
想象一下一个拥有 100 多个路由的 Laravel 项目,其中包括访客,用户,管理员等分离的模块。你真的要将所有内容写在一个文件中吗?那么如何将它们分组,并且为 URL 添加前缀呢?看看有哪些办法。
这个简单,因为 Laravel 已经帮你做了。有如下两个文件:
因此,如果你的项目同时具有前端页面和 API (使用场景越来越广),请把 API 的路由放在 api.php 里。【相关推荐:laravel视频教程】
例如,如果你有 /users 页面,又有 /api/users/ 端点,把他们分别写在自己属于自己路由文件里,以免在同一文件中出现同一相同名称而产生混淆。
但我最近还是从 官方 Laravel 项目中看到了反例。在 Laravel Horizon 中,Taylor 只有 API 路由,但他没有分开写,还是写在了 routes/web.php :
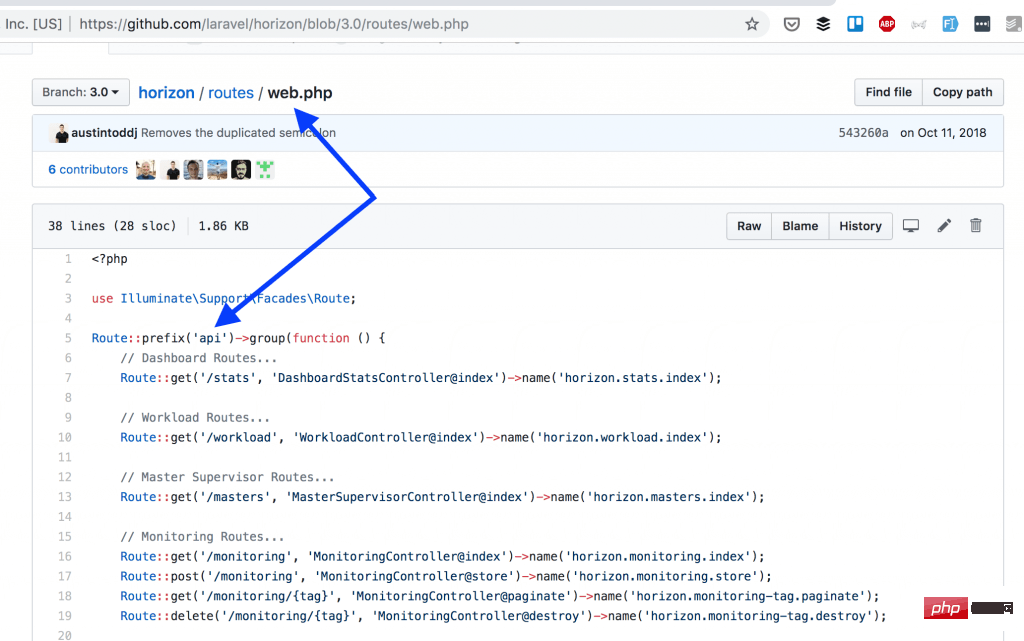
另一个例子证明 Laravel 还是非常的个人化,甚至 Taylor 自己也没有 100% 按照标准来。
下面例子也是来自 Laravel 官方文档 的示例:
Route::middleware(['first', 'second'])->group(function () {
Route::get('/', function () {
// 使用 first 和 second 中间件
});
Route::get('user/profile', function () {
// 使用 first 和 second 中间件
});
});最基本的用法是将不同的路由分组包含在不同的中间件里面。例如,你希望一个组默认受 auth 中间件限制,另一组受单独的 admin 自定义中间件限制等。
这样,你还可以使用 名称 和 前缀 等路由分组方法。同样,官方文档中给出了示例:
Route::prefix('admin')->group(function () {
Route::get('users', function () {
// 匹配 URL 「/admin/users」
});
});
Route::name('admin.')->group(function () {
Route::get('users', function () {
// 路由名为 「admin.users」...
})->name('users');
});另外,如果您要将所有中间件 + 名称 + 前缀添加到一个组中,则将它们放入数组中更容易理解:
// 而不是这样做:
Route::name('admin.')->prefix('admin')->middleware('admin')->group(function () {
// ...
});
// 可以使用数组
Route::group([
'name' => 'admin.',
'prefix' => 'admin',
'middleware' => 'auth'
], function () {
// ...
});我们将其结合为一个拥有三个路由分组的真实示例:
以下是将所有内容分组到 routes / web.php 文件中的一种方法:
Route::group([
'name' => 'admin.',
'prefix' => 'admin',
'middleware' => 'admin'
], function () {
// URL链接:/admin/users
// 路由名称:admin.users
Route::get('users', function () {
return 'Admin: user list';
})->name('users');
});
Route::group([
'name' => 'user.',
'prefix' => 'user',
'middleware' => 'auth'
], function () {
// URL链接:/user/profile
// 路由名称:user.profile
Route::get('profile', function () {
return 'User profile';
})->name('profile');
});
Route::group([
'name' => 'front.',
'prefix' => 'front'
], function () {
// 这里没有中间件
// URL链接:/front/about-us
// 路由名称:front.about
Route::get('about-us', function () {
return 'About us page';
})->name('about');
});在上面的例子中,我们没有使用控制器,只是返回了静态文本作为示例。 让我们添加一个控制器,来点小花样 — 我们会将它们构造到各自不同的命名空间的文件夹中,如下所示:
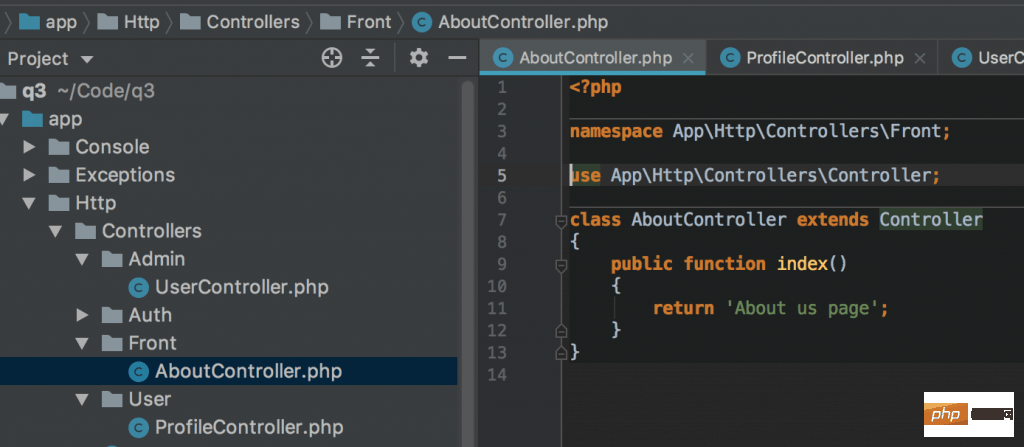
然后我们可以在路由文件中使用它们:
Route::group([
'name' => 'front.',
'prefix' => 'front'
], function () {
Route::get('about-us', 'Front.boutController@index')->name('about');
});但是如果在这个组中我们有很多控制器呢? 我们应该一直添加Front.omeController 吗? 当然不是。您也可以将命名空间作为参数之一。
Route::group([
'name' => 'front.',
'prefix' => 'front',
'namespace' => 'Front',
], function () {
Route::get('about-us', 'AboutController@index')->name('about');
Route::get('contact', 'ContactController@index')->name('contact');
});上面的情况,分为了3个组,实际上这是被简化的, 实际项目的结构稍有不同 – 是 两 个组:front 和 auth 。 然后在 auth 中,有两个子组:user 和 admin 。为此, 我们可以在 routes/web.php中创建子组,并分配不同的中间件/前缀等。
Route::group([
'middleware' => 'auth',
], function() {
Route::group([
'name' => 'admin.',
'prefix' => 'admin',
'middleware' => 'admin'
], function () {
// URL: /admin/users
// Route name: admin.users
Route::get('users', 'UserController@index')->name('users');
});
Route::group([
'name' => 'user.',
'prefix' => 'user',
], function () {
// URL: /user/profile
// Route name: user.profile
Route::get('profile', 'ProfileController@index')->name('profile');
});
});我们甚至可以多层嵌套,这是开源项目的一个示例。 Akaunting:
Route::group(['middleware' => 'language'], function () {
Route::group(['middleware' => 'auth'], function () {
Route::group(['prefix' => 'uploads'], function () {
Route::get('{id}', 'Common.ploads@get');
Route::get('{id}/show', 'Common.ploads@show');
Route::get('{id}/download', 'Common.ploads@download');
});
Route::group(['middleware' => 'permission:read-admin-panel'], function () {
Route::group(['prefix' => 'wizard'], function () {
Route::get('/', 'Wizard.ompanies@edit')->name('wizard.index');
// ...另一个例子来自另一个流行的Laravel CRM,名为Monica:
Route::middleware(['auth', 'verified', 'mfa'])->group(function () {
Route::name('dashboard.')->group(function () {
Route::get('/dashboard', 'DashboardController@index')->name('index');
Route::get('/dashboard/calls', 'DashboardController@calls');
Route::get('/dashboard/notes', 'DashboardController@notes');
Route::get('/dashboard/debts', 'DashboardController@debts');
Route::get('/dashboard/tasks', 'DashboardController@tasks');
Route::post('/dashboard/setTab', 'DashboardController@setTab');
});有一个服务于所有路由设置的文件 – app/Providers/RouteServiceProvider.php. 它具有绑定两个路由文件 – web 和 API 的 map() 方法:
public function map()
{
$this->mapApiRoutes();
$this->mapWebRoutes();
}
protected function mapWebRoutes()
{
Route::middleware('web')
->namespace($this->namespace)
->group(base_path('routes/web.php'));
}
protected function mapApiRoutes()
{
Route::prefix('api')
->middleware('api')
->namespace($this->namespace)
->group(base_path('routes/api.php'));
}您是否注意到方法中提及的 middleware, namespace 和 prefix ? 这是您可以为整个文件设置全局配置的地方,因此不必为文件中的每个路由组重复这些设置。
它主要用于 API 路由,因为它们的设置通常是相同的,如下所示:
protected function mapApiRoutes(){
Route::group([
'middleware' => ['api'],
'namespace' => $this->namespace,
'prefix' => 'api/v1',
], function ($router) {
require base_path('routes/api.php');
});}上述方法将在所有 API URLs 的开头加上 api/v1/ 前缀。
如果您有大量的路由,并且希望将它们分组到单独的文件中,那么您可以使用上一节中提到的相同文件 – app/Providers/RouteServiceProvider.php。如果您仔细查看它的 map() 方法,您将在末尾看到注释位置:
public function map(){
$this->mapApiRoutes();
$this->mapWebRoutes();
//}如果愿意,您可以将其解释为添加更多文件的“邀请”。因此,您可以在此文件内创建另一个方法,例如 mapAdminRoutes(),然后将其添加到 map() 方法, 您的文件将被自动注册并加载。
但是,就我个人而言,我看不出这种方法有什么优势,而且我也没有经常看到这种做法。它会带来更多的路由分离,但有时您会迷失在那些文件中,不确定在哪里查找特定的路由。
说到更大的路由并迷失在那里,我们有一个 Artisan 命令可以帮助定位某个路由。
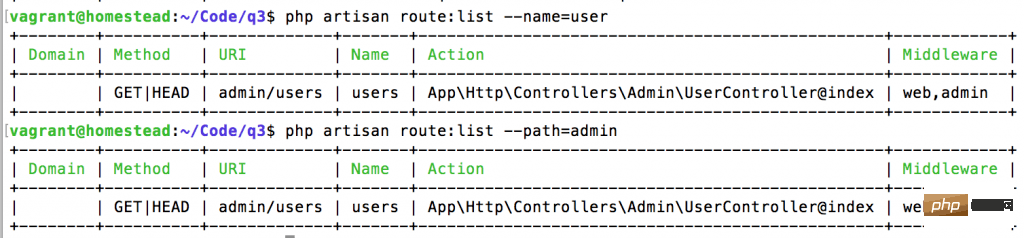
您可能知道 php artisan route:list 将展示项目中的所有路由
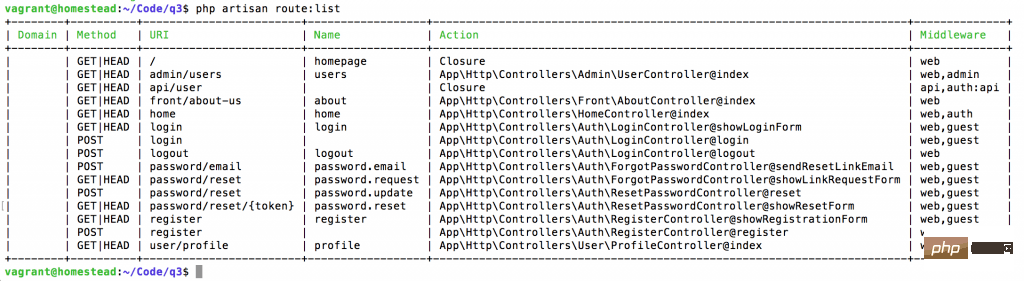
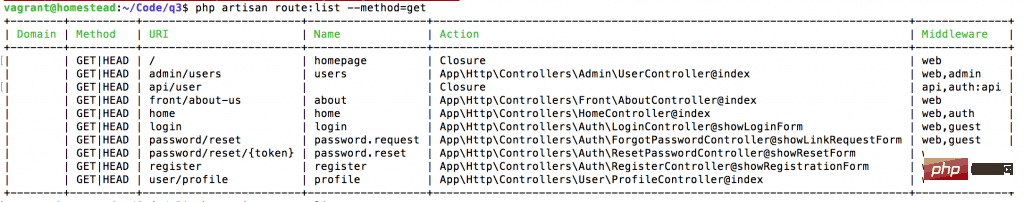
但您知道还有更多的过滤功能来找到您想要的东西吗? 只需添加带参数的 –method, 或 –name, 或 –path 。
通过 method 过滤 – GET, POST 等:
按名称或 URL 部分过滤:
这就是我所能告诉的关于在大型项目中分组路由的全部内容。你还有其他例子吗?请在评论中分享。
原文地址:https://laraveldaily.com/how-to-structure-routes-in-large-laravel-projects/译文地址:https://learnku.com/laravel/t/38917
更多编程相关知识,请访问:编程视频!!
以上就是聊聊怎么在大型Laravel项目中组织路由的详细内容,更多请关注php中文网其它相关文章!

Copyright 2014-2025 https://www.php.cn/ All Rights Reserved | php.cn | 湘ICP备2023035733号