How to Simplify Hardware Acceleration of Robots Using ROS 2
Translator | Li Rui
Reviewer | Sun Shujuan
When developing robots, system integration often takes up most of the project resources, which is more important than developing the final application. . With the emergence of low-end industrial collaborative robots, there have been software developers focused solely on developing software that runs on existing hardware. However, there is a crucial relationship between a robot's hardware and software capabilities. Design control over computing hardware needs to be retained to create more professional, energy-efficient, safe, and high-performance robots.

Hardware Challenges and Software Skills Robotics experts must overcome the obstacles faced by hardware if they hope to deliver the better, faster robots that the future will demand. In the post-Moore computing world, upgrading hardware to adopt the latest generation of microprocessors will not deliver the desired application performance upgrades. Its path forward no longer lies in waiting for the latest chip. Hardware acceleration is often the only way to achieve the necessary gains.
This hardware challenge complicates the work of developers in disciplines such as robotics, whose skills are often biased toward developing software. This means they must face the prospect of designing adaptive computing hardware if they are to meet market demand for new industrial robots. Businesses using robots to increase productivity in areas such as production lines and warehouses are looking for devices that offer additional flexibility, finer position control, superior vision-based capabilities, improved data capture and lower power consumption.
The main principle of robotics hardware acceleration is that, unlike traditional control-driven approaches, a hybrid control and data-driven approach to software development allows teams to design custom computing architectures that allocate the optimal amount of hardware to the application resource.
In terms of implementation, a heterogeneous computing model is required. This takes advantage of CPUs and GPUs, which excel at control flow calculations, while leveraging the strengths of FPGAs to handle data flow calculations. This approach provides both flexibility and full control over the CPU/GPU to implement complex calculations with low power consumption, high performance, low latency and the determinism of hardware acceleration. Various vendors are now offering adaptive system-on-chip (SoC) and system-on-module (SOM) devices, such as the AMD-Xilinx Kria™ SOM and its associated Kria robotics stack, that offer the benefits of this hybrid computing model. This table compares these different models.
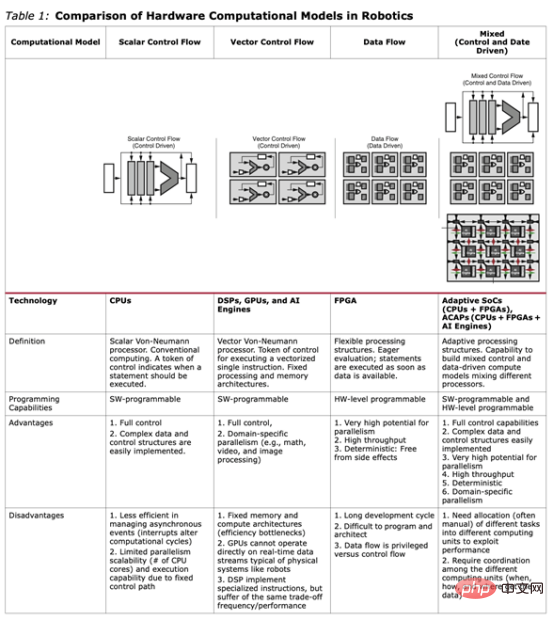 Adaptive systems on chips (SoCs) and system-on-modules (SOMs) allow robotics experts to build machine behavior by programming the architecture that creates the correct data paths and control mechanisms. However, sophisticated engineering skills are required to program such architectures using established tools and techniques.
Adaptive systems on chips (SoCs) and system-on-modules (SOMs) allow robotics experts to build machine behavior by programming the architecture that creates the correct data paths and control mechanisms. However, sophisticated engineering skills are required to program such architectures using established tools and techniques.
Roboticians lack the appropriate hardware and embedded design expertise and are accustomed to building behaviors in the form of computational graphs to solve current robotic tasks. They often use C to create complex real-time deterministic systems through advanced software engineering practices.
Built on Robot Operating System (ROS)
A different approach is now needed to help roboticists take advantage of available hardware acceleration technology. Ideally, this approach should let them create custom hardware in a familiar development environment (such as ROS) and simulate it using familiar tools (such as Gazebo).
ROS is the de facto industry standard for robotics application development, even more so since the advent of ROS2 in 2020. This has become the default software development kit (SDK) for robotics applications across industries, with many groups now using ROS and Gazebo.
Previous initiatives to integrate adaptive computing into ROS have addressed this challenge from a hardware engineer's perspective. They assume that users have previous experience with embedded and hardware flows and are therefore familiar with concepts such as RTL, HDL, and HLS and the design tools used to operate them. Likewise, deploying to embedded targets requires some understanding of Yocto, OpenEmbedded, and related tools.
Understanding that most robotics experts do not come from this background, the ROS2 Hardware Acceleration Working Group (HAWG) is taking a ROS-centric approach to integrating embedded processes directly into the ROS ecosystem. It aims to provide an experience similar to what roboticists enjoy when building a ROS workspace in a desktop workstation.
HAWG’s work builds on published research on optimizing ROS computational graphs to take advantage of adaptive computing, as well as recommendations on tools and methods for accelerating parts of graphs in programmable logic. Beyond this, HAWG is now proposing an architecture (pictured below) that focuses on familiar languages like C and OpenCL.
##ROS 2 and HAWG stack together facilitate hardware acceleration
The proposed architecture is platform-agnostic and therefore suitable for edge facilities, workstations, data centers or cloud computing platforms, and technology-agnostic to allow targeting FPGA, CPU and GPU and easily ported to various modules and motherboards.
Ultimately, this work should enable most robotics experts to take advantage of the opportunities of hardware acceleration to implement the next generation of advanced and complex robots.
Original title: Simplifying hardware acceleration for robots with ROS 2, author: Ben Dickson
The above is the detailed content of How to Simplify Hardware Acceleration of Robots Using ROS 2. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1662
1662
 14
14
 1418
1418
 52
52
 1311
1311
 25
25
 1261
1261
 29
29
 1234
1234
 24
24
 Four recommended AI-assisted programming tools
Apr 22, 2024 pm 05:34 PM
Four recommended AI-assisted programming tools
Apr 22, 2024 pm 05:34 PM
This AI-assisted programming tool has unearthed a large number of useful AI-assisted programming tools in this stage of rapid AI development. AI-assisted programming tools can improve development efficiency, improve code quality, and reduce bug rates. They are important assistants in the modern software development process. Today Dayao will share with you 4 AI-assisted programming tools (and all support C# language). I hope it will be helpful to everyone. https://github.com/YSGStudyHards/DotNetGuide1.GitHubCopilotGitHubCopilot is an AI coding assistant that helps you write code faster and with less effort, so you can focus more on problem solving and collaboration. Git
 After 2 months, the humanoid robot Walker S can fold clothes
Apr 03, 2024 am 08:01 AM
After 2 months, the humanoid robot Walker S can fold clothes
Apr 03, 2024 am 08:01 AM
Editor of Machine Power Report: Wu Xin The domestic version of the humanoid robot + large model team completed the operation task of complex flexible materials such as folding clothes for the first time. With the unveiling of Figure01, which integrates OpenAI's multi-modal large model, the related progress of domestic peers has been attracting attention. Just yesterday, UBTECH, China's "number one humanoid robot stock", released the first demo of the humanoid robot WalkerS that is deeply integrated with Baidu Wenxin's large model, showing some interesting new features. Now, WalkerS, blessed by Baidu Wenxin’s large model capabilities, looks like this. Like Figure01, WalkerS does not move around, but stands behind a desk to complete a series of tasks. It can follow human commands and fold clothes
 How can AI make robots more autonomous and adaptable?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 07:18 PM
How can AI make robots more autonomous and adaptable?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 07:18 PM
In the field of industrial automation technology, there are two recent hot spots that are difficult to ignore: artificial intelligence (AI) and Nvidia. Don’t change the meaning of the original content, fine-tune the content, rewrite the content, don’t continue: “Not only that, the two are closely related, because Nvidia is expanding beyond just its original graphics processing units (GPUs). The technology extends to the field of digital twins and is closely connected to emerging AI technologies. "Recently, NVIDIA has reached cooperation with many industrial companies, including leading industrial automation companies such as Aveva, Rockwell Automation, Siemens and Schneider Electric, as well as Teradyne Robotics and its MiR and Universal Robots companies. Recently,Nvidiahascoll
 The first robot to autonomously complete human tasks appears, with five fingers that are flexible and fast, and large models support virtual space training
Mar 11, 2024 pm 12:10 PM
The first robot to autonomously complete human tasks appears, with five fingers that are flexible and fast, and large models support virtual space training
Mar 11, 2024 pm 12:10 PM
This week, FigureAI, a robotics company invested by OpenAI, Microsoft, Bezos, and Nvidia, announced that it has received nearly $700 million in financing and plans to develop a humanoid robot that can walk independently within the next year. And Tesla’s Optimus Prime has repeatedly received good news. No one doubts that this year will be the year when humanoid robots explode. SanctuaryAI, a Canadian-based robotics company, recently released a new humanoid robot, Phoenix. Officials claim that it can complete many tasks autonomously at the same speed as humans. Pheonix, the world's first robot that can autonomously complete tasks at human speeds, can gently grab, move and elegantly place each object to its left and right sides. It can autonomously identify objects
 Which AI programmer is the best? Explore the potential of Devin, Tongyi Lingma and SWE-agent
Apr 07, 2024 am 09:10 AM
Which AI programmer is the best? Explore the potential of Devin, Tongyi Lingma and SWE-agent
Apr 07, 2024 am 09:10 AM
On March 3, 2022, less than a month after the birth of the world's first AI programmer Devin, the NLP team of Princeton University developed an open source AI programmer SWE-agent. It leverages the GPT-4 model to automatically resolve issues in GitHub repositories. SWE-agent's performance on the SWE-bench test set is similar to Devin, taking an average of 93 seconds and solving 12.29% of the problems. By interacting with a dedicated terminal, SWE-agent can open and search file contents, use automatic syntax checking, edit specific lines, and write and execute tests. (Note: The above content is a slight adjustment of the original content, but the key information in the original text is retained and does not exceed the specified word limit.) SWE-A
 Learn how to develop mobile applications using Go language
Mar 28, 2024 pm 10:00 PM
Learn how to develop mobile applications using Go language
Mar 28, 2024 pm 10:00 PM
Go language development mobile application tutorial As the mobile application market continues to boom, more and more developers are beginning to explore how to use Go language to develop mobile applications. As a simple and efficient programming language, Go language has also shown strong potential in mobile application development. This article will introduce in detail how to use Go language to develop mobile applications, and attach specific code examples to help readers get started quickly and start developing their own mobile applications. 1. Preparation Before starting, we need to prepare the development environment and tools. head
 Cloud Whale Xiaoyao 001 sweeping and mopping robot has a 'brain'! | Experience
Apr 26, 2024 pm 04:22 PM
Cloud Whale Xiaoyao 001 sweeping and mopping robot has a 'brain'! | Experience
Apr 26, 2024 pm 04:22 PM
Sweeping and mopping robots are one of the most popular smart home appliances among consumers in recent years. The convenience of operation it brings, or even the need for no operation, allows lazy people to free their hands, allowing consumers to "liberate" from daily housework and spend more time on the things they like. Improved quality of life in disguised form. Riding on this craze, almost all home appliance brands on the market are making their own sweeping and mopping robots, making the entire sweeping and mopping robot market very lively. However, the rapid expansion of the market will inevitably bring about a hidden danger: many manufacturers will use the tactics of sea of machines to quickly occupy more market share, resulting in many new products without any upgrade points. It is also said that they are "matryoshka" models. Not an exaggeration. However, not all sweeping and mopping robots are
 Ten humanoid robots shaping the future
Mar 22, 2024 pm 08:51 PM
Ten humanoid robots shaping the future
Mar 22, 2024 pm 08:51 PM
The following 10 humanoid robots are shaping our future: 1. ASIMO: Developed by Honda, ASIMO is one of the most well-known humanoid robots. Standing 4 feet tall and weighing 119 pounds, ASIMO is equipped with advanced sensors and artificial intelligence capabilities that allow it to navigate complex environments and interact with humans. ASIMO's versatility makes it suitable for a variety of tasks, from assisting people with disabilities to delivering presentations at events. 2. Pepper: Created by Softbank Robotics, Pepper aims to be a social companion for humans. With its expressive face and ability to recognize emotions, Pepper can participate in conversations, help in retail settings, and even provide educational support. Pepper's




