 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 JS Tutorial
JS Tutorial
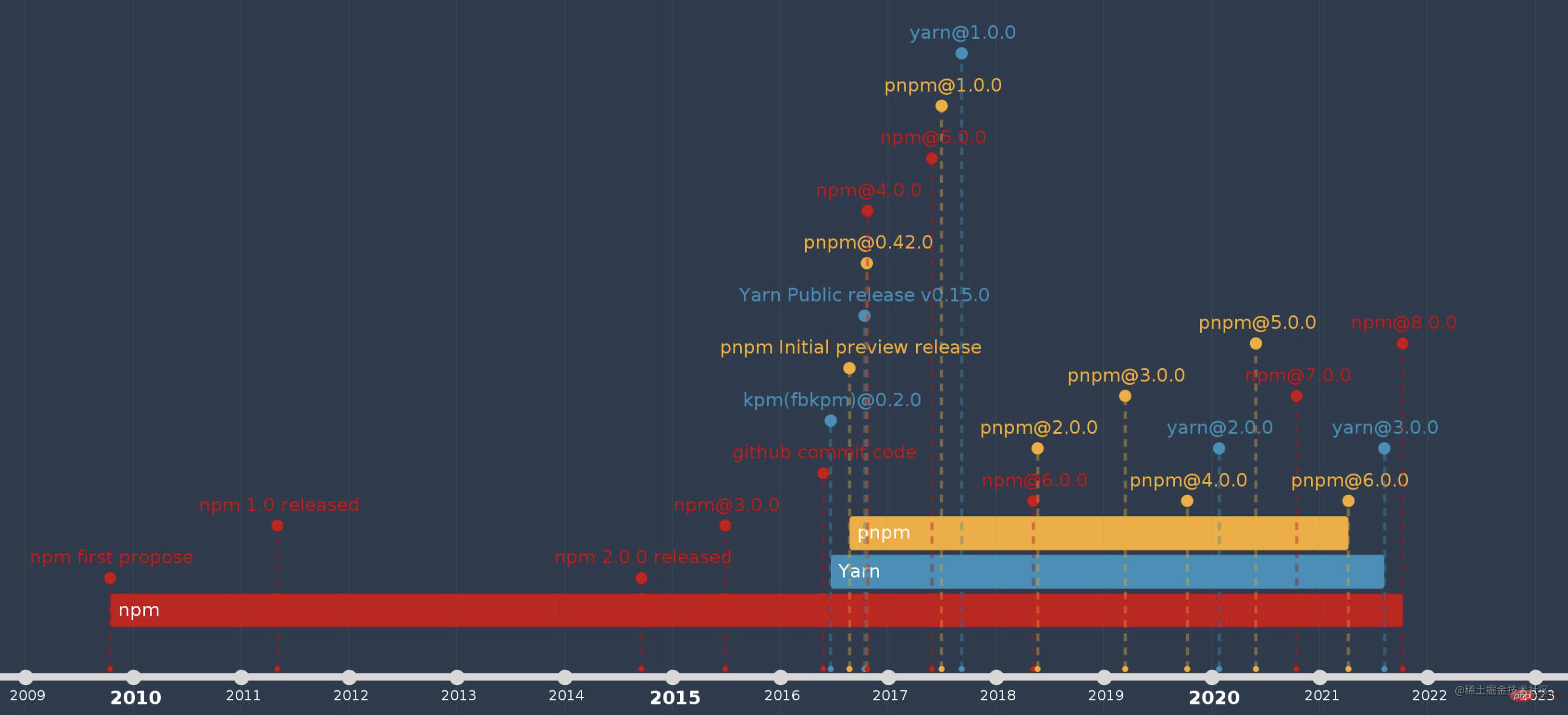
 An article to talk about the five stages of Node package management development
An article to talk about the five stages of Node package management development
An article to talk about the five stages of Node package management development
Since the birth of Node in 2009, the Node ecosystem has developed and prospered. Node package managers derived from the Node ecosystem have flourished, and npm, kpm, pnpm, yarn, cnpm, etc. have appeared successively. In fact, the development of the Node package manager is mainly divided into 5 stages. Let's take a look at the key features and representative products of each stage~
Phase One: Slash and Burn
To be precise, Node did not exist without a package manager. In 2009, when Node.js came out, the prototype of npm was also released. . [Related tutorial recommendations: nodejs video tutorial, Programming teaching]
npm’s full name is Node.js Package Manager; from A brief history of Node.js You can see it inside
2009 Node.js is born The first form of npm is created
Let’s talk about what it was like when the Node package manager didn’t appear. What I did more at that time was
Looking online The official website of each software, such as jQuery;
Find the download address and download the zip package;
Unzip it and put it in a project called libs directory;
If you want to make it more convenient, paste the CDN link directly into the HTML
Modular management at that time? Version number management? Depend on upgrade? None of them exist!
Phase 2: Nested installation
In 2009, Node.js was born, and the prototype of npm was also brewing. Version 1.0 was released in 2011; npm is built around Semantic version control is designed with the idea of semver. By default, Node package developers will upgrade the version number according to semver specifications when upgrading the custom version number of dependent packages.
Pronoun: Node package management standardization, node_modules directory nested storage dependencies
Representative products: npm v1, v2 version
Key features:
(1) Nested installation of dependent packages, dependencies of the same version will be installed redundantly
(2) Uncertainty of dependent package installation: The latest version of the dependency package is installed by default (a fixed version can be set)
(3) Serial installation of dependencies is slow; offline caching is not supported
Explanation 1: Dependencies Nested installation , if A depends on B and B depends on C, the node_modules directory is as follows
node_modules - package-A -- node_modules --- package-B ----- node_modules ------ package-C -------- some-really-really-really-long-file-name-in-package-c.js
Problem: Too many dependencies will be nested. This causes nesting hell. At the same time, there will be a large number of redundant installations of the same dependent packages, causing node_modules to be too large, requiring programmers to regularly rm -rf node_modules. However, in Windows systems, many programs cannot handle file paths exceeding 260 characters. Name, early Windows users of npm have seen this pop-up window

##Explanation 2: For each npm install, the latest version of dependencies is installed by default, causing Dependency installation Uncertainty Problem:
semver standardizes the version number composition: X.Y.Z-[state], the version number upgrade specifications are as follows
- API, but backward compatible, the upgrade minor version number
- Z is the patch version number: When backward compatible defect fixes are made,
- state can be: alpha (internal testing), beta (Public beta), gamma (quite mature beta), rc (pre-release)
- Uncertain version reason
Solution 1: You can use the npm config set save-exact true command to turn off the use of ^ in front of the version number. Default behavior
- Summary: Unable to solve the problem of the dependent library's own dependencies installing the latest version by default
- npm-shrinkwrap.json
- file to record accurate versions for all libraries and all nested dependent libraries
Summary: lock files will not be generated by default. The user is required to execute the instruction manually; it depends on the user knowing this instruction, which is relatively cumbersome - Phase 3: Flat installation
In 2015, in order to solve The problems of nested installation and non-specified versions of npm1 and npm2 have been completely rewritten. The npm program has been completely rewritten.
#Represents the product:npm v3 version
Brief description of the principle: When npm install, first build the dependency tree and then install all dependencies in the node_modules root directory. When sub-dependencies encounter different versions of dependencies with the same name, they will be installed in Under your own node_modules
Key features:
(1) Reduce redundant installation: rely on flat installation, which reduces the installation of redundant packages under certain circumstances
Existing problems:
(1) "Ghost dependency", "Phantom dependency" Problem
(2) "Twin strangers", "Dependency package" "Clone" problem
(3) The directory is not fixed: the installation order of dependencies determines the node_module directory structure
Explanation 1: The installation order of dependencies determines the node_modules directory structure
The following scenario: App1 depends on packageA and packageC and packageG and packageH, and packageA and packageC both depend on packageB v1.0, and packageG and packageH both depend on packageB's v2.0 version
If you install packageA or packageC first, the node_modules directory is as follows

If you install packageG or packageH first, the node_modules directory is as follows

In response to the above situation, npm provides the command npm dedupe, which can manually organize & simplify the directory structure of node_modules. The organized directory structure of node_modules is consistent and is not affected by the installation order of dependent packages.
Explanation 2: It may not necessarily reduce the installation of redundant packages
Through Example 1, it can be seen that although dependent packages are installed flat, the same version still exists Dependent packages, there are redundant packages
Explanation 3: "Twin Strangers" Problem
Refer to example 1, the same version of dependent packages is installed twice, is placed in two places, this phenomenon is called "twin strangers"
Explanation 4: "Ghost dependency" Problem
node_modules Dependencies in the first-level directory Packages can be used directly by developers, but the dependency packages are not defined in package.json. Such dependency packages are called "ghost dependencies". If "ghost dependencies" are used in front-end projects, problems may occur later.
Because this "ghost dependency" may be removed later along with the upgrade of other dependencies, it will no longer exist in node_modules. When executing npm install, the "ghost dependency" will not be installed subjectively. As a result, the project cannot find dependent packages and then reports an error.
Phase 4: Security, Speed Up
In 2016, yarn and pnpm release versions appeared one after another, which to a certain extent solved the uncertainty of the previous installation version and the installation speed. Compared with npm, yarn's first capabilities are more eye-catching, ensuring consistency & security, and improving installation speed
Synonyms: Dependent installation is relatively safe, Speed up
Representative products: yarn release version, pnpm release version, npm v5 version (npm v4 has not changed much, v5 has taken a big step forward)
Key features:
(1) Security: The version lock file is generated by default, ensuring that the dependent version is the same every time you install it
(2) Speed up: Added offline cache Installation, parallel installation, automatic retry after installation exception
(3) workspace: yarn is supported from v1 version, and can efficiently manage the dependency packages of multiple projects; npm v7 only supports workspace
Existing problems:
(1)Ghost dependency
(2)Repeated installation of single-project and repeated installation of dependency packages across projects
(3) The directory is not fixed: the installation order of dependencies determines the node_module directory structure
Explanation 1: About security
yarn v0.x version takes the lead, npm v5.x version follows Subsequently, when downloading dependencies, a dependency lock file is generated by default, which accurately locks the version at a value of
- yarn's .lock file: it only records the installed dependency version and needs to be combined with package.json Determine the node_modules directory structure
- npm's .lock file: records the installed dependency version and the node_modules directory structure
Summary: Avoids the need to install dependencies on different terminals Version inconsistency problem, but the "ghost dependency" problem still exists
Explanation 2: About speed improvement - offline caching
npm v2 version supports caching, but requires online detection , to use cached dependencies
yarn v0.x version is the first to support offline caching. Packages downloaded from the network will be cached globally. The next installation will give priority to searching locally and copy directly if found
npm v5 version rewrites the cache system and also supports offline installation, greatly improving the installation speed
Explanation 3: About speed-up - parallel installation
yarn was the first to support dependencies Packages are installed in parallel. Previously, npm installed dependencies serially. Later, npm also optimized parallel installation
Explanation 4: After installing dependencies, the node_modules directory is automatically organized
Start time :yarn v1.x version, npm v4.x version
- If the
.lockfile is deleted from the project, the node_modules directory will be automatically sorted out when the dependencies are initially installed; for versions prior to npm v4.x, the user needs to manually execute the instructionsnpm dedupeOrganize the dependency directory - Since node_modules is a flat management dependency, deep dependencies may be installed in the first-level directory; when installing different versions of dependencies in the project, if a dependency version conflict is encountered, it will automatically Move deep dependencies from the first-level directory to the parent dependency directory[Verified]
Phase 5: More secure, high-speed, low-cost
Facing the maturity of pnpm, developers are enjoying the dividends brought by pnpm such as safer, higher speed, and lower storage consumption, solving the problem of "ghost dependency" and solving the problem of repeated dependency
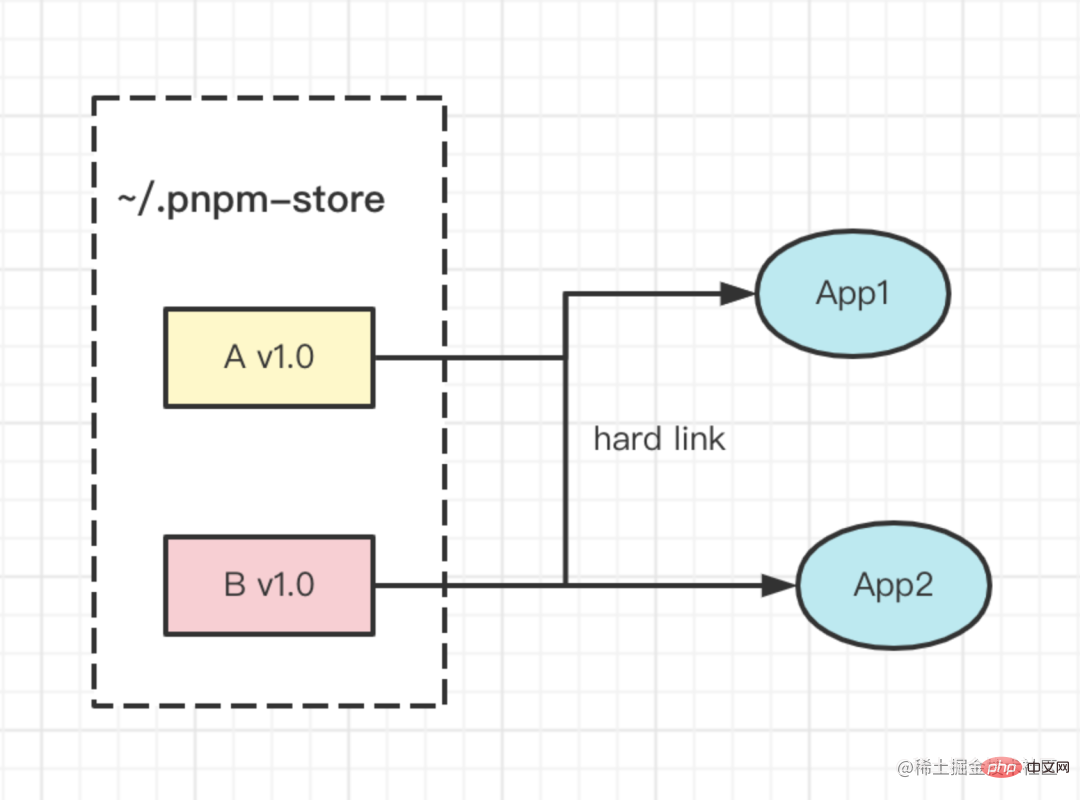
Pronoun: Safe (depending on installation WYSIWYG), high speed (no repeated installation), low storage consumption (hard link and soft link)
Representative product: pnpm
Key features:
(1) Extremely fast: The storage center centrally manages dependencies and directly hard links to the project node_modules/.pnpm. Compared with the previous working method, a large number of IO operations from global node_modules copy to the project are reduced
(2) The disk utilization is extremely high:
- Share dependencies of the same version across projects: hard links, soft links
- Maximize reuse of different versions of the same dependency: only add Diff files that store different versions
(3 ) High security: The node_modules directory structure is the package.json dependency list, which solves the "ghost dependency" problem
The performance is as follows:

For more node-related knowledge, please visit: nodejs tutorial!
The above is the detailed content of An article to talk about the five stages of Node package management development. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to delete node in nvm
Dec 29, 2022 am 10:07 AM
How to delete node in nvm
Dec 29, 2022 am 10:07 AM
How to delete node with nvm: 1. Download "nvm-setup.zip" and install it on the C drive; 2. Configure environment variables and check the version number through the "nvm -v" command; 3. Use the "nvm install" command Install node; 4. Delete the installed node through the "nvm uninstall" command.
 How to use express to handle file upload in node project
Mar 28, 2023 pm 07:28 PM
How to use express to handle file upload in node project
Mar 28, 2023 pm 07:28 PM
How to handle file upload? The following article will introduce to you how to use express to handle file uploads in the node project. I hope it will be helpful to you!
 An in-depth analysis of Node's process management tool 'pm2”
Apr 03, 2023 pm 06:02 PM
An in-depth analysis of Node's process management tool 'pm2”
Apr 03, 2023 pm 06:02 PM
This article will share with you Node's process management tool "pm2", and talk about why pm2 is needed, how to install and use pm2, I hope it will be helpful to everyone!
 Pi Node Teaching: What is a Pi Node? How to install and set up Pi Node?
Mar 05, 2025 pm 05:57 PM
Pi Node Teaching: What is a Pi Node? How to install and set up Pi Node?
Mar 05, 2025 pm 05:57 PM
Detailed explanation and installation guide for PiNetwork nodes This article will introduce the PiNetwork ecosystem in detail - Pi nodes, a key role in the PiNetwork ecosystem, and provide complete steps for installation and configuration. After the launch of the PiNetwork blockchain test network, Pi nodes have become an important part of many pioneers actively participating in the testing, preparing for the upcoming main network release. If you don’t know PiNetwork yet, please refer to what is Picoin? What is the price for listing? Pi usage, mining and security analysis. What is PiNetwork? The PiNetwork project started in 2019 and owns its exclusive cryptocurrency Pi Coin. The project aims to create a one that everyone can participate
 Let's talk about how to use pkg to package Node.js projects into executable files.
Dec 02, 2022 pm 09:06 PM
Let's talk about how to use pkg to package Node.js projects into executable files.
Dec 02, 2022 pm 09:06 PM
How to package nodejs executable file with pkg? The following article will introduce to you how to use pkg to package a Node project into an executable file. I hope it will be helpful to you!
 What to do if npm node gyp fails
Dec 29, 2022 pm 02:42 PM
What to do if npm node gyp fails
Dec 29, 2022 pm 02:42 PM
npm node gyp fails because "node-gyp.js" does not match the version of "Node.js". The solution is: 1. Clear the node cache through "npm cache clean -f"; 2. Through "npm install -g n" Install the n module; 3. Install the "node v12.21.0" version through the "n v12.21.0" command.
 Token-based authentication with Angular and Node
Sep 01, 2023 pm 02:01 PM
Token-based authentication with Angular and Node
Sep 01, 2023 pm 02:01 PM
Authentication is one of the most important parts of any web application. This tutorial discusses token-based authentication systems and how they differ from traditional login systems. By the end of this tutorial, you will see a fully working demo written in Angular and Node.js. Traditional Authentication Systems Before moving on to token-based authentication systems, let’s take a look at traditional authentication systems. The user provides their username and password in the login form and clicks Login. After making the request, authenticate the user on the backend by querying the database. If the request is valid, a session is created using the user information obtained from the database, and the session information is returned in the response header so that the session ID is stored in the browser. Provides access to applications subject to
 What is a single sign-on system? How to implement it using nodejs?
Feb 24, 2023 pm 07:33 PM
What is a single sign-on system? How to implement it using nodejs?
Feb 24, 2023 pm 07:33 PM
What is a single sign-on system? How to implement it using nodejs? The following article will introduce to you how to use node to implement a single sign-on system. I hope it will be helpful to you!





