How to check SSH version in Linux
Check method: 1. Open "/etc/ssh/sshd_config" with a text editor and check the "Protocol" field. If "Protocol 2" is displayed, it means that the server only supports SSH2. If "Protocol 1" is displayed It means that the server supports both at the same time. 2. Force ssh to use a specific SSH protocol and judge by checking the response of the SSH server. 3. Use the scanssh tool with the syntax "sudo scanssh -s ssh ip address".

#The operating environment of this tutorial: linux7.3 system, Dell G3 computer.
Secure Shell (SSH) allows remote login or remote execution of commands through an encrypted secure communication channel. SSH is designed to replace insecure plaintext protocols such as telnet, rsh, and rlogin. SSH provides a number of required features such as authentication, encryption, data integrity, authorization and forwarding/tunneling.
SSH exists in two versions 1 and 2 (SSH1 and SSH2). What's the difference between these two? How to check the SSH protocol version on Linux?
SSH1 vs. SSH2
There are some minor version differences in the SSH protocol specification, but there are two main major versions: SSH1 (version 1.XX) and SSH2 (version 2.00).
In fact, SSH1 and SSH2 are two completely different and incompatible protocols. SSH2 significantly improves many aspects of SSH1. First of all, SSH is a macro design. Several different functions (such as authentication, transmission, connection) are packaged into a single protocol. SSH2 brings more powerful security features than SSH1, such as MAC-based integrity check, flexible session key updates, fully negotiated encryption algorithms, public key certificates, and more.
SSH2 is standardized by the IETF, and its implementation is widely deployed and accepted in the industry. Due to the popularity and encryption advantages of SSH2 over SSH1, many products have dropped support for SSH1. At the time of writing this article, OpenSSH still supports SSH1 and SSH2, however in all modern Linux distributions, OpenSSH servers disable SSH1 by default.
Linux check SSH version
Method 1
If you want to check local OpenSSH server support For the SSH protocol version, you can refer to the file /etc/ssh/sshd_config. Open /etc/ssh/sshd_config with a text editor and look at the "Protocol" field.
If it is displayed as follows, it means that the server only supports SSH2.
Protocol 2
If it is displayed as follows, it means that the server supports both SSH1 and SSH2.
Protocol 1
Method 2
If you cannot access /etc/ssh/sshd_config because the OpenSSH service is running on the remote server. You can use an SSH client called ssh to check the supported protocols. Specifically, it forces ssh to use a specific SSH protocol, and then we check the response of the SSH server.
The following command forces ssh to use SSH1:
ssh -1 user@remote_server
The following command forces ssh to use SSH2:
ssh -2 user@remote_server
If the remote SSH server only supports SSH2, then the first one with " -1" option will cause an error message like the following:
Protocol major versions differ: 1 vs. 2
If the SSH server supports both SSH1 and SSH2, then both commands are valid.
Method 3
Another way to check the version is to run an SSH scanning tool called scanssh. This command line tool is useful when you want to check a group of IP addresses or an entire local network to upgrade an SSH1-compatible SSH server.
The following is the basic SSH version scanning syntax.
sudo scanssh -s ssh -n [ports] [IP addresses or CIDR prefix]
The "-n" option can specify the SSH port to scan. You can use Duhao separation to scan multiple ports. Without this option, scanssh will scan port 22 by default.
Use the following command to discover the SSH server in the 192.168.1.0/24 local network and check the SSH protocol v version:
sudo scan -s ssh 192.168.1.0/24
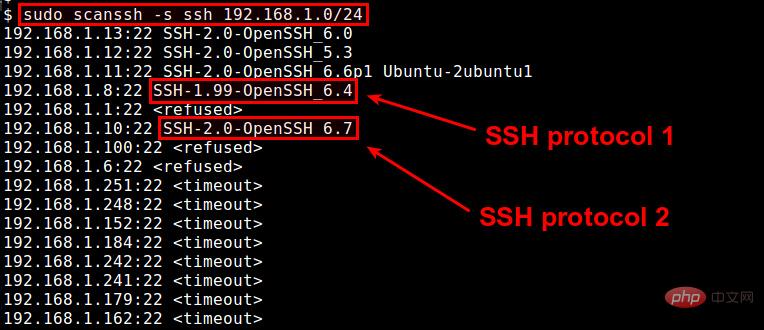
If scanssh is A specific IP address reports "SSH-1.XX-XXXX", which implies that the minimum version supported by the associated SSH server is SSH1. If the remote server only supports SSH2, scanssh will display "SSH-2.0-XXXX".
Related recommendations: "Linux Video Tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of How to check SSH version in Linux. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1677
1677
 14
14
 1429
1429
 52
52
 1333
1333
 25
25
 1278
1278
 29
29
 1257
1257
 24
24
 Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
The five basic components of the Linux system are: 1. Kernel, 2. System library, 3. System utilities, 4. Graphical user interface, 5. Applications. The kernel manages hardware resources, the system library provides precompiled functions, system utilities are used for system management, the GUI provides visual interaction, and applications use these components to implement functions.
 How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
To view the Git repository address, perform the following steps: 1. Open the command line and navigate to the repository directory; 2. Run the "git remote -v" command; 3. View the repository name in the output and its corresponding address.
 How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
Although Notepad cannot run Java code directly, it can be achieved by using other tools: using the command line compiler (javac) to generate a bytecode file (filename.class). Use the Java interpreter (java) to interpret bytecode, execute the code, and output the result.
 How to run sublime after writing the code
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:51 AM
How to run sublime after writing the code
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:51 AM
There are six ways to run code in Sublime: through hotkeys, menus, build systems, command lines, set default build systems, and custom build commands, and run individual files/projects by right-clicking on projects/files. The build system availability depends on the installation of Sublime Text.
 What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
The main uses of Linux include: 1. Server operating system, 2. Embedded system, 3. Desktop operating system, 4. Development and testing environment. Linux excels in these areas, providing stability, security and efficient development tools.
 git software installation
Apr 17, 2025 am 11:57 AM
git software installation
Apr 17, 2025 am 11:57 AM
Installing Git software includes the following steps: Download the installation package and run the installation package to verify the installation configuration Git installation Git Bash (Windows only)
 laravel installation code
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:30 PM
laravel installation code
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:30 PM
To install Laravel, follow these steps in sequence: Install Composer (for macOS/Linux and Windows) Install Laravel Installer Create a new project Start Service Access Application (URL: http://127.0.0.1:8000) Set up the database connection (if required)
 How to set important Git configuration global properties
Apr 17, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
How to set important Git configuration global properties
Apr 17, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
There are many ways to customize a development environment, but the global Git configuration file is one that is most likely to be used for custom settings such as usernames, emails, preferred text editors, and remote branches. Here are the key things you need to know about global Git configuration files.




