How to use the start method and run method in Java thread
start method and run method
$start()$ method is used to start a thread. At this time, the thread is ready (Runnable) state, not running. Once the $cpu$ time slice is obtained, the $run()$ method starts to be executed. Directly calling the $run()$ method only calls a method in a class, which is essentially executed in the current thread. Therefore, it can only be achieved by using the $start()$ method to call the $run()$ method. True multithreading.
Sample code
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test4")
public class Test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread("t1"){
@Override
public void run() {
log.debug("running");
}
};
t1.run();
}
}The above code is a direct call to the $run()$ method. You can see in the printed information that the $main$ thread executed this method.
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test4")
public class Test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread("t1"){
@Override
public void run() {
log.debug("running");
}
};
t1.start();
}
}And if you use the $start()$ method to start, it is the real $run$ method executed by the $t1$ thread.
Note
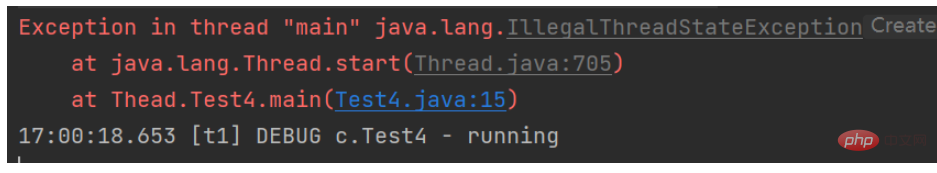
It should be noted that when the $Thread$ object calls the $start()$ method, it will enter the ready state. When it is in the ready state, $start() cannot be called. $ method, otherwise $IllegalThreadStateException$ exception will be thrown, as shown in the following code
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test4")
public class Test4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread("t1"){
@Override
public void run() {
log.debug("running");
}
};
t1.start();
t1.start();
}
}Exception information:
sleep method With the yield method
sleep
Calling the $sleep()$ method will change the current thread from the $Running$ state to the $Time Waiting$ state (blocking)
Other threads can use the $interrupt$ method to interrupt the sleeping thread. At this time, the $sleep$ method will throw InterruptedException
After sleeping The thread may not be executed immediately
It is recommended to use $TimeUnit$’s $sleep$ instead of $Thread$’s $sleep$ to obtain better readability Sample code
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test5")
public class Test5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread("t1"){
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
t1.start();
log.debug("t1 state {}", t1.getState());
//让主线程休眠500ms
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.debug("t1 state {}", t1.getState());
}
}
//17:13:21.729 [main] DEBUG c.Test5 - t1 state RUNNABLE
//17:13:22.245 [main] DEBUG c.Test5 - t1 state TIMED_WAITINGIn the above code, the $t1$ thread is started first. At this time, the state of the printing thread should be in the $RUNNABLE$ state, and letting the main thread sleep prevents the main thread from executing printing first, but it has not yet Enter the $sleep()$ state. When the $sleep$ method in $run()$ is executed, the thread enters the $TIMED WAITING$ state
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test6")
public class Thread6 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t1 = new Thread("t1") {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
log.debug("enter sleep");
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.debug("wake up");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
t1.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
log.debug("interrupt t1");
//被唤醒
t1.interrupt();
}
}Execution result
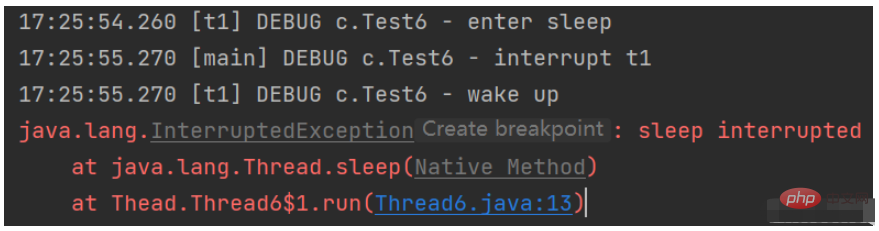
In the above code, when the $start$ method is started, the $t1$ thread enters the sleep state, prints prompt information, the sleep time is $2s$, and interrupts $t1$ after sleeping $1s$ in the $main$ thread. When the thread sleeps, the interrupt message is prompted and the $interrupt()$ method is called. At this time, the thread is interrupted and an exception is thrown.
$TimeUnit$ class adds a new unit to sleep in, which is more readable, but there is essentially no difference, just unit conversion
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);//该语句作用是睡眠一秒
yield
Calling $yield$ will cause the current process to enter the $Runnable$ ready state from $Running$, and then schedule and execute other threads. The specific implementation depends on the task scheduler of the operating system, (that is, when When there are no other tasks in the task scheduler, even if $cpu$ is given up, the thread will continue to execute) $sleep$ will enter the blocking state after execution. If the sleep time does not end at this time, $cpu$ will not be allocated to the thread. , but $yield$ enters the ready state, that is, if no other thread needs to be executed, the thread will also be assigned a time slice. This is the biggest difference between $sleep$ and $yield$. Thread priority
Thread Priority
will prompt the scheduler to schedule the thread first, but it is just a prompt, the scheduler can ignore it
If $cpu$ is busy, then the one with higher priority will get more time slice, but when $cpu$ is idle, the priority is almost no
sleep application-prevent cpu from occupying 100%
When $cpu$ is not used for calculation, do not let $while(true )$ idling wastes $cpu$. At this time, you can use $yield$ or $sleep$ to hand over the use of $cpu$ to other programs.
while (true) {
try {
Thread.sleep(50);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}You can use $wait$ or condition variables to achieve similar results. Effect
The difference is that the latter two require locking and corresponding wake-up operations, which are generally suitable for scenarios where synchronization is required
$sleep$is suitable for scenarios where lock synchronization is not required
join Method
Print results of the following program:
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test6")
public class Test6 {
static int r = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
test();
}
private static void test() {
log.debug("开始");
Thread t = new Thread("t1") {
@Override
public void run() {
log.debug("开始");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.debug("结束");
r = 10;
}
};
t.start();
log.debug("r的值是{}", r);
log.debug("结束");
}
}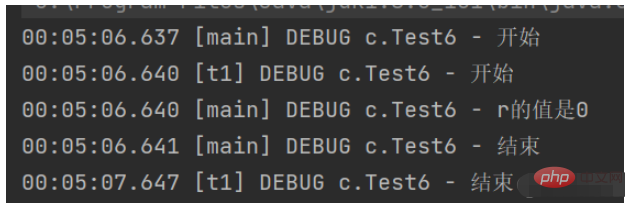
Because the main thread and $t1$ thread are parallel, $t1$ It takes $1s$ for the thread to calculate the value of $r$, and the main thread prints out the value of $r$ at the beginning, so the printed value is 0
Solution:
Add $t.join();$ after $t.start();$. The function of $join$ is to wait for a thread to finish running.
From the perspective of the caller, it is synchronous to wait for the result to be returned before continuing execution, and it is asynchronous to continue execution without waiting for the result to be returned.
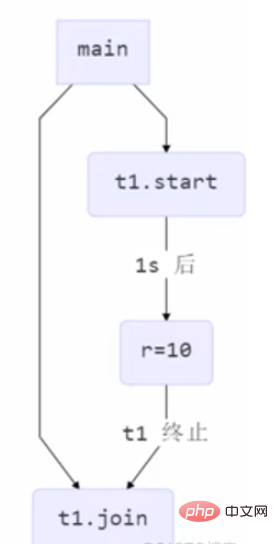
So the $join$ method actually allows it to be executed synchronously
Effective waiting
$join(milliseconds)$ method There can be a parameter to pass in the waiting time. If the thread execution time is greater than the waiting time, it will stop waiting after the waiting time is up. If the thread execution time is less than the waiting time, the waiting will end after the thread execution is completed. The set waiting time will not expire.
interrupt方法
打断$sleep, wait, join$的线程,即打断阻塞状态的线程
打断$sleep$的线程,会清空打断状态
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test7")
public class Test7 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t = new Thread("t1"){
@Override
public void run() {
log.debug("sleep...");
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
t.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
log.debug("interrupt");
t.interrupt();
log.debug("打断标记: {}", t.isInterrupted());
}
}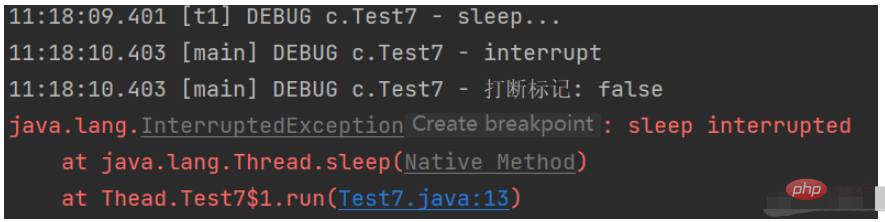
打断正常运行的线程,不会清空打断状态
因此我们可以在线程中判断打断标记,来决定是否被打断,以及执行被打断之前的收尾工作。
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test8")
public class Test8 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t = new Thread("t1"){
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
if (Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
log.debug("线程被打断了");
break;
}
}
}
};
t.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
log.debug("interrupt");
t.interrupt();
}
}守护线程
默认情况下,$java$需要等待所有线程都运行结束,才会结束。有一种特殊的线程叫做守护线程,只要其他非守护线程运行结束了,即使守护线程的代码没有执行完毕,也会强制结束。
@Slf4j(topic = "c.Test10")
public class Test10 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t = new Thread("t1") {
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
}
}
};
//设置线程为守护线程
t.setDaemon(true);
t.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
log.debug("主线程结束");
}
}如果不把$t$设置为守护线程,则因为线程内部的死循环,导致程序不会结束运行。
The above is the detailed content of How to use the start method and run method in Java thread. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1657
1657
 14
14
 1415
1415
 52
52
 1309
1309
 25
25
 1257
1257
 29
29
 1229
1229
 24
24
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP is a scripting language widely used on the server side, especially suitable for web development. 1.PHP can embed HTML, process HTTP requests and responses, and supports a variety of databases. 2.PHP is used to generate dynamic web content, process form data, access databases, etc., with strong community support and open source resources. 3. PHP is an interpreted language, and the execution process includes lexical analysis, grammatical analysis, compilation and execution. 4.PHP can be combined with MySQL for advanced applications such as user registration systems. 5. When debugging PHP, you can use functions such as error_reporting() and var_dump(). 6. Optimize PHP code to use caching mechanisms, optimize database queries and use built-in functions. 7
 PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and the choice should be based on project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, with simple syntax and high execution efficiency. 2. Python is suitable for data science and machine learning, with concise syntax and rich libraries.
 PHP vs. Other Languages: A Comparison
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP vs. Other Languages: A Comparison
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP is suitable for web development, especially in rapid development and processing dynamic content, but is not good at data science and enterprise-level applications. Compared with Python, PHP has more advantages in web development, but is not as good as Python in the field of data science; compared with Java, PHP performs worse in enterprise-level applications, but is more flexible in web development; compared with JavaScript, PHP is more concise in back-end development, but is not as good as JavaScript in front-end development.
 PHP vs. Python: Core Features and Functionality
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP vs. Python: Core Features and Functionality
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:16 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages and are suitable for different scenarios. 1.PHP is suitable for web development and provides built-in web servers and rich function libraries. 2. Python is suitable for data science and machine learning, with concise syntax and a powerful standard library. When choosing, it should be decided based on project requirements.
 Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Capsules are three-dimensional geometric figures, composed of a cylinder and a hemisphere at both ends. The volume of the capsule can be calculated by adding the volume of the cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere at both ends. This tutorial will discuss how to calculate the volume of a given capsule in Java using different methods. Capsule volume formula The formula for capsule volume is as follows: Capsule volume = Cylindrical volume Volume Two hemisphere volume in, r: The radius of the hemisphere. h: The height of the cylinder (excluding the hemisphere). Example 1 enter Radius = 5 units Height = 10 units Output Volume = 1570.8 cubic units explain Calculate volume using formula: Volume = π × r2 × h (4
 PHP's Impact: Web Development and Beyond
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:10 AM
PHP's Impact: Web Development and Beyond
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:10 AM
PHPhassignificantlyimpactedwebdevelopmentandextendsbeyondit.1)ItpowersmajorplatformslikeWordPressandexcelsindatabaseinteractions.2)PHP'sadaptabilityallowsittoscaleforlargeapplicationsusingframeworkslikeLaravel.3)Beyondweb,PHPisusedincommand-linescrip
 PHP: The Foundation of Many Websites
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP: The Foundation of Many Websites
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:07 AM
The reasons why PHP is the preferred technology stack for many websites include its ease of use, strong community support, and widespread use. 1) Easy to learn and use, suitable for beginners. 2) Have a huge developer community and rich resources. 3) Widely used in WordPress, Drupal and other platforms. 4) Integrate tightly with web servers to simplify development deployment.




