Analyze terminal operation examples in Java Stream API
1. Java Stream pipeline data processing operation
In the article written before this issue, I once introduced to you that Java Stream pipeline flow is used Java API for simplifying the processing of collection class elements. The process of use is divided into three stages. Before starting this article, I think I still need to introduce these three stages to some new friends, as shown in the picture:
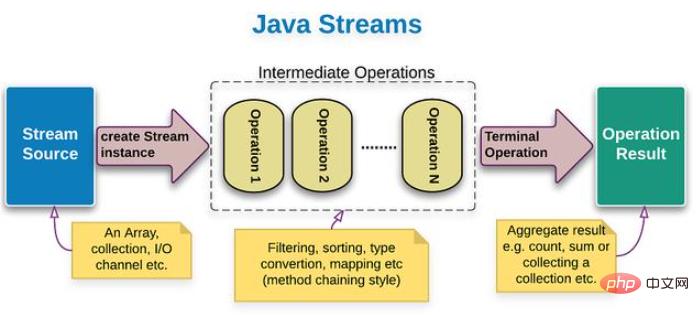
The first stage (in the picture Blue): Convert a collection, array, or line text file into a java Stream pipeline stream
Second stage (dotted line part in the figure): Pipeline streaming data processing operation, processing pipeline every element in . The output elements from the previous pipe serve as the input elements for the next pipe.
The third stage (green in the picture): pipeline flow result processing operation, which is the core content of this article.
Before starting to learn, it is still necessary to review an example we told you before:
List<String> nameStrs = Arrays.asList("Monkey", "Lion", "Giraffe","Lemur");
List<String> list = nameStrs.stream()
.filter(s -> s.startsWith("L"))
.map(String::toUpperCase)
.sorted()
.collect(toList());
System.out.println(list);First use the stream() method to convert the string List For the pipeline stream Stream
, and then perform pipeline data processing operations, first use the filter function to filter all strings starting with uppercase L, then convert the strings in the pipeline to uppercase letters toUpperCase, and then call the sorted method to sort. The usage of these APIs has been introduced in previous articles of this article. Lambda expressions and function references are also used.
Finally, use the collect function for result processing and convert the java Stream pipeline stream into a List. The final output of the list is: [LEMUR, LION]
If you do not use the java Stream pipeline flow, think about how many lines of code you need to complete the above function? Back to the topic, this article is going to introduce you to the third stage: what operations can be done on the pipeline stream processing results? Let’s get started!
2. ForEach and ForEachOrdered
If we just want to print out the processing results of the Stream pipeline stream instead of performing type conversion, we can use the forEach() method or forEachOrdered() method .
Stream.of("Monkey", "Lion", "Giraffe", "Lemur", "Lion")
.parallel()
.forEach(System.out::println);
Stream.of("Monkey", "Lion", "Giraffe", "Lemur", "Lion")
.parallel()
.forEachOrdered(System.out::println);The parallel() function indicates that the elements in the pipeline are processed in parallel instead of serially, so that the processing speed is faster. However, this may cause the later elements in the pipeline flow to be processed first, and the previous elements to be processed later, that is, the order of the elements cannot be guaranteed.
forEachOrdered can be understood from the name, although it may be possible in the data processing order. There is no guarantee, but the forEachOrdered method can ensure that the order in which the elements are output is consistent with the order in which the elements enter the pipeline stream. That is, it looks like the following (the forEach method cannot guarantee this order):
Monkey
Lion
Giraffe
Lemur
Lion
3. Collection of elements collect
The most common usage of java Stream is: first, convert the collection class into a pipeline stream, second, process the pipeline stream data, and third, convert the pipeline stream processing result into a collection class. Then the collect() method provides us with the function of converting the pipeline stream processing results into a collection class.
3.1. Collect as Set
Collect the processing results of the Stream through the Collectors.toSet() method and collect all elements into the Set collection.
Set<String> collectToSet = Stream.of( "Monkey", "Lion", "Giraffe", "Lemur", "Lion" ) .collect(Collectors.toSet()); //最终collectToSet 中的元素是:[Monkey, Lion, Giraffe, Lemur],注意Set会去重。
3.2. Collected into List
Similarly, elements can be collected into List using the toList() collector.
List<String> collectToList = Stream.of( "Monkey", "Lion", "Giraffe", "Lemur", "Lion" ).collect(Collectors.toList()); // 最终collectToList中的元素是: [Monkey, Lion, Giraffe, Lemur, Lion]
3.3. Common collection methods
The element collection methods introduced above are all dedicated. For example, use Collectors.toSet() to collect a Set type collection; use Collectors.toList() to collect a List type collection. So, is there a more general way to collect data elements to collect data into any Collection interface subtype? Therefore, here is a general way to collect elements. You can collect data elements into any Collection type: that is, by providing a constructor to the required Collection type.
LinkedList<String> collectToCollection = Stream.of( "Monkey", "Lion", "Giraffe", "Lemur", "Lion" ).collect(Collectors.toCollection(LinkedList::new)); //最终collectToCollection中的元素是: [Monkey, Lion, Giraffe, Lemur, Lion]
Note: LinkedList::new is used in the code, which actually calls the constructor of LinkedList to collect elements into Linked List. Of course, you can also use methods such as LinkedHashSet::new and PriorityQueue::new to collect data elements into other collection types, which is more versatile.
3.4. Collect into Array
Collect the processing results of the Stream through the toArray(String[]::new) method and collect all elements into a string array.
String[] toArray = Stream.of( "Monkey", "Lion", "Giraffe", "Lemur", "Lion" ) .toArray(String[]::new); //最终toArray字符串数组中的元素是: [Monkey, Lion, Giraffe, Lemur, Lion]
3.5. Collected into Map
Use the Collectors.toMap() method to collect data elements into the Map, but a problem arises: whether the elements in the pipeline are used as keys or as value. We used a Function.identity() method, which simply returns a "t -> t" (the input is the lambda expression of the output). In addition, use the pipeline stream processing function distinct() to ensure the uniqueness of the Map key value.
Map<String, Integer> toMap = Stream.of(
"Monkey", "Lion", "Giraffe", "Lemur", "Lion"
)
.distinct()
.collect(Collectors.toMap(
Function.identity(), //元素输入就是输出,作为key
s -> (int) s.chars().distinct().count()// 输入元素的不同的字母个数,作为value
));
// 最终toMap的结果是: {Monkey=6, Lion=4, Lemur=5, Giraffe=6}3.6. Grouping By groupingBy
Collectors.groupingBy is used to implement grouping collection of elements. The following code demonstrates how to collect different data elements into different Lists based on the first letter and encapsulate them. for Map.
Map<Character, List<String>> groupingByList = Stream.of(
"Monkey", "Lion", "Giraffe", "Lemur", "Lion"
)
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(
s -> s.charAt(0) , //根据元素首字母分组,相同的在一组
// counting() // 加上这一行代码可以实现分组统计
));
// 最终groupingByList内的元素: {G=[Giraffe], L=[Lion, Lemur, Lion], M=[Monkey]}
//如果加上counting() ,结果是: {G=1, L=3, M=1}这是该过程的说明:groupingBy第一个参数作为分组条件,第二个参数是子收集器。
四、其他常用方法
boolean containsTwo = IntStream.of(1, 2, 3).anyMatch(i -> i == 2);
// 判断管道中是否包含2,结果是: true
long nrOfAnimals = Stream.of(
"Monkey", "Lion", "Giraffe", "Lemur"
).count();
// 管道中元素数据总计结果nrOfAnimals: 4
int sum = IntStream.of(1, 2, 3).sum();
// 管道中元素数据累加结果sum: 6
OptionalDouble average = IntStream.of(1, 2, 3).average();
//管道中元素数据平均值average: OptionalDouble[2.0]
int max = IntStream.of(1, 2, 3).max().orElse(0);
//管道中元素数据最大值max: 3
IntSummaryStatistics statistics = IntStream.of(1, 2, 3).summaryStatistics();
// 全面的统计结果statistics: IntSummaryStatistics{count=3, sum=6, min=1, average=2.000000, max=3}The above is the detailed content of Analyze terminal operation examples in Java Stream API. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP is a scripting language widely used on the server side, especially suitable for web development. 1.PHP can embed HTML, process HTTP requests and responses, and supports a variety of databases. 2.PHP is used to generate dynamic web content, process form data, access databases, etc., with strong community support and open source resources. 3. PHP is an interpreted language, and the execution process includes lexical analysis, grammatical analysis, compilation and execution. 4.PHP can be combined with MySQL for advanced applications such as user registration systems. 5. When debugging PHP, you can use functions such as error_reporting() and var_dump(). 6. Optimize PHP code to use caching mechanisms, optimize database queries and use built-in functions. 7
 PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and the choice should be based on project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, with simple syntax and high execution efficiency. 2. Python is suitable for data science and machine learning, with concise syntax and rich libraries.
 PHP vs. Other Languages: A Comparison
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP vs. Other Languages: A Comparison
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP is suitable for web development, especially in rapid development and processing dynamic content, but is not good at data science and enterprise-level applications. Compared with Python, PHP has more advantages in web development, but is not as good as Python in the field of data science; compared with Java, PHP performs worse in enterprise-level applications, but is more flexible in web development; compared with JavaScript, PHP is more concise in back-end development, but is not as good as JavaScript in front-end development.
 PHP vs. Python: Core Features and Functionality
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP vs. Python: Core Features and Functionality
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages and are suitable for different scenarios. 1.PHP is suitable for web development and provides built-in web servers and rich function libraries. 2. Python is suitable for data science and machine learning, with concise syntax and a powerful standard library. When choosing, it should be decided based on project requirements.
 Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Capsules are three-dimensional geometric figures, composed of a cylinder and a hemisphere at both ends. The volume of the capsule can be calculated by adding the volume of the cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere at both ends. This tutorial will discuss how to calculate the volume of a given capsule in Java using different methods. Capsule volume formula The formula for capsule volume is as follows: Capsule volume = Cylindrical volume Volume Two hemisphere volume in, r: The radius of the hemisphere. h: The height of the cylinder (excluding the hemisphere). Example 1 enter Radius = 5 units Height = 10 units Output Volume = 1570.8 cubic units explain Calculate volume using formula: Volume = π × r2 × h (4
 PHP: The Foundation of Many Websites
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP: The Foundation of Many Websites
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
The reasons why PHP is the preferred technology stack for many websites include its ease of use, strong community support, and widespread use. 1) Easy to learn and use, suitable for beginners. 2) Have a huge developer community and rich resources. 3) Widely used in WordPress, Drupal and other platforms. 4) Integrate tightly with web servers to simplify development deployment.
 Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Java is a popular programming language that can be learned by both beginners and experienced developers. This tutorial starts with basic concepts and progresses through advanced topics. After installing the Java Development Kit, you can practice programming by creating a simple "Hello, World!" program. After you understand the code, use the command prompt to compile and run the program, and "Hello, World!" will be output on the console. Learning Java starts your programming journey, and as your mastery deepens, you can create more complex applications.






