MySQL stored procedure advanced SQL statement summary
This article brings you relevant knowledge about mysql, which mainly introduces the relevant content about advanced SQL statements of stored procedures. Let’s take a look at it together. I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

Recommended learning: mysql video tutorial
MySQL advanced SQL statements (stored procedures)
1. Overview of stored procedures
1.1 What is a stored procedure
A stored procedure is a set of SQL statements designed to accomplish a specific function.
During the use of stored procedures, commonly used or complex tasks are written in advance using SQL statements and stored with a specified name. This process is compiled and optimized and stored in the database server. When you need to use this stored procedure, you just need to call it. Stored procedures are faster and more efficient in execution than traditional SQL.
1.2 Advantages of stored procedures
- After execution once, the generated binary code will reside Buffer to improve execution efficiency.
- A collection of SQL statements plus control statements, with high flexibility.
- It is stored on the server side and reduces the network load when called by the client.
- Can be called multiple times and can be modified at any time without affecting client calls.
- Can complete all database operations and control the information access permissions of the database.
2. Create, call and view stored procedures
2.1 Create stored procedures
delimiter $$ #将语句的结束符号从分号;临时改为两个$$(可以自定义) create procedure proc () #创建存储过程,过程名为proc,不带参数 -> begin #过程体以关键字begin开始 -> select * from store_info; #过程体语句 -> end $$ #过程体以关键字end结束 delimiter ; #将语句的结束符号恢复为分号
Example:
delimiter $$create procedure proc01 ()-> bengin -> create table student(id int,name char(10),age int);-> insert into student values(1,'zhangsan',18);-> insert into student values(2,'lisi',18);-> select * from student;-> end $$delimiter ;
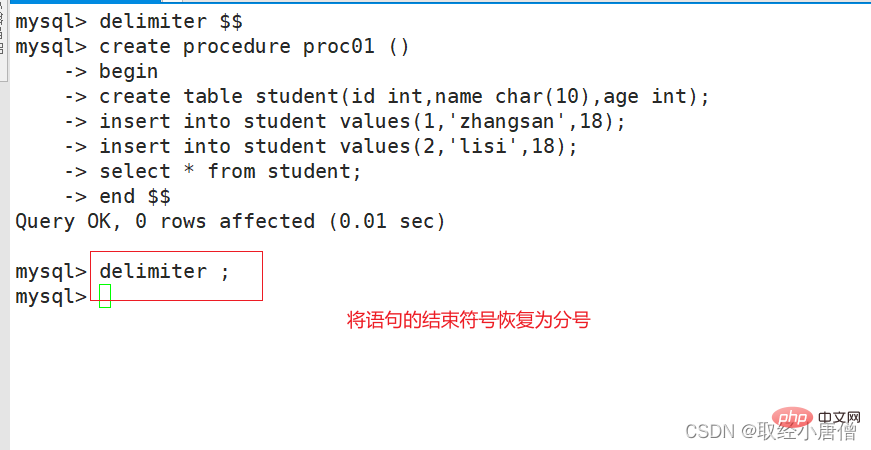
##2.2 Calling and viewing stored procedurescall proc; #调用存储过程
show create procedure [数据库.]存储过程名; #查看某个存储过程的具体信息
show create procedure proc;
show create procedure proc\G
show procedure status [like '%proc%'] \G
Copy after login
Example:
call proc; #调用存储过程 show create procedure [数据库.]存储过程名; #查看某个存储过程的具体信息 show create procedure proc; show create procedure proc\G show procedure status [like '%proc%'] \G
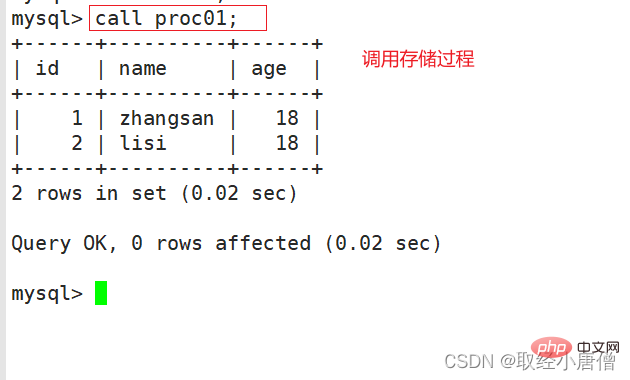
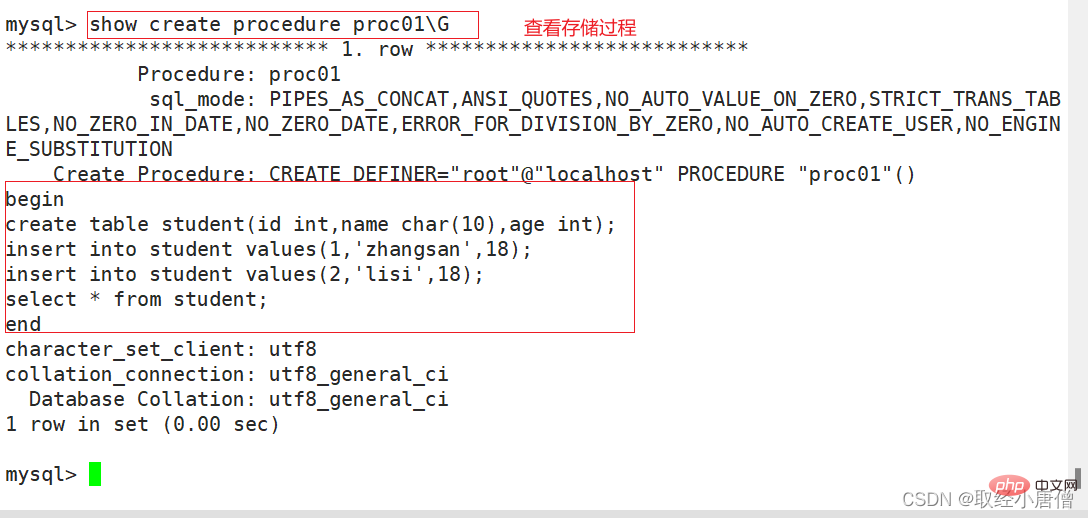
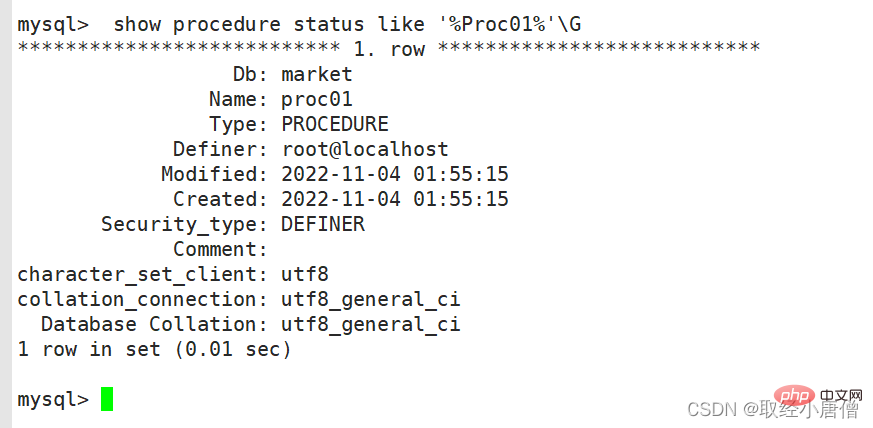
call proc01; show create procedure proc01; show create procedure proc01\G #查看存储过程的具体信息 show procedure status like '%Proc01%'\G
##2.3 Delete stored procedures #存储过程内容的修改方法是通过删除原有存储过程,之后再以相同的名称创建新的存储过程。
drop procedure if exists proc;
#仅当存在时删除,不添加If EXISTS 时,如果指定的过程不存在,则产生一个错误。
Copy after loginExample:
#存储过程内容的修改方法是通过删除原有存储过程,之后再以相同的名称创建新的存储过程。 drop procedure if exists proc; #仅当存在时删除,不添加If EXISTS 时,如果指定的过程不存在,则产生一个错误。
drop procedure if exists proc01;
3. Parameters of the stored procedure
- IN input parameters
- : Indicates that the caller passes a value to the process. (The incoming value can be a literal or a variable) OUT output parameter
- : Indicates that the procedure passes the value to the caller. (Multiple values can be returned) (The outgoing value can only be a variable) INOUT input and output parameters
- : It means that the caller passes the value to the process, and the process passes the value to the caller. Out value. (The value can only be a variable) Note: Variable names cannot contain underscores.
delimiter $$create procedure proc2(in stuname char(20)) #参数为stuname,数据类型一定要与下面的where语句后字段的数据类型相同-> begin
-> select * from student where name = stuname;-> end $$delimiter ;call proc2('zhangsan'); #调用存储过程,并传入参数‘zhangsan’
4. Control statements of stored procedures

4.1 Conditional statement: if-then-else … end if delimiter $$
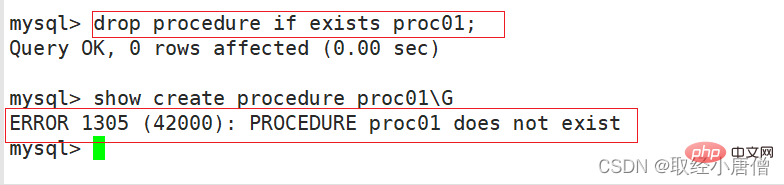
create procedure proc03(in innum int) #创建存储过程proc03,参数为innum,类型为int
-> begin
-> declare var int; #定义变量var为int类型
-> set var=innum*2; #变量var的值等于传入的参数值乘2
-> if var>=10 then #当var的值大于10时,id值会加1,否则减1
-> update ss set id=id+1;
-> else
-> update ss set id=id-1;
-> end if;
-> end $$
delimiter ;
call proc03(8); #调用存储过程,并传入参数8
call proc03(3); #调用存储过程,并传入参数3
Copy after login
delimiter $$ create procedure proc03(in innum int) #创建存储过程proc03,参数为innum,类型为int -> begin -> declare var int; #定义变量var为int类型 -> set var=innum*2; #变量var的值等于传入的参数值乘2 -> if var>=10 then #当var的值大于10时,id值会加1,否则减1 -> update ss set id=id+1; -> else -> update ss set id=id-1; -> end if; -> end $$ delimiter ; call proc03(8); #调用存储过程,并传入参数8 call proc03(3); #调用存储过程,并传入参数3
##4.2 Loop statement: while ·· ·· end while delimiter $$ #修改默认结束符为$$
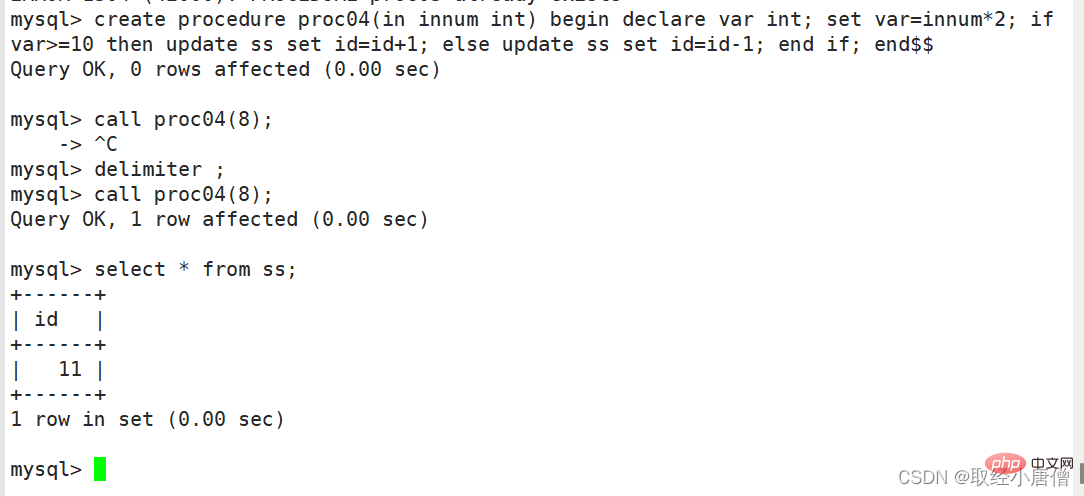
create procedure proc05() #创建存储过程proc04
-> begin #过程体以关键字begin开始
-> declare var int(10); #定义变量var为int类型
-> set var=0; #var的起始值为0
-> while var insert into ss values(var);
-> set var=var+1; #每次循环后var值自增1
-> end while; #结束while循环
-> end $$ #创建存储过程结束
delimiter ; #重新修改默认结束符为原始的;
call proc05; #调用存储过程proc04
Copy after login
delimiter $$ #修改默认结束符为$$ create procedure proc05() #创建存储过程proc04 -> begin #过程体以关键字begin开始 -> declare var int(10); #定义变量var为int类型 -> set var=0; #var的起始值为0 -> while var insert into ss values(var); -> set var=var+1; #每次循环后var值自增1 -> end while; #结束while循环 -> end $$ #创建存储过程结束 delimiter ; #重新修改默认结束符为原始的; call proc05; #调用存储过程proc04
Recommended learning:  mysql video tutorial
mysql video tutorial
The above is the detailed content of MySQL stored procedure advanced SQL statement summary. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1669
1669
 14
14
 1428
1428
 52
52
 1329
1329
 25
25
 1273
1273
 29
29
 1256
1256
 24
24
 Laravel Introduction Example
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
Laravel Introduction Example
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
Laravel is a PHP framework for easy building of web applications. It provides a range of powerful features including: Installation: Install the Laravel CLI globally with Composer and create applications in the project directory. Routing: Define the relationship between the URL and the handler in routes/web.php. View: Create a view in resources/views to render the application's interface. Database Integration: Provides out-of-the-box integration with databases such as MySQL and uses migration to create and modify tables. Model and Controller: The model represents the database entity and the controller processes HTTP requests.
 MySQL and phpMyAdmin: Core Features and Functions
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:12 AM
MySQL and phpMyAdmin: Core Features and Functions
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:12 AM
MySQL and phpMyAdmin are powerful database management tools. 1) MySQL is used to create databases and tables, and to execute DML and SQL queries. 2) phpMyAdmin provides an intuitive interface for database management, table structure management, data operations and user permission management.
 MySQL vs. Other Programming Languages: A Comparison
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:22 AM
MySQL vs. Other Programming Languages: A Comparison
Apr 19, 2025 am 12:22 AM
Compared with other programming languages, MySQL is mainly used to store and manage data, while other languages such as Python, Java, and C are used for logical processing and application development. MySQL is known for its high performance, scalability and cross-platform support, suitable for data management needs, while other languages have advantages in their respective fields such as data analytics, enterprise applications, and system programming.
 Laravel framework installation method
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
Laravel framework installation method
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
Article summary: This article provides detailed step-by-step instructions to guide readers on how to easily install the Laravel framework. Laravel is a powerful PHP framework that speeds up the development process of web applications. This tutorial covers the installation process from system requirements to configuring databases and setting up routing. By following these steps, readers can quickly and efficiently lay a solid foundation for their Laravel project.
 Explain the purpose of foreign keys in MySQL.
Apr 25, 2025 am 12:17 AM
Explain the purpose of foreign keys in MySQL.
Apr 25, 2025 am 12:17 AM
In MySQL, the function of foreign keys is to establish the relationship between tables and ensure the consistency and integrity of the data. Foreign keys maintain the effectiveness of data through reference integrity checks and cascading operations. Pay attention to performance optimization and avoid common errors when using them.
 Compare and contrast MySQL and MariaDB.
Apr 26, 2025 am 12:08 AM
Compare and contrast MySQL and MariaDB.
Apr 26, 2025 am 12:08 AM
The main difference between MySQL and MariaDB is performance, functionality and license: 1. MySQL is developed by Oracle, and MariaDB is its fork. 2. MariaDB may perform better in high load environments. 3.MariaDB provides more storage engines and functions. 4.MySQL adopts a dual license, and MariaDB is completely open source. The existing infrastructure, performance requirements, functional requirements and license costs should be taken into account when choosing.
 SQL vs. MySQL: Clarifying the Relationship Between the Two
Apr 24, 2025 am 12:02 AM
SQL vs. MySQL: Clarifying the Relationship Between the Two
Apr 24, 2025 am 12:02 AM
SQL is a standard language for managing relational databases, while MySQL is a database management system that uses SQL. SQL defines ways to interact with a database, including CRUD operations, while MySQL implements the SQL standard and provides additional features such as stored procedures and triggers.
 What software is better for yi framework? Recommended software for yi framework
Apr 18, 2025 pm 11:03 PM
What software is better for yi framework? Recommended software for yi framework
Apr 18, 2025 pm 11:03 PM
Abstract of the first paragraph of the article: When choosing software to develop Yi framework applications, multiple factors need to be considered. While native mobile application development tools such as XCode and Android Studio can provide strong control and flexibility, cross-platform frameworks such as React Native and Flutter are becoming increasingly popular with the benefits of being able to deploy to multiple platforms at once. For developers new to mobile development, low-code or no-code platforms such as AppSheet and Glide can quickly and easily build applications. Additionally, cloud service providers such as AWS Amplify and Firebase provide comprehensive tools




