 Backend Development
Backend Development
 C#.Net Tutorial
C#.Net Tutorial
 Introduction to C language: talk about basic knowledge (data types, variables, functions, arrays, etc.)
Introduction to C language: talk about basic knowledge (data types, variables, functions, arrays, etc.)
Introduction to C language: talk about basic knowledge (data types, variables, functions, arrays, etc.)
This article will help you learn C language and talk about the basic knowledge of C language (data types, variables, functions, arrays, etc.). I hope it will be helpful to everyone!

What is C language
- Simply put
C language is a computer language , widely used in low-level development, using the language to write code programs and solve problems
So for the computer major, C language and learning C language are very important
Computer Language Development
As far as computers are concerned, the initial implementation of binary code (1/0) was achieved by powering on the computer to communicate with the computer and then forming a binary code
But It was too troublesome, so we developed mnemonics (assembly language), and then formed the B language, and then developed the C language
And then various interpreted languages appeared (Java, python, etc.)
Write the first C language code
- Tools
Recommended VS2019 compiler
Basic format
#include<stdio.h>
//<>内是头文件名称;stdio代表standard input output; 即标准输入输出头文件(与后面所执行任务要用的库语言所关联)
int main() //主函数,程序的入口(有且只有一个);
{ //int 代表整型;即表示main函数调用返回整型值
任务;
return 0;
}Data type
char character short (int) short integer type int integer type long (int) long integer type long long (int) long integer type
float single-precision floating-point type double double-precision floating-point type (integer type is used for integers, and floating point type is used for decimals)
There are so many data types, it is for more convenience It’s good to apply for memory space from computer (try to save space and optimize memory )
unit
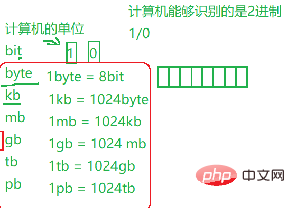
From the above The memory applied for each data type is: 1 2 4 4 8 4 8 (unit bytes, individual differences vary depending on the number of computers)
Example; short is 2 bytes, which is 16 bits (binary)
Range: the minimum is all 0, which means 0; the maximum is all 1, the range obtained by the weight bit is 2*10^16-1
Variables
- Type
Variables are divided into local variables and global variables
Scope
Local variables: In the local scope where local variables are located
Global variables: the entire project
Life cycle
Local variables: the period starts when entering the local scope and ends when leaving
Global variables: the life cycle of the program
Note: When the defined variable has the same name, the local priority## in the local scope #;
C language and law stipulate thatvariables must be defined at the front of the current code block.
Constant Type of constant in C language:
- Literal constant: 3.14, "abc", etc.
- Constant variables modified by const: const—constant attributes, the essence is constants defined by variables
- #define: Example: #define MAX 100
- Enumeration constants: enum Enumeration: enumerate one by one; Example: enum Sex {male, female, secret}
Function
In the coding process, it is inevitable to encounter the repeated use of a certain set of statements. Creating a function at this time can make coding much easier and faster - simplifying reuse.
- For example, create an addition function (custom)
int Add(int x, int y)
{
int z = 0;
z = x + y;
return z;
}
int main()
{
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
int ret = 0;
ret = Add(a, b);
printf("%d\n", ret)
return 0;
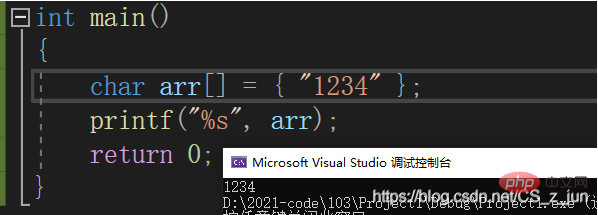
}Array
The array is an Grouping a collection of elements of the same type
- Creating an array is also equivalent to applying for space from the computer. It is a connected space with a label
- For this array, its label starts from 0 Initially, the elements in the array are generally accessed in the form of array subscripts
- The array name is also a special address
Operator
Arithmetic: Multiply* Division/Remainder % Addition Subtraction-
Shift (2 Base): First represent the number in binary and shift it, and then represent it into the corresponding number after the shift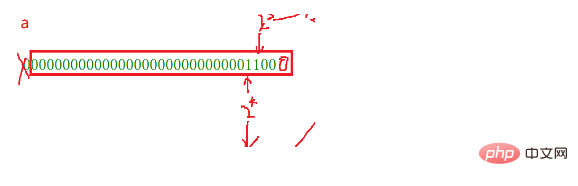
位操作

- 按位于:两个数以二进制竖着排列,有0则为0,都是1才为1

- 按位或:两个数以二进制竖着排列,有1则为1,都是0才为0
- 按位于:两个数以二进制竖着排列,相同则为0,相异才为1
赋值
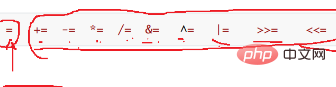
注意区别=与==:一个是赋值,一个是判断相等
单目操作
(操作数个数决定是单还是其他,例 1+2:1和2是操作数,为双目操作符)

关系/逻辑/条件

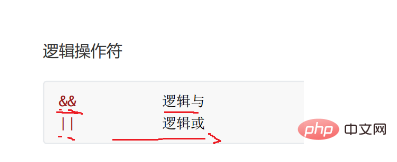
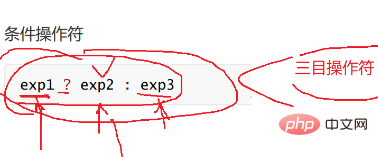
- 解释: 表达式1成立,结果为表达式2,否则为3
逗号表达式

- 解释:从左向右依次计算,结果去最后一个表达式
关键字

字符串
定义
即“ ”中的内容(例:“abc”)
结束标志
- “\0”(\0不做字符串的内容)
- 注:字符串可以存放在字符数组中;C语言无字符串类型
局别
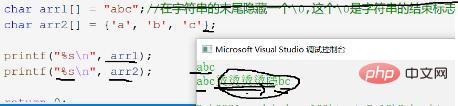
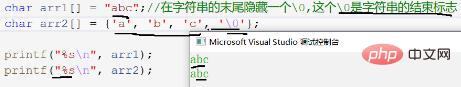
- 示图1中的arr2数组元素型初始化,它的长度未定义,会随机生成,直到遇到“\0”,来结束字符串
求字符串长度
sizeof(arr[])计算内容包括“\0”,算作一个bite
strlen(arr)不包括“\0”,计算字符串内容长度(需要审引库函数—
)
转义字符
\0是一个字符,还有\t,\n等代表不同意思的字符
转义字符则是转变原来的意思
例如你想单纯打印\n,那么则需要在“\n”前再打一个“\”,来转变“\n”原本的意思
注释
注释即用来注明,解释代码步骤的意思,让自己和读者能更好的理解
C语言——/* */ C++——//
- 注意:除了用来解释,还可以删除不需要的代码;注解不能嵌套使用
选择语句
if(条件) 多选择:if(条件) 执行语句; 执行语句; else \\反之 else if(条件) 执行语句; 执行语句; else...
循环
while循环:
初始化;
while(条件)
{ 执行和调整语句;}
for循环
for(初始化;条件;调整)
{ 执行语句; }
do while循环
do
{ 执行和调整语句;}
while(条件)注:while先判断条件,符合再执行语句,而do while循环先执行语句,再判断条件是否再进行循环;在长幅篇的代码中,用for循环比较适合,用while不利于更改如果有需要的话
相关推荐:《C视频教程》
The above is the detailed content of Introduction to C language: talk about basic knowledge (data types, variables, functions, arrays, etc.). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 C language data structure: data representation and operation of trees and graphs
Apr 04, 2025 am 11:18 AM
C language data structure: data representation and operation of trees and graphs
Apr 04, 2025 am 11:18 AM
C language data structure: The data representation of the tree and graph is a hierarchical data structure consisting of nodes. Each node contains a data element and a pointer to its child nodes. The binary tree is a special type of tree. Each node has at most two child nodes. The data represents structTreeNode{intdata;structTreeNode*left;structTreeNode*right;}; Operation creates a tree traversal tree (predecision, in-order, and later order) search tree insertion node deletes node graph is a collection of data structures, where elements are vertices, and they can be connected together through edges with right or unrighted data representing neighbors.
 The truth behind the C language file operation problem
Apr 04, 2025 am 11:24 AM
The truth behind the C language file operation problem
Apr 04, 2025 am 11:24 AM
The truth about file operation problems: file opening failed: insufficient permissions, wrong paths, and file occupied. Data writing failed: the buffer is full, the file is not writable, and the disk space is insufficient. Other FAQs: slow file traversal, incorrect text file encoding, and binary file reading errors.
 CS-Week 3
Apr 04, 2025 am 06:06 AM
CS-Week 3
Apr 04, 2025 am 06:06 AM
Algorithms are the set of instructions to solve problems, and their execution speed and memory usage vary. In programming, many algorithms are based on data search and sorting. This article will introduce several data retrieval and sorting algorithms. Linear search assumes that there is an array [20,500,10,5,100,1,50] and needs to find the number 50. The linear search algorithm checks each element in the array one by one until the target value is found or the complete array is traversed. The algorithm flowchart is as follows: The pseudo-code for linear search is as follows: Check each element: If the target value is found: Return true Return false C language implementation: #include#includeintmain(void){i
 How debian readdir integrates with other tools
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:42 AM
How debian readdir integrates with other tools
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:42 AM
The readdir function in the Debian system is a system call used to read directory contents and is often used in C programming. This article will explain how to integrate readdir with other tools to enhance its functionality. Method 1: Combining C language program and pipeline First, write a C program to call the readdir function and output the result: #include#include#include#includeintmain(intargc,char*argv[]){DIR*dir;structdirent*entry;if(argc!=2){
 C language multithreaded programming: a beginner's guide and troubleshooting
Apr 04, 2025 am 10:15 AM
C language multithreaded programming: a beginner's guide and troubleshooting
Apr 04, 2025 am 10:15 AM
C language multithreading programming guide: Creating threads: Use the pthread_create() function to specify thread ID, properties, and thread functions. Thread synchronization: Prevent data competition through mutexes, semaphores, and conditional variables. Practical case: Use multi-threading to calculate the Fibonacci number, assign tasks to multiple threads and synchronize the results. Troubleshooting: Solve problems such as program crashes, thread stop responses, and performance bottlenecks.
 How to output a countdown in C language
Apr 04, 2025 am 08:54 AM
How to output a countdown in C language
Apr 04, 2025 am 08:54 AM
How to output a countdown in C? Answer: Use loop statements. Steps: 1. Define the variable n and store the countdown number to output; 2. Use the while loop to continuously print n until n is less than 1; 3. In the loop body, print out the value of n; 4. At the end of the loop, subtract n by 1 to output the next smaller reciprocal.
 How to define the call declaration format of c language function
Apr 04, 2025 am 06:03 AM
How to define the call declaration format of c language function
Apr 04, 2025 am 06:03 AM
C language functions include definitions, calls and declarations. Function definition specifies function name, parameters and return type, function body implements functions; function calls execute functions and provide parameters; function declarations inform the compiler of function type. Value pass is used for parameter pass, pay attention to the return type, maintain a consistent code style, and handle errors in functions. Mastering this knowledge can help write elegant, robust C code.
 Integers in C: a little history
Apr 04, 2025 am 06:09 AM
Integers in C: a little history
Apr 04, 2025 am 06:09 AM
Integers are the most basic data type in programming and can be regarded as the cornerstone of programming. The job of a programmer is to give these numbers meanings. No matter how complex the software is, it ultimately comes down to integer operations, because the processor only understands integers. To represent negative numbers, we introduced two's complement; to represent decimal numbers, we created scientific notation, so there are floating-point numbers. But in the final analysis, everything is still inseparable from 0 and 1. A brief history of integers In C, int is almost the default type. Although the compiler may issue a warning, in many cases you can still write code like this: main(void){return0;} From a technical point of view, this is equivalent to the following code: intmain(void){return0;}





