Java BigDecimal class application example code analysis
1. Introduction
The main design goal of float and double types is for scientific calculations and engineering calculations. They perform binary floating-point operations, which are carefully designed to provide fast approximate calculations with high accuracy over a wide range of values. However, they do not provide completely accurate results and should not be used where accurate results are required. However, business calculations often require accurate results, and BigDecimal comes in handy at this time.
2. Introduction to knowledge points
1. Overview
2. Construction method
3. Operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division
4. Source code description
5. Summary
6. Refining exercises
Code demonstration:
package com.Test;
import Test2.MyDate;
import java.awt.*;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.GregorianCalendar;
import java.util.Properties;
public class Main {
private final static String name = "磊哥的java历险记-@51博客";
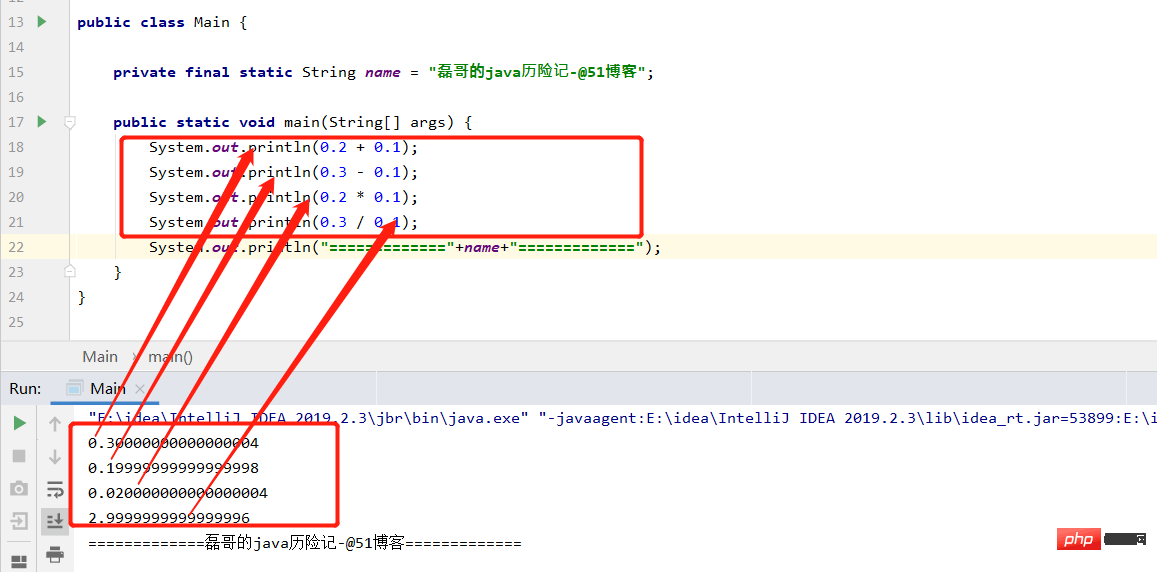
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(0.2 + 0.1);
System.out.println(0.3 - 0.1);
System.out.println(0.2 * 0.1);
System.out.println(0.3 / 0.1);
System.out.println("============="+name+"=============");
}
}
- (1) public BigDecimal(double val): Convert double representation to BigDecimal (note: not recommended)
- (2) public BigDecimal(int val): Convert int representation to BigDecimal
- (3) public BigDecimal(String val): Convert String Convert the representation to BigDecimal
Code demonstration:
package com.Test;
import Test2.MyDate;
import java.awt.*;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.GregorianCalendar;
import java.util.Properties;
public class Main {
private final static String name = "磊哥的java历险记-@51博客";
public static void main(String[] args){
BigDecimal bigDecimal =new BigDecimal(2);
BigDecimal bDouble = new BigDecimal(2.3);
BigDecimal bString = new BigDecimal("2.3");
System.out.println("bigDecimal="+ bigDecimal);
System.out.println("bDouble="+ bDouble);
System.out.println("bString="+ bString);
System.out.println("============="+name+"=============");
}
}The running results are as follows:
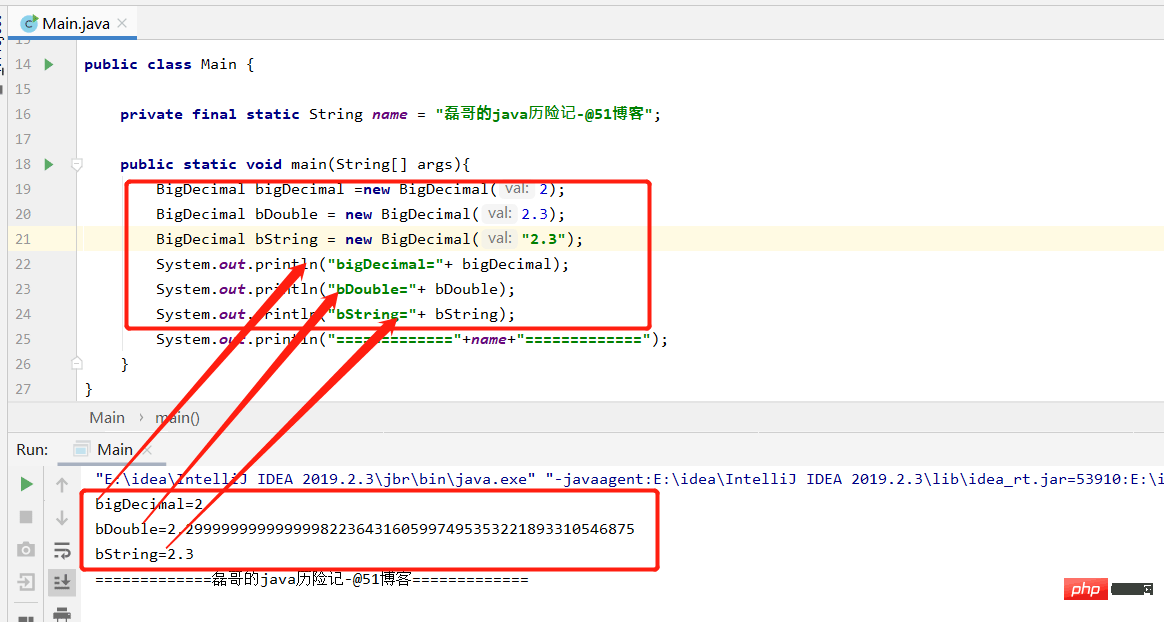
of BigDecimal Code demonstration:
package com.Test;
import Test2.MyDate;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
public class Main {
private final static String name = "磊哥的java历险记-@51博客";
public static void main(String[] args) {
BigDecimal bDouble1 =BigDecimal.valueOf(2.3);
BigDecimal bDouble2 = new BigDecimal(Double.toString(2.3));
System.out.println("bDouble1="+ bDouble1);
System.out.println("bDouble2="+ bDouble2);
System.out.println("============="+name+"=============");
}
}The results are as follows:
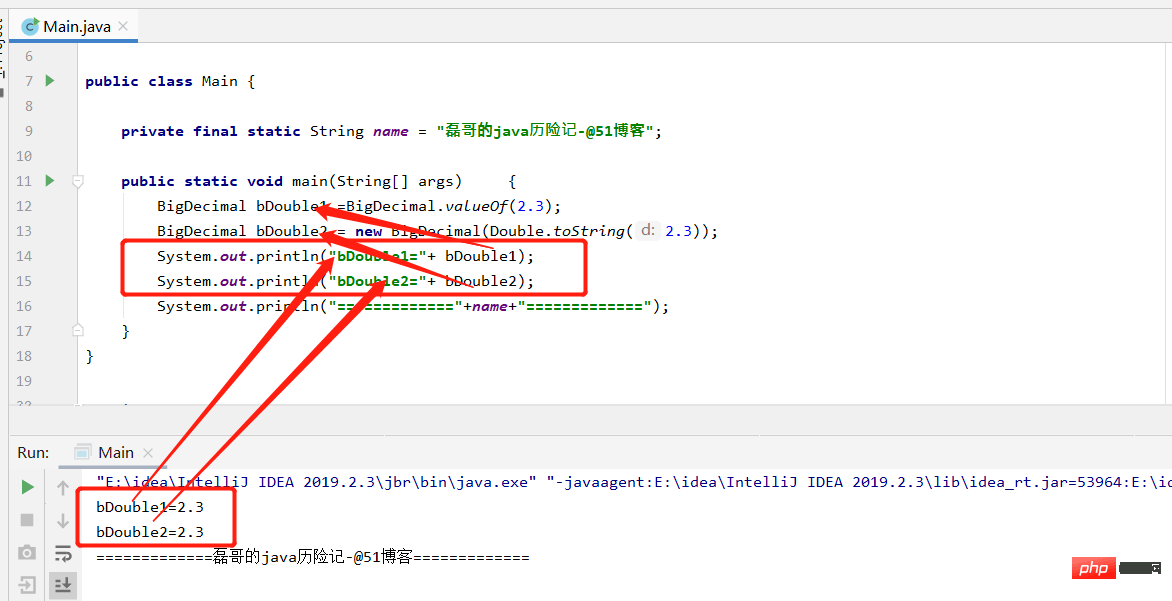
- (1) public BigDecimal add(BigDecimal value); addition
- (2) public BigDecimal subtract(BigDecimal value); //Subtraction
- (3) public BigDecimal multiply(BigDecimal value); //Multiplication (4) public BigDecimal divide(BigDecimal value); Division
Code demonstration:
package com.Test;
import Test2.MyDate;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
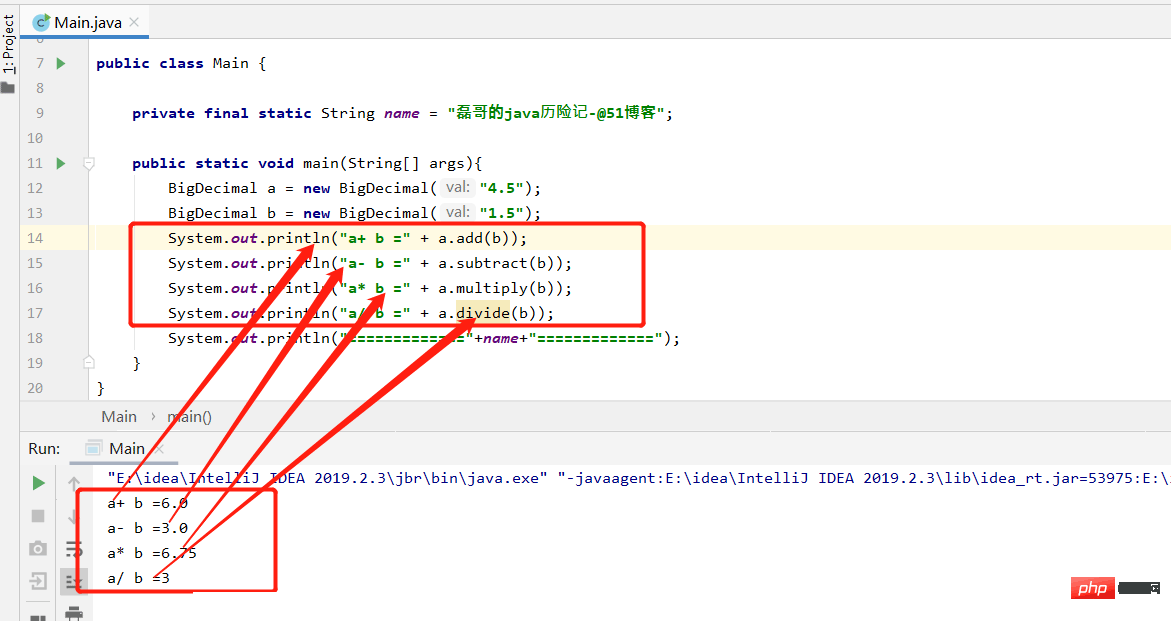
public class Main {
private final static String name = "磊哥的java历险记-@51博客";
public static void main(String[] args){
BigDecimal a = new BigDecimal("4.5");
BigDecimal b = new BigDecimal("1.5");
System.out.println("a+ b =" + a.add(b));
System.out.println("a- b =" + a.subtract(b));
System.out.println("a* b =" + a.multiply(b));
System.out.println("a/ b =" + a.divide(b));
System.out.println("============="+name+"=============");
}
}
In fact, the divide method can pass three parameters:
public BigDecimal divide(BigDecimal divisor, int scale, introundingMode) 第一参数表示除数, 第二个参数表示小数点后保留位数, 第三个参数表示舍入模式,只有在作除法运算或四舍五入时才用到舍入模式,有下面这几种
(1)ROUND_CEILING //向正无穷方向舍入
(2)ROUND_DOWN //向零方向舍入
(3)ROUND_FLOOR //向负无穷方向舍入
(4)ROUND_HALF_DOWN //向(距离)最近的一边舍入,除非两边(的距离)是相等,如果是这样,向下舍入, 例如1.55 保留一位小数结果为1.5
(5)ROUND_HALF_EVEN //向(距离)最近的一边舍入,除非两边(的距离)是相等,如果是这样,如果保留位数是奇数,使用ROUND_HALF_UP,如果是偶数,使用ROUND_HALF_DOWN
(6)ROUND_HALF_UP //向(距离)最近的一边舍入,除非两边(的距离)是相等,如果是这样,向上舍入, 1.55保留一位小数结果为1.6
(7)ROUND_UNNECESSARY //计算结果是精确的,不需要舍入模式
(8)ROUND_UP //向远离0的方向舍入
按照各自的需要,可传入合适的第三个参数。四舍五入采用 ROUND_HALF_UP
需要对BigDecimal进行截断和四舍五入可用setScale方法,例:
代码演示:
public static void main(String[] args) {
BigDecimal a = newBigDecimal("4.5635");
//保留3位小数,且四舍五入
a = a.setScale(3,RoundingMode.HALF_UP);
System.out.println(a);
}注:减乘除其实最终都返回的是一个新的BigDecimal对象,因为BigInteger与BigDecimal都是不可变的(immutable)的,在进行每一步运算时,都会产生一个新的对象
代码演示:
package com.Test;
import Test2.MyDate;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
public class Main {
private final static String name = "磊哥的java历险记-@51博客";
public static void main(String[] args){
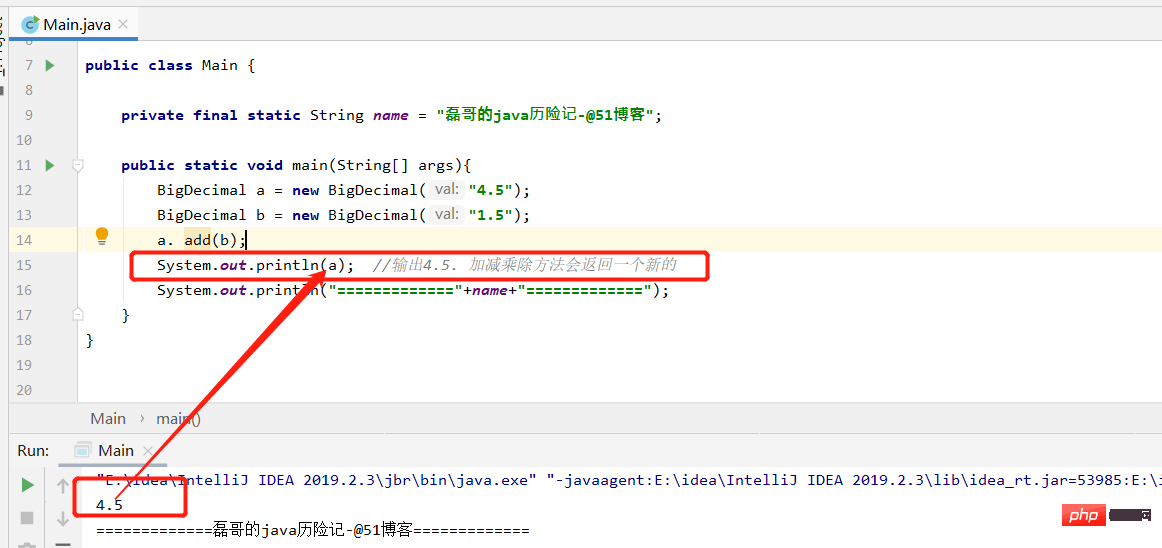
BigDecimal a = new BigDecimal("4.5");
BigDecimal b = new BigDecimal("1.5");
a. add(b);
System.out.println(a); //输出4.5. 加减乘除方法会返回一个新的
System.out.println("============="+name+"=============");
}
}
5、总结
(1)商业计算使用BigDecimal。
(2)尽量使用参数类型为String的构造函数。
(3)BigDecimal都是不可变的(immutable)的,在进行每一步运算时,都会产wf 所以在做加减乘除运算时千万要保存操作后的值。
(4)我们往往容易忽略JDK底层的一些实现细节,导致出现错误,需要多加注意。
6、精炼练习
在银行结算或支付中,我们经常会用到BigDecimal的相关方法。
6.1 题目
(1)使用BigDecimal创建出浮点类型的数字
(2)使用BigDecimal进行加减乘除运算
6.2 实验步骤
(1)声明一个类Test
(2)在Test类中,完成BigDecimal的构造和方法使用
代码演示:
package com.Test;
import Test2.MyDate;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
public class Main {
private final static String name = "磊哥的java历险记-@51博客";
public static void main(String[] args){
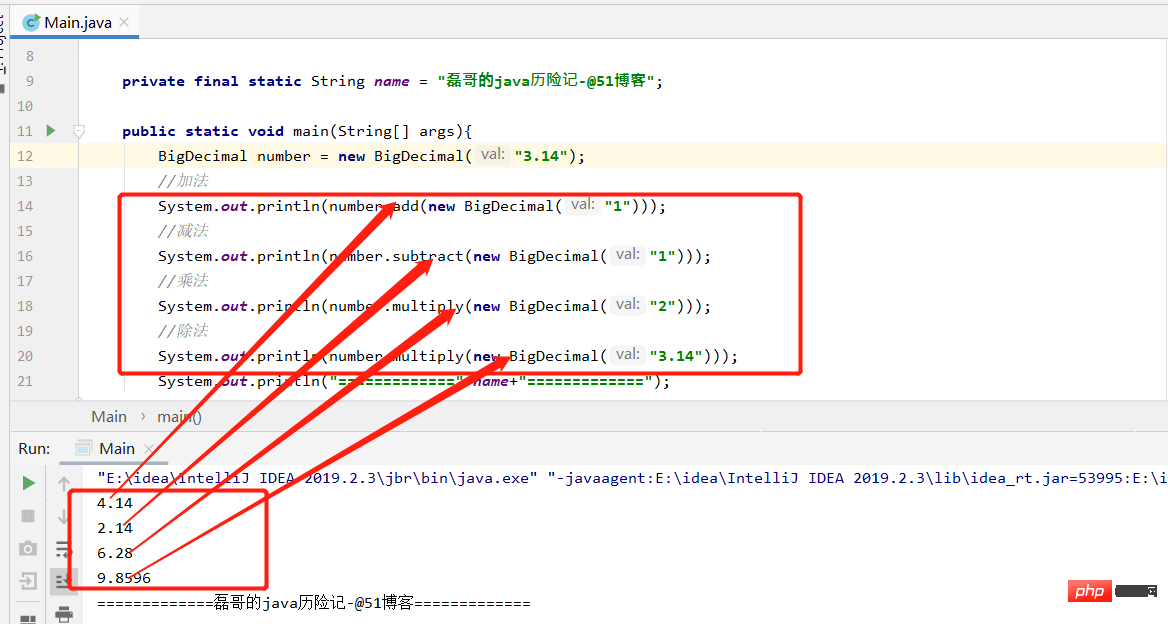
BigDecimal number = new BigDecimal("3.14");
//加法
System.out.println(number.add(new BigDecimal("1")));
//减法
System.out.println(number.subtract(new BigDecimal("1")));
//乘法
System.out.println(number.multiply(new BigDecimal("2")));
//除法
System.out.println(number.multiply(new BigDecimal("3.14")));
System.out.println("============="+name+"=============");
}
}
The above is the detailed content of Java BigDecimal class application example code analysis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1665
1665
 14
14
 1423
1423
 52
52
 1321
1321
 25
25
 1269
1269
 29
29
 1249
1249
 24
24
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP is a scripting language widely used on the server side, especially suitable for web development. 1.PHP can embed HTML, process HTTP requests and responses, and supports a variety of databases. 2.PHP is used to generate dynamic web content, process form data, access databases, etc., with strong community support and open source resources. 3. PHP is an interpreted language, and the execution process includes lexical analysis, grammatical analysis, compilation and execution. 4.PHP can be combined with MySQL for advanced applications such as user registration systems. 5. When debugging PHP, you can use functions such as error_reporting() and var_dump(). 6. Optimize PHP code to use caching mechanisms, optimize database queries and use built-in functions. 7
 PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and the choice should be based on project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, with simple syntax and high execution efficiency. 2. Python is suitable for data science and machine learning, with concise syntax and rich libraries.
 PHP vs. Other Languages: A Comparison
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP vs. Other Languages: A Comparison
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP is suitable for web development, especially in rapid development and processing dynamic content, but is not good at data science and enterprise-level applications. Compared with Python, PHP has more advantages in web development, but is not as good as Python in the field of data science; compared with Java, PHP performs worse in enterprise-level applications, but is more flexible in web development; compared with JavaScript, PHP is more concise in back-end development, but is not as good as JavaScript in front-end development.
 PHP vs. Python: Core Features and Functionality
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP vs. Python: Core Features and Functionality
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages and are suitable for different scenarios. 1.PHP is suitable for web development and provides built-in web servers and rich function libraries. 2. Python is suitable for data science and machine learning, with concise syntax and a powerful standard library. When choosing, it should be decided based on project requirements.
 PHP's Impact: Web Development and Beyond
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:10 AM
PHP's Impact: Web Development and Beyond
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:10 AM
PHPhassignificantlyimpactedwebdevelopmentandextendsbeyondit.1)ItpowersmajorplatformslikeWordPressandexcelsindatabaseinteractions.2)PHP'sadaptabilityallowsittoscaleforlargeapplicationsusingframeworkslikeLaravel.3)Beyondweb,PHPisusedincommand-linescrip
 PHP: The Foundation of Many Websites
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP: The Foundation of Many Websites
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
The reasons why PHP is the preferred technology stack for many websites include its ease of use, strong community support, and widespread use. 1) Easy to learn and use, suitable for beginners. 2) Have a huge developer community and rich resources. 3) Widely used in WordPress, Drupal and other platforms. 4) Integrate tightly with web servers to simplify development deployment.
 PHP vs. Python: Use Cases and Applications
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
PHP vs. Python: Use Cases and Applications
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
PHP is suitable for web development and content management systems, and Python is suitable for data science, machine learning and automation scripts. 1.PHP performs well in building fast and scalable websites and applications and is commonly used in CMS such as WordPress. 2. Python has performed outstandingly in the fields of data science and machine learning, with rich libraries such as NumPy and TensorFlow.




