 bytes are missing, the completion is {1, 2,3,4,5,a,b,c,d,e,6,6,6,6,6,6}
ISO10126Padding: If the plaintext block is less than 16 bytes (128bit), the corresponding number of bytes is added to the end of the plaintext block. The last character value is equal to the number of missing characters, and the other characters are filled with random numbers.
For example, plain text: {1,2,3,4,5,a,b,c,d,e}, if 6 bytes are missing, it may be completed as {1 ,2,3,4,5,a,b,c,d,e,5,c,3,G,$,6}
4.Java implementation
Note: AES encryption contains Base64 encryption
##Encryption: AES encryption-> Base64 encryption-> Ciphertext
Decryption: Base64 decryption-> AES decryption-> Plain text
Test address: Click here
4.1 Generate keys and offsets
Generate 16 random numbers of uppercase and lowercase letters and numbers:
private static final String SYMBOLS = "0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ"; // 数字和26个字母组成
private static final Random RANDOM = new SecureRandom();
/**
* 获取长度为 6 的随机字母+数字
* @return 随机数字
*/
public static String getRandomNumber() {
char[] nonceChars = new char[16]; //指定长度为6位/自己可以要求设置
for (int index = 0; index < nonceChars.length; ++index) {
nonceChars[index] = SYMBOLS.charAt(RANDOM.nextInt(SYMBOLS.length()));
}
return new String(nonceChars);
}4.2 AESUtil.java source code
import org.apache.commons.lang3.RandomStringUtils;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.util.Base64Utils;
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import javax.crypto.spec.IvParameterSpec;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
/**
* AES加密工具类
*
* @author ACGkaka
* @since 2021-06-18 19:11:03
*/
public class AESUtil {
/**
* 日志相关
*/
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AESUtil.class);
/**
* 编码
*/
private static final String ENCODING = "UTF-8";
/**
* 算法定义
*/
private static final String AES_ALGORITHM = "AES";
/**
* 指定填充方式
*/
private static final String CIPHER_PADDING = "AES/ECB/PKCS5Padding";
private static final String CIPHER_CBC_PADDING = "AES/CBC/PKCS5Padding";
/**
* 偏移量(CBC中使用,增强加密算法强度)
*/
private static final String IV_SEED = "1234567812345678";
/**
* AES加密
* @param content 待加密内容
* @param aesKey 密码
* @return
*/
public static String encrypt(String content, String aesKey){
if(StringUtils.isBlank(content)){
LOGGER.info("AES encrypt: the content is null!");
return null;
}
//判断秘钥是否为16位
if(StringUtils.isNotBlank(aesKey) && aesKey.length() == 16){
try {
//对密码进行编码
byte[] bytes = aesKey.getBytes(ENCODING);
//设置加密算法,生成秘钥
SecretKeySpec skeySpec = new SecretKeySpec(bytes, AES_ALGORITHM);
// "算法/模式/补码方式"
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(CIPHER_PADDING);
//选择加密
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, skeySpec);
//根据待加密内容生成字节数组
byte[] encrypted = cipher.doFinal(content.getBytes(ENCODING));
//返回base64字符串
return Base64Utils.encodeToString(encrypted);
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.info("AES encrypt exception:" + e.getMessage());
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}else {
LOGGER.info("AES encrypt: the aesKey is null or error!");
return null;
}
}
/**
* 解密
*
* @param content 待解密内容
* @param aesKey 密码
* @return
*/
public static String decrypt(String content, String aesKey){
if(StringUtils.isBlank(content)){
LOGGER.info("AES decrypt: the content is null!");
return null;
}
//判断秘钥是否为16位
if(StringUtils.isNotBlank(aesKey) && aesKey.length() == 16){
try {
//对密码进行编码
byte[] bytes = aesKey.getBytes(ENCODING);
//设置解密算法,生成秘钥
SecretKeySpec skeySpec = new SecretKeySpec(bytes, AES_ALGORITHM);
// "算法/模式/补码方式"
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(CIPHER_PADDING);
//选择解密
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, skeySpec);
//先进行Base64解码
byte[] decodeBase64 = Base64Utils.decodeFromString(content);
//根据待解密内容进行解密
byte[] decrypted = cipher.doFinal(decodeBase64);
//将字节数组转成字符串
return new String(decrypted, ENCODING);
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.info("AES decrypt exception:" + e.getMessage());
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}else {
LOGGER.info("AES decrypt: the aesKey is null or error!");
return null;
}
}
/**
* AES_CBC加密
*
* @param content 待加密内容
* @param aesKey 密码
* @return
*/
public static String encryptCBC(String content, String aesKey){
if(StringUtils.isBlank(content)){
LOGGER.info("AES_CBC encrypt: the content is null!");
return null;
}
//判断秘钥是否为16位
if(StringUtils.isNotBlank(aesKey) && aesKey.length() == 16){
try {
//对密码进行编码
byte[] bytes = aesKey.getBytes(ENCODING);
//设置加密算法,生成秘钥
SecretKeySpec skeySpec = new SecretKeySpec(bytes, AES_ALGORITHM);
// "算法/模式/补码方式"
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(CIPHER_CBC_PADDING);
//偏移
IvParameterSpec iv = new IvParameterSpec(IV_SEED.getBytes(ENCODING));
//选择加密
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, skeySpec, iv);
//根据待加密内容生成字节数组
byte[] encrypted = cipher.doFinal(content.getBytes(ENCODING));
//返回base64字符串
return Base64Utils.encodeToString(encrypted);
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.info("AES_CBC encrypt exception:" + e.getMessage());
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}else {
LOGGER.info("AES_CBC encrypt: the aesKey is null or error!");
return null;
}
}
/**
* AES_CBC解密
*
* @param content 待解密内容
* @param aesKey 密码
* @return
*/
public static String decryptCBC(String content, String aesKey){
if(StringUtils.isBlank(content)){
LOGGER.info("AES_CBC decrypt: the content is null!");
return null;
}
//判断秘钥是否为16位
if(StringUtils.isNotBlank(aesKey) && aesKey.length() == 16){
try {
//对密码进行编码
byte[] bytes = aesKey.getBytes(ENCODING);
//设置解密算法,生成秘钥
SecretKeySpec skeySpec = new SecretKeySpec(bytes, AES_ALGORITHM);
//偏移
IvParameterSpec iv = new IvParameterSpec(IV_SEED.getBytes(ENCODING));
// "算法/模式/补码方式"
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(CIPHER_CBC_PADDING);
//选择解密
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, skeySpec, iv);
//先进行Base64解码
byte[] decodeBase64 = Base64Utils.decodeFromString(content);
//根据待解密内容进行解密
byte[] decrypted = cipher.doFinal(decodeBase64);
//将字节数组转成字符串
return new String(decrypted, ENCODING);
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.info("AES_CBC decrypt exception:" + e.getMessage());
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}else {
LOGGER.info("AES_CBC decrypt: the aesKey is null or error!");
return null;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// AES支持三种长度的密钥:128位、192位、256位。
// 代码中这种就是128位的加密密钥,16字节 * 8位/字节 = 128位。
String random = RandomStringUtils.random(16, "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz1234567890");
System.out.println("随机key:" + random);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("---------加密---------");
String aesResult = encrypt("测试AES加密12", random);
System.out.println("aes加密结果:" + aesResult);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("---------解密---------");
String decrypt = decrypt(aesResult, random);
System.out.println("aes解密结果:" + decrypt);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("--------AES_CBC加密解密---------");
String cbcResult = encryptCBC("测试AES加密12456", random);
System.out.println("aes_cbc加密结果:" + cbcResult);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("---------解密CBC---------");
String cbcDecrypt = decryptCBC(cbcResult, random);
System.out.println("aes解密结果:" + cbcDecrypt);
System.out.println();
}
}4.3 Execution results
随机key:golrtt58318fx7ol ---------加密--------- aes加密结果:Xy8W9lCeVue9Ao36z+duM7D7WeS5tdBihIMb1q9KpNg= ---------解密--------- aes解密结果:测试AES加密12 --------AES_CBC加密解密--------- aes_cbc加密结果:xs3ypQXyd62P9jB0+RvOqxFnHIHBIlVdqoZLuqYNBLw= ---------解密CBC--------- aes解密结果:测试AES加密12456
4.4 Online verification
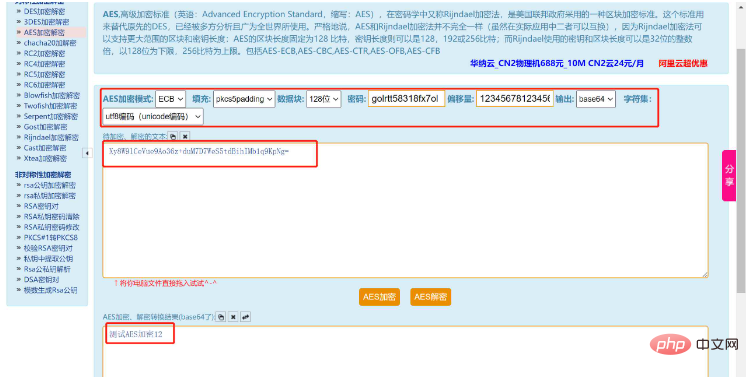
The above is the detailed content of How to perform AES encryption and decryption operations in Java. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1653
1653
 14
14
 1413
1413
 52
52
 1304
1304
 25
25
 1251
1251
 29
29
 1224
1224
 24
24
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP is a scripting language widely used on the server side, especially suitable for web development. 1.PHP can embed HTML, process HTTP requests and responses, and supports a variety of databases. 2.PHP is used to generate dynamic web content, process form data, access databases, etc., with strong community support and open source resources. 3. PHP is an interpreted language, and the execution process includes lexical analysis, grammatical analysis, compilation and execution. 4.PHP can be combined with MySQL for advanced applications such as user registration systems. 5. When debugging PHP, you can use functions such as error_reporting() and var_dump(). 6. Optimize PHP code to use caching mechanisms, optimize database queries and use built-in functions. 7
 PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and the choice should be based on project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, with simple syntax and high execution efficiency. 2. Python is suitable for data science and machine learning, with concise syntax and rich libraries.
 PHP vs. Other Languages: A Comparison
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP vs. Other Languages: A Comparison
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP is suitable for web development, especially in rapid development and processing dynamic content, but is not good at data science and enterprise-level applications. Compared with Python, PHP has more advantages in web development, but is not as good as Python in the field of data science; compared with Java, PHP performs worse in enterprise-level applications, but is more flexible in web development; compared with JavaScript, PHP is more concise in back-end development, but is not as good as JavaScript in front-end development.
 PHP vs. Python: Core Features and Functionality
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP vs. Python: Core Features and Functionality
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages and are suitable for different scenarios. 1.PHP is suitable for web development and provides built-in web servers and rich function libraries. 2. Python is suitable for data science and machine learning, with concise syntax and a powerful standard library. When choosing, it should be decided based on project requirements.
 Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Capsules are three-dimensional geometric figures, composed of a cylinder and a hemisphere at both ends. The volume of the capsule can be calculated by adding the volume of the cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere at both ends. This tutorial will discuss how to calculate the volume of a given capsule in Java using different methods. Capsule volume formula The formula for capsule volume is as follows: Capsule volume = Cylindrical volume Volume Two hemisphere volume in, r: The radius of the hemisphere. h: The height of the cylinder (excluding the hemisphere). Example 1 enter Radius = 5 units Height = 10 units Output Volume = 1570.8 cubic units explain Calculate volume using formula: Volume = π × r2 × h (4
 PHP: The Foundation of Many Websites
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP: The Foundation of Many Websites
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
The reasons why PHP is the preferred technology stack for many websites include its ease of use, strong community support, and widespread use. 1) Easy to learn and use, suitable for beginners. 2) Have a huge developer community and rich resources. 3) Widely used in WordPress, Drupal and other platforms. 4) Integrate tightly with web servers to simplify development deployment.
 PHP's Impact: Web Development and Beyond
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:10 AM
PHP's Impact: Web Development and Beyond
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:10 AM
PHPhassignificantlyimpactedwebdevelopmentandextendsbeyondit.1)ItpowersmajorplatformslikeWordPressandexcelsindatabaseinteractions.2)PHP'sadaptabilityallowsittoscaleforlargeapplicationsusingframeworkslikeLaravel.3)Beyondweb,PHPisusedincommand-linescrip




