What are the characteristics of front-end development es6
Features: 1. Add new variable declaration methods const and let; 2. Template string, which solves the pain points of es5 in the string function; 3. Provides default values for parameters so that when parameters are not available Used when being passed; 4. Arrow function, which is a shortcut for writing functions; 5. Object initialization abbreviation, used to solve the problem of duplicate name of key-value pairs; 6. Destructuring; 7. Expansion operator; 8. Import and export; 9. Promise; 10. Generators; 11. async function; 12. Class.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, ECMAScript version 6, Dell G3 computer.
1. Variable declaration const and let
Before ES6, we all used varKeyword declares variables. No matter where it is declared, it is considered to be declared at the top of the function (if not at the top of the function, it is at the top of the global scope). This is function variable promotion. For example:
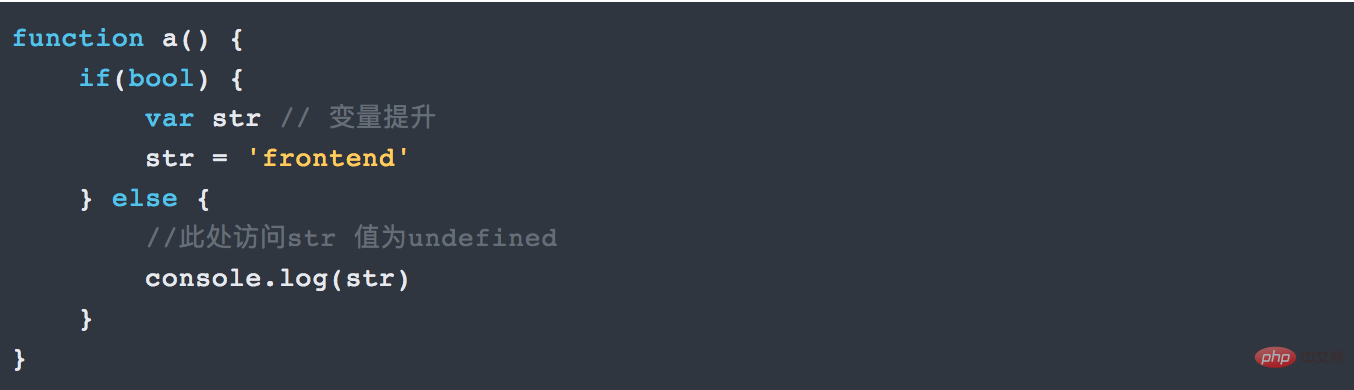
#Don't care whether bool is true or false. In fact, str will be created anyway. (If not declared, null is returned)
After es6, we usually use let and const to declare. let represents variables and const represents constants. Both let and const are block-level scopes. How to understand this block-level scope?
- Inside a function
- Inside a code block
Generally speaking, the code block within {} curly brackets is let and const scope.

let 's scope is in the current code block where it is located, but will not be promoted to the top of the current function.
const Declared variables will be considered constants, which means that their values cannot be modified after they are set.
If const is an object, the value contained in the object can be modified. As long as the address pointed to by the object has not changed.
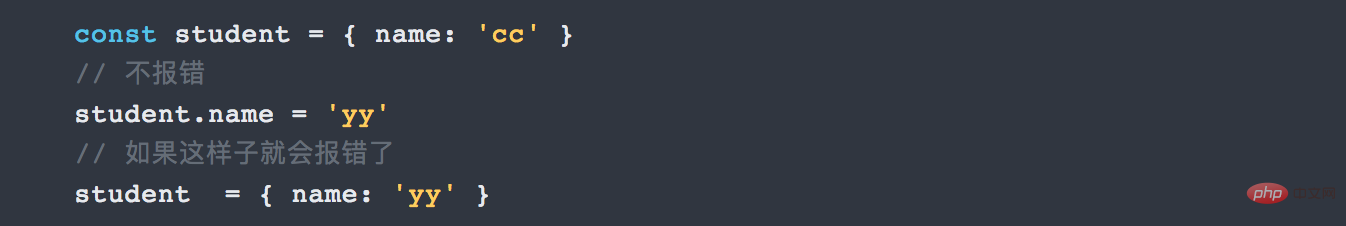
2. Template string
es6 template characters are simply developed Good news for developers, it solves the pain points of es5 in the string function.
2.1 Basic string formatting
Embed expressions into strings for splicing. Use ${} to define.
//ES5
var way = 'String'
console.log('ES5:' + way)
//ES6
let way = 'String Template'
console.log(`ES6: ${way}`)
2.2 Multi-line string concatenation
In ES5, we use backslash() to do more Line string or string concatenation line by line. ES6 backtick (``) does it directly.

2.3 More methods
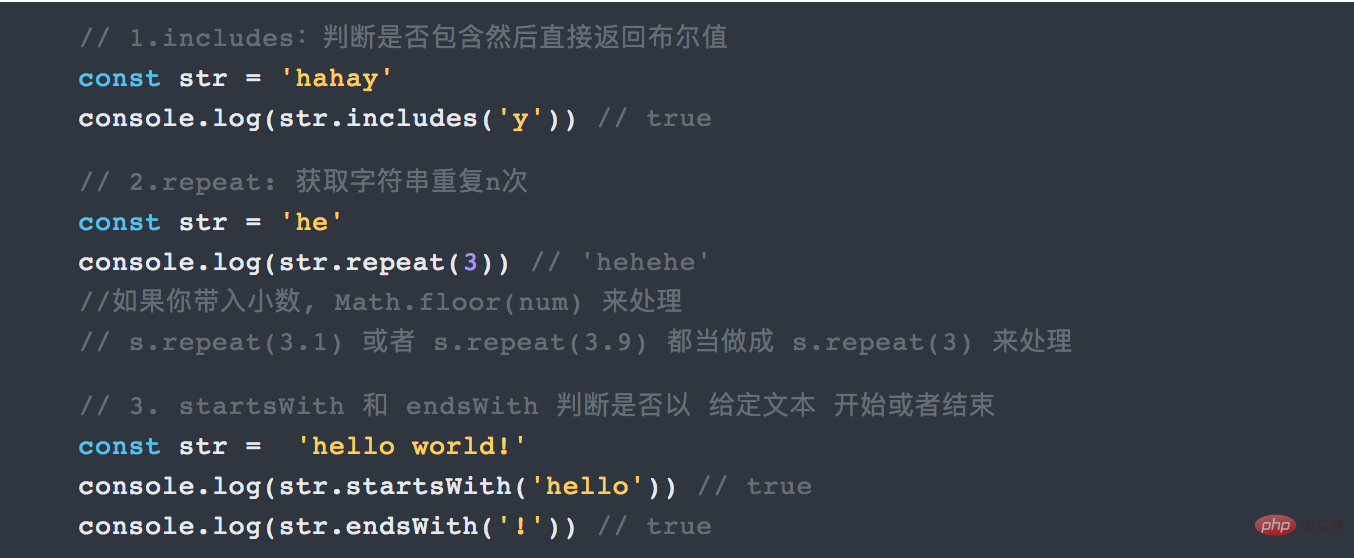
3. New function features
3.1 Function default parameters
In ES5, what are the default values of parameters we define for functions?
function action(num) {
num = num || 200;
//当传入num时,num为传入的值
//当没传入参数时,num即有了默认值200
return num;
}But students who observe carefully will definitely find that when num is passed in as 0, it is false, but our actual need is to get num = 0. At this time, num = 200 is obviously different from our actual situation. The desired effect is obviously different.
ES6 provides default values for parameters. This parameter is initialized when the function is defined so that it can be used when the parameter is not passed in.
function action( num = 200 ){
console.log(num)
}
action(0); //0
action(); //200
action(300) //300
3.2 Arrow function
A very interesting part of ES6 is the shortcut way to write functions. That is the arrow function.
The three most intuitive features of arrow functions:
- No need for the function keyword to create a function
- Omit the return keyword
- Inherit the current The this keyword of the context

# tells a small detail.
When your function has one and only one parameter, you can omit the parentheses. You can omit {} and return when your function returns one and only one expression. For example:
var people = name => 'hello' + name
As a reference:
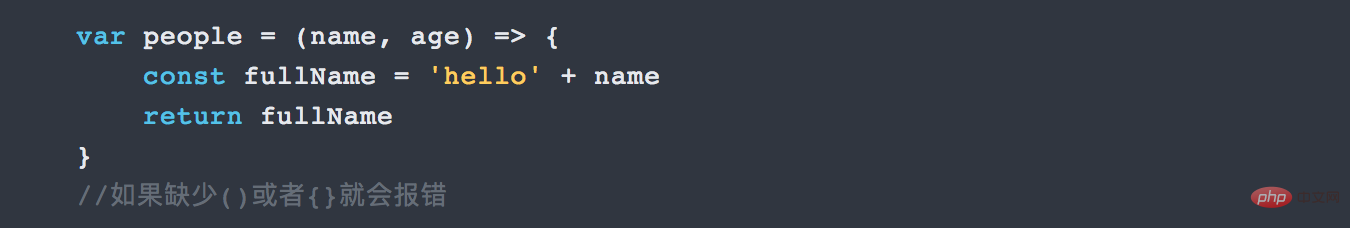
Here is a written test question: Simplify and restructure the following ES5 code into an ES6 method
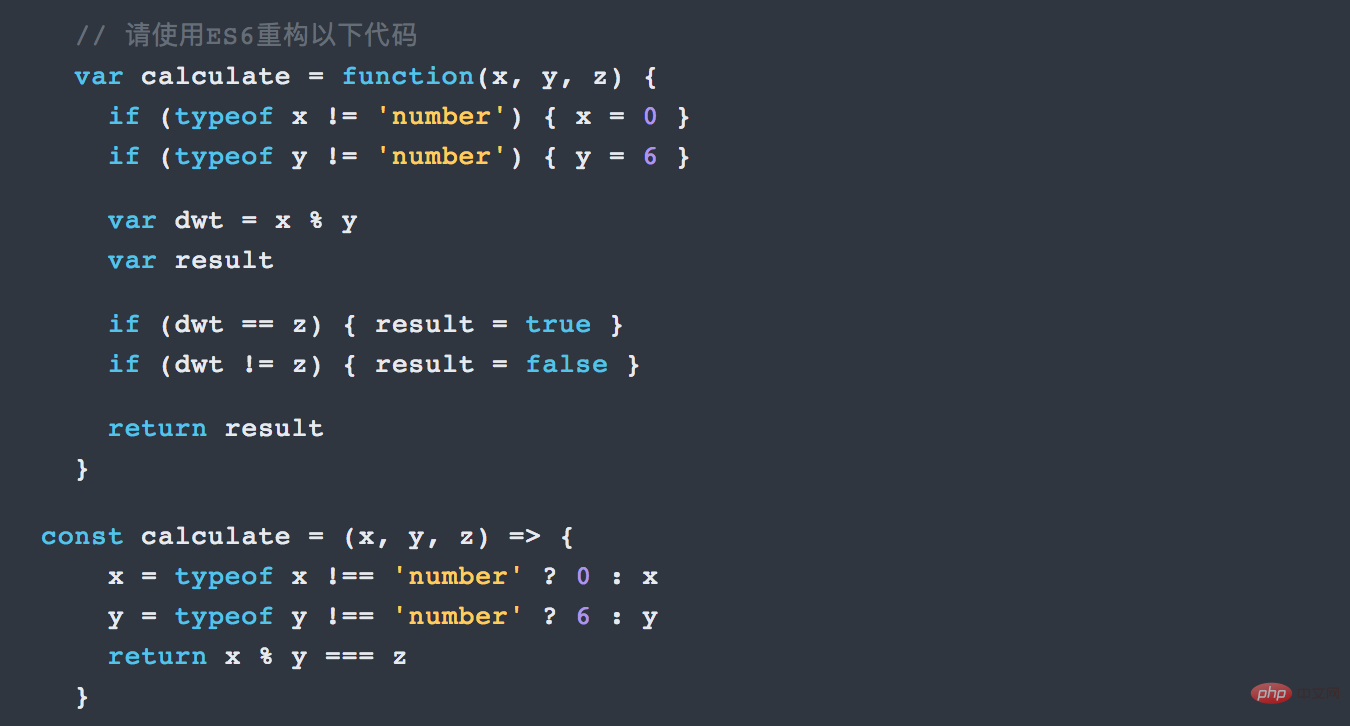
4. Expanded object functions
##4.1 Object initialization abbreviation
ES5 We write objects in the form of key-value pairs, and it is possible for key-value pairs to have duplicate names. For example:

Object.assign() method to implement shallow copying.
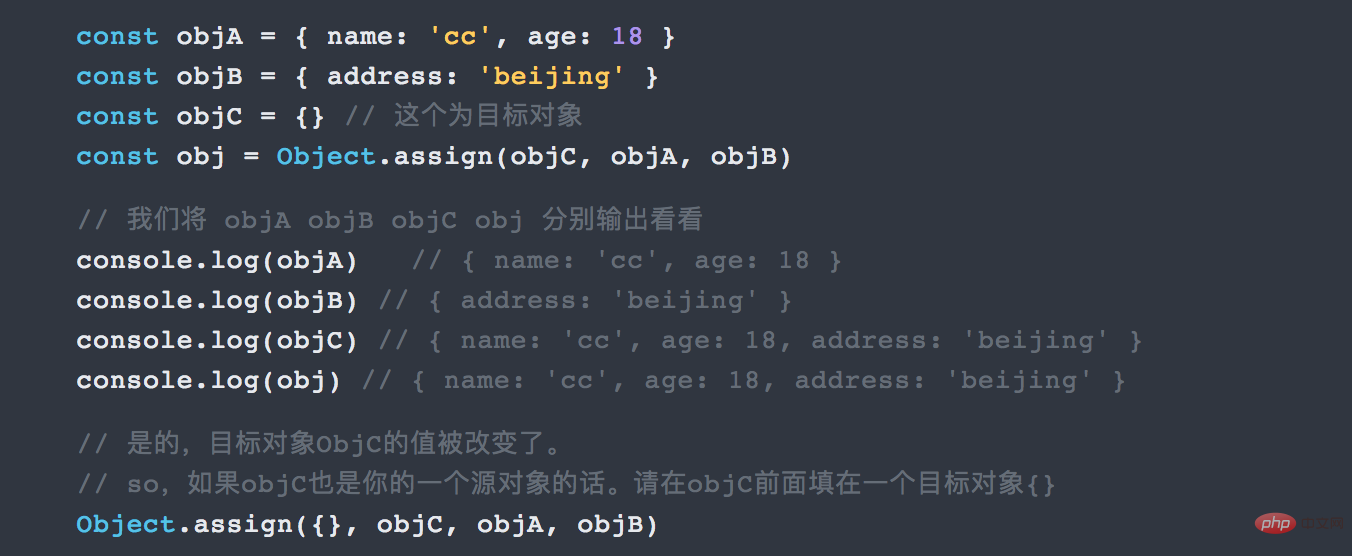
##5. More convenient data access--deconstructing the
array and objects are the most commonly used and important representation forms in JS. To simplify extracting information, ES6 adds destructuring, which is the process of breaking a data structure into smaller parts.
ES5 we extract the information in the object in the following form:
 Does it feel familiar? Yes, this is how we obtained object information before ES6 , obtained one by one. Now, destructuring allows us to retrieve data from an object or array and store it as a variable, for example:
Does it feel familiar? Yes, this is how we obtained object information before ES6 , obtained one by one. Now, destructuring allows us to retrieve data from an object or array and store it as a variable, for example:
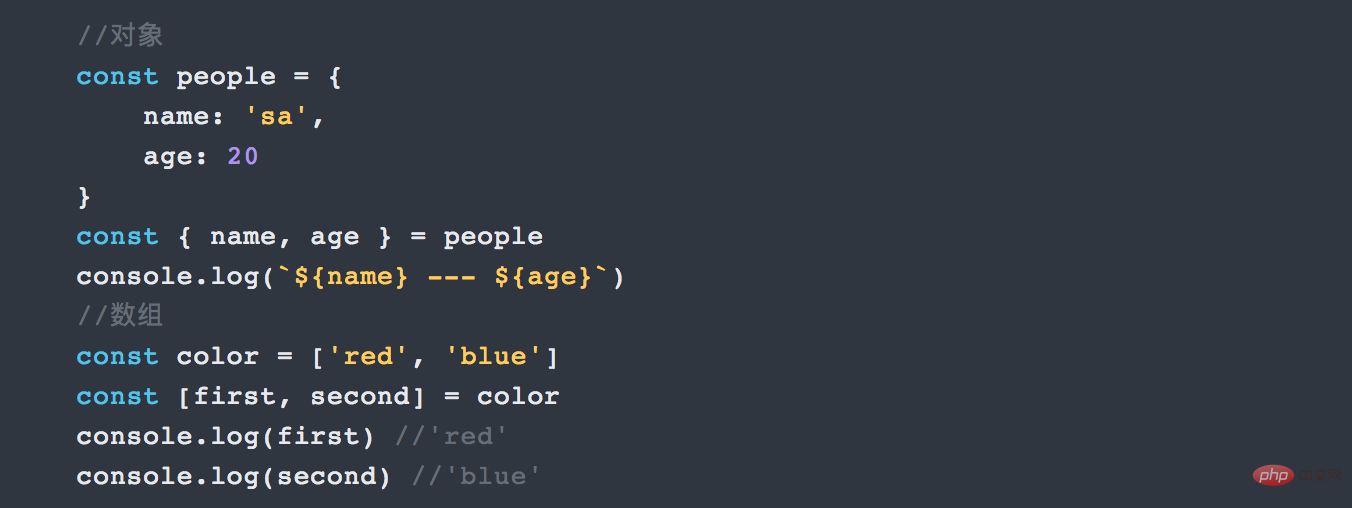 Interview question:
Interview question:
6. Spread Operator Spread operator
Another interesting feature in ES6 is that Spread Operator also has three dots
... Next, we will show its use. Assemble objects or arrays:
 For Object, it can also be used to combine into new Object. (ES2017 stage-2 proposal) Of course, if there are duplicate attribute names, the right side will overwrite the left side.
For Object, it can also be used to combine into new Object. (ES2017 stage-2 proposal) Of course, if there are duplicate attribute names, the right side will overwrite the left side.
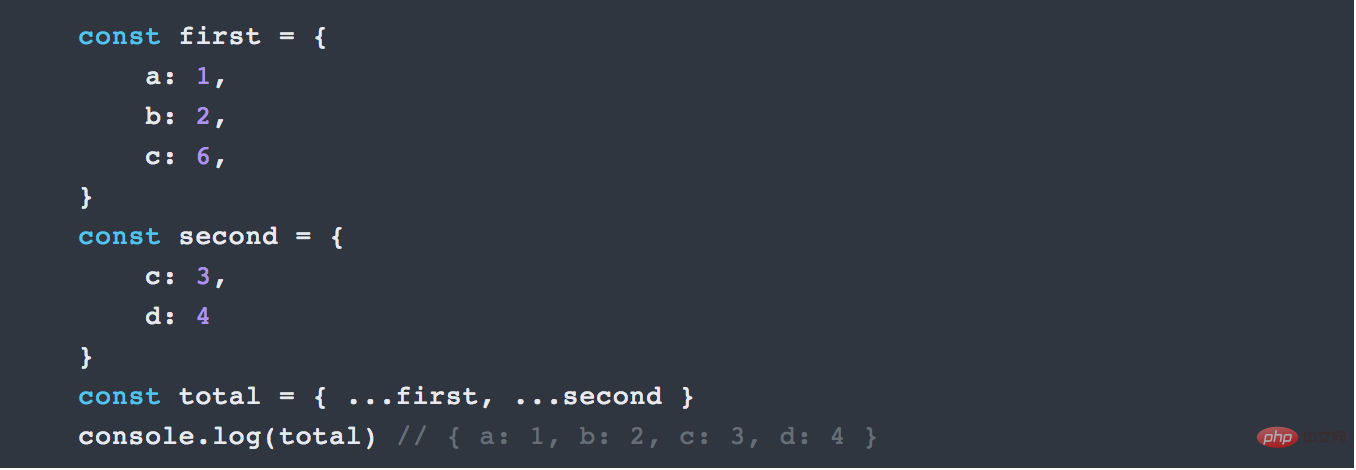
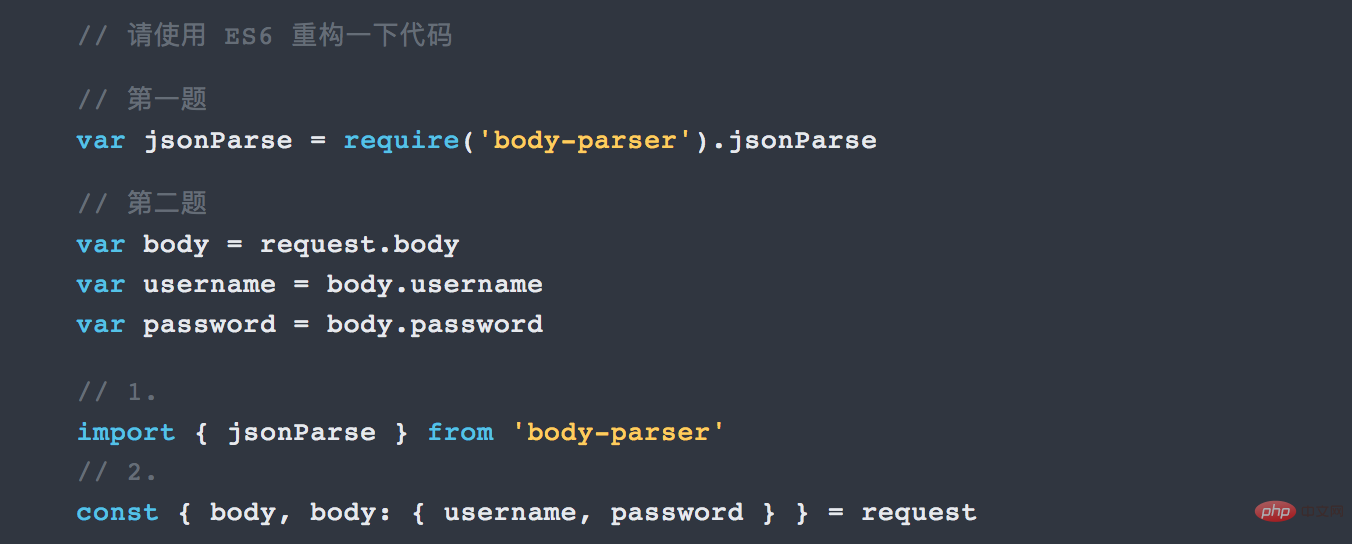
##7. Import and export
7.1 import import module, export export module
What is the difference between importing with or without curly brackets. The following is a summary: 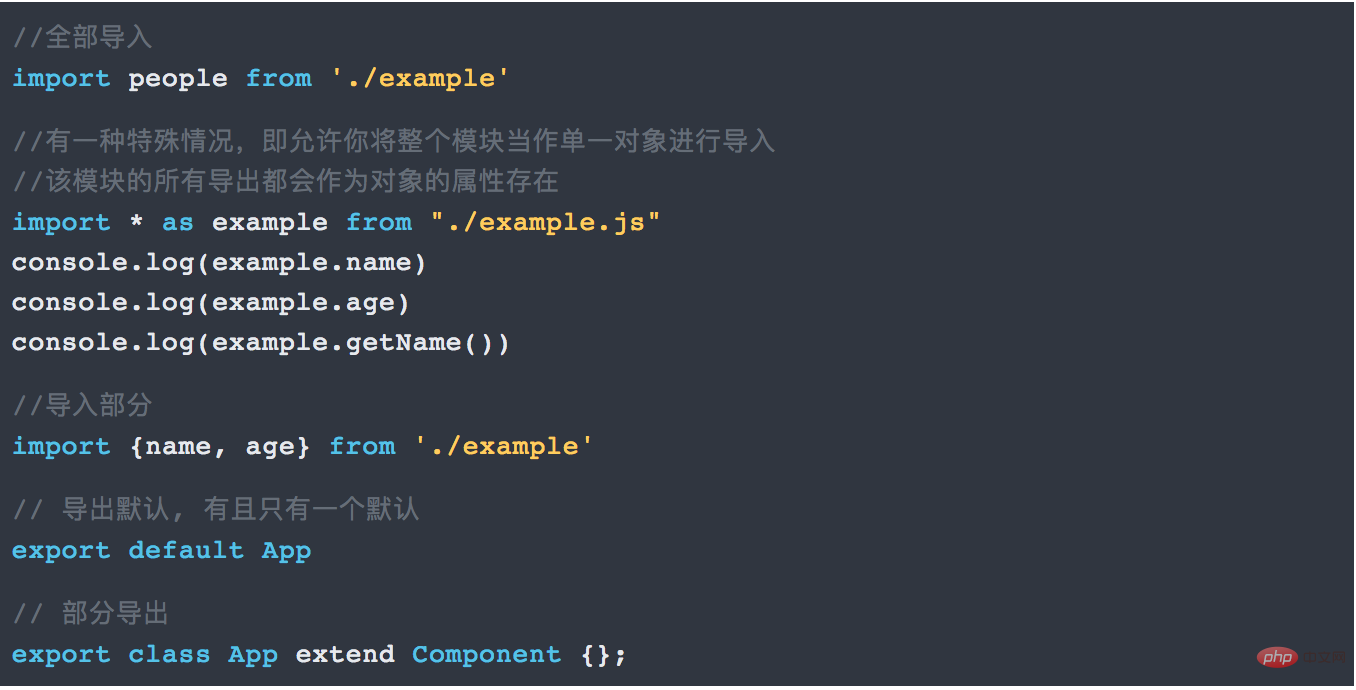
- export default people
- , use
import people
There can be only one export default in a file. But there can be multiple exports.to import (without braces). - When using export name, use import{name}
- to import (remember to bring the curly brackets).
When there is one export default people and multiple export names or export ages in a file, use import people,{name,age} - to import.
When there are n multiple exports in a file to export many modules, in addition to importing one by one, you can also use import * asexample
8. Promise
Too many callbacks or nesting of code before promise, poor readability and coupling High degree and low scalability. Through the Promise mechanism, the flat code structure greatly improves the readability of the code; using synchronous programming to write asynchronous code and preserve the linear code logic greatly reduces the code coupling and improves the scalability of the program. .
To put it bluntly, it is to write asynchronous code in a synchronous way. Initiate an asynchronous request: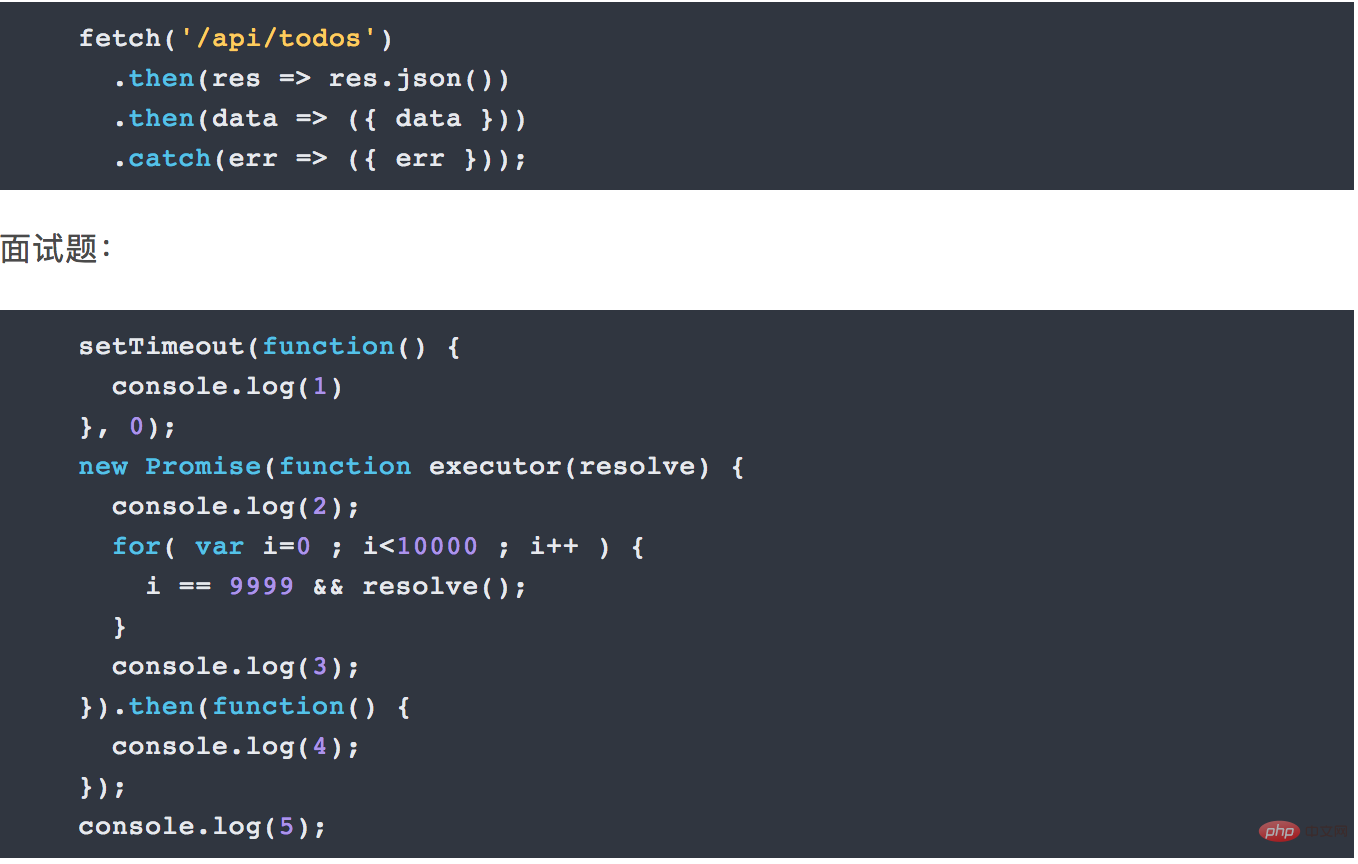
##9. Generators
A generator is a function that returns an iterator. The generator function is also a kind of function. The most intuitive manifestation is that it has one more asterisk * than the ordinary function. The yield keyword can be used in its function body. What is interesting is that the function will pause after each yield. Here is a more vivid example in life. When we go to the bank to handle business, we have to get a queuing number from the machine in the lobby. Once you get your queue number, the machine will not automatically issue the next ticket for you. In other words, the ticket machine is "paused" and will not continue to spit out tickets until the next person wakes it up again.
OK. Let’s talk about iterators. When you call a generator, it returns an iterator object. This iterator object has a method called next to help you restart the generator function and get the next value. The next method not only returns a value, the object it returns has two properties: done and value. value is the value you obtained, and done is used to indicate whether your generator has stopped providing values. Continuing to use the example of just picking up tickets, each queue number is the value here, and whether the paper for printing tickets is used up is the done here.

What are the uses of generators and iterators?
Much of the excitement surrounding generators is directly related to asynchronous programming. Asynchronous calls are very difficult for us. Our function does not wait for the asynchronous call to complete before executing. You may think of using a callback function (of course there are other solutions such as Promise such as Async/await).
The generator allows our code to wait. There is no need for nested callback functions. Using a generator ensures that the execution of the function is paused when the asynchronous call completes before our generator function runs a line of code.
Then the problem is, we can’t manually call the next() method all the time. You need a method that can call the generator and start the iterator. Something like this:

#Perhaps the most interesting and exciting aspect of generators and iterators is the ability to create clean-looking code for asynchronous operations. Instead of using callback functions everywhere, you can create code that looks synchronous but actually uses yield to wait for the asynchronous operation to complete.
10. async function
es6 introduces the async function, making asynchronous operations more convenient.
What is the async function? In a word, it is syntactic sugar for the Generator function.

After comparison, you will find that the async function is to replace the asterisk (*) of the Generator function with async, and replace yield with await, and that's it.
The improvement of the async function to the Generator function is reflected in the following four points:
Built-in executor
Better Semantics
Wider applicability
The return value is Promise
11. Basic Grammar of Class
In JavaScript language, the traditional way to generate instance objects is through the constructor:

es6 provides a writing method that is closer to traditional languages and introduces the concept of Class as a template for objects. Classes can be defined through the class keyword.
Basically, es6's %(red)[class] can be regarded as just a syntactic sugar. Most of its functions can be achieved by es5. The new %(red)[class] writing method is just It just makes the writing of object prototypes clearer and more like the syntax of object-oriented programming. The above code is rewritten using es6's %(red)[class], as follows.

The above code defines a "class". You can see that there is a constructor method in it. This is the constructor method, and the this keyword represents the instance object. In other words, the constructor Point of es5 corresponds to the constructor of the Point class of es6.
In addition to the construction method, the Point class also defines a toString method. Note that when defining a "class" method, you do not need to add the keyword function in front, just put the function definition directly. In addition, there is no need to separate the methods with commas, otherwise an error will be reported.
es6 classes can be regarded as another way of writing constructors.
[Recommended learning: javascript video tutorial]



Built-in executor
Better Semantics
Wider applicability
The return value is Promise


The above is the detailed content of What are the characteristics of front-end development es6. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to reverse an array in ES6
Oct 26, 2022 pm 06:19 PM
How to reverse an array in ES6
Oct 26, 2022 pm 06:19 PM
In ES6, you can use the reverse() method of the array object to achieve array reversal. This method is used to reverse the order of the elements in the array, putting the last element first and the first element last. The syntax "array.reverse()". The reverse() method will modify the original array. If you do not want to modify it, you need to use it with the expansion operator "...", and the syntax is "[...array].reverse()".
 Is async for es6 or es7?
Jan 29, 2023 pm 05:36 PM
Is async for es6 or es7?
Jan 29, 2023 pm 05:36 PM
async is es7. async and await are new additions to ES7 and are solutions for asynchronous operations; async/await can be said to be syntactic sugar for co modules and generator functions, solving js asynchronous code with clearer semantics. As the name suggests, async means "asynchronous". Async is used to declare that a function is asynchronous; there is a strict rule between async and await. Both cannot be separated from each other, and await can only be written in async functions.
 Why does the mini program need to convert es6 to es5?
Nov 21, 2022 pm 06:15 PM
Why does the mini program need to convert es6 to es5?
Nov 21, 2022 pm 06:15 PM
For browser compatibility. As a new specification for JS, ES6 adds a lot of new syntax and API. However, modern browsers do not have high support for the new features of ES6, so ES6 code needs to be converted to ES5 code. In the WeChat web developer tools, babel is used by default to convert the developer's ES6 syntax code into ES5 code that is well supported by all three terminals, helping developers solve development problems caused by different environments; only in the project Just configure and check the "ES6 to ES5" option.
 How to find different items in two arrays in es6
Nov 01, 2022 pm 06:07 PM
How to find different items in two arrays in es6
Nov 01, 2022 pm 06:07 PM
Steps: 1. Convert the two arrays to set types respectively, with the syntax "newA=new Set(a);newB=new Set(b);"; 2. Use has() and filter() to find the difference set, with the syntax " new Set([...newA].filter(x =>!newB.has(x)))", the difference set elements will be included in a set collection and returned; 3. Use Array.from to convert the set into an array Type, syntax "Array.from(collection)".
 How to implement array deduplication in es5 and es6
Jan 16, 2023 pm 05:09 PM
How to implement array deduplication in es5 and es6
Jan 16, 2023 pm 05:09 PM
In es5, you can use the for statement and indexOf() function to achieve array deduplication. The syntax "for(i=0;i<array length;i++){a=newArr.indexOf(arr[i]);if(a== -1){...}}". In es6, you can use the spread operator, Array.from() and Set to remove duplication; you need to first convert the array into a Set object to remove duplication, and then use the spread operator or the Array.from() function to convert the Set object back to an array. Just group.
 What does es6 temporary Zenless Zone Zero mean?
Jan 03, 2023 pm 03:56 PM
What does es6 temporary Zenless Zone Zero mean?
Jan 03, 2023 pm 03:56 PM
In es6, the temporary dead zone is a syntax error, which refers to the let and const commands that make the block form a closed scope. Within a code block, before a variable is declared using the let/const command, the variable is unavailable and belongs to the variable's "dead zone" before the variable is declared; this is syntactically called a "temporary dead zone". ES6 stipulates that variable promotion does not occur in temporary dead zones and let and const statements, mainly to reduce runtime errors and prevent the variable from being used before it is declared, resulting in unexpected behavior.
 Is require an es6 syntax?
Oct 21, 2022 pm 04:09 PM
Is require an es6 syntax?
Oct 21, 2022 pm 04:09 PM
No, require is the modular syntax of the CommonJS specification; and the modular syntax of the es6 specification is import. require is loaded at runtime, and import is loaded at compile time; require can be written anywhere in the code, import can only be written at the top of the file and cannot be used in conditional statements or function scopes; module attributes are introduced only when require is run. Therefore, the performance is relatively low. The properties of the module introduced during import compilation have slightly higher performance.
 How to determine how many items there are in an array in es6
Jan 18, 2023 pm 07:22 PM
How to determine how many items there are in an array in es6
Jan 18, 2023 pm 07:22 PM
In ES6, you can use the length attribute of the array object to determine how many items there are in the array, that is, to get the number of elements in the array; this attribute can return the number of elements in the array, just use the "array.length" statement. Returns a value representing the number of elements of the array object, that is, the length value.






