In which directory is the image compiled by docker placed?
The image is placed in the docker root directory. The content of the image layer is generally in the aufs path of the Docker directory, the specific address is "/var/lib/docker/aufs/"; for each image layer, a corresponding json file will be saved, the path is "/var/lib/docker /graph".
The operating environment of this tutorial: Ubuntu 14.04 system, docker-1.7.1 version, Dell G3 computer.
Docker image content
There will always be the first time when you understand the Docker image. Since then, of course, there has been growth. The author’s own understanding You might as well share the process with everyone:
First contact with Docker: I believe that many enthusiasts will have the same understanding as me: Docker image represents a Contents of the file system of the container;
Initial contact with the joint file system: The concept of the joint file system made me aware of the technology of image hierarchical management, each layer of image All are part of the container file system content.
Study the relationship between images and containers: Containers are a dynamic environment, and the files in each layer of images are static content. However, ENV and VOLUME in Dockerfile , CMD and other contents ultimately need to be implemented into the running environment of the container, and these contents cannot be directly located in the file system contents contained in each layer of the image. So how should Docker manage this part of the content?
In addition, in the third step above, there is another situation that I believe everyone is familiar with. The size of many mirror layers is 0, and there is no file content inside the mirror layer. What's going on?
You can recall that in "Docker Image Detailed Discussion (1): Container File System", about the generation of empty images, it mentioned "updating the json file of the image". In fact, the foreshadowing laid in the previous article hints at the truth - Docker image content consists of the image layer file content and the image json file. Regardless of static content or dynamic information, Docker updates it in the json file.
The json file of each Docker image layer plays a very important role. Its main functions are as follows:
Record the information related to the Docker image Content related to container dynamic information
Record the real difference relationship between parent and child Docker images
Make up for the lack of integrity of the Docker image content and dynamic content
The json file of the Docker image can be considered as the metadata information of the image, and its importance is self-evident. .
Docker image storage location
Theoretical analysis of Docker image content seems a bit confusing, regardless of the Docker image layer file or json The document is a bit boring to read. If you can get a glimpse of the real environment in Docker, I believe it will be of great help to your understanding of mirroring technology.
Let’s go straight to the topic and start with the storage of Docker images to see where the contents of these image layer files and the image json files are stored. (The experimental environment shown below: the host operating system is Ubuntu 14.04, the Docker version is 1.7.1, the graphdriver type is aufs, and only contains one image of ubuntu:14.04.)
View the image Layer composition
We can view ubuntu:14.04 through the command docker history ubuntu:14.04, the results are as follows:
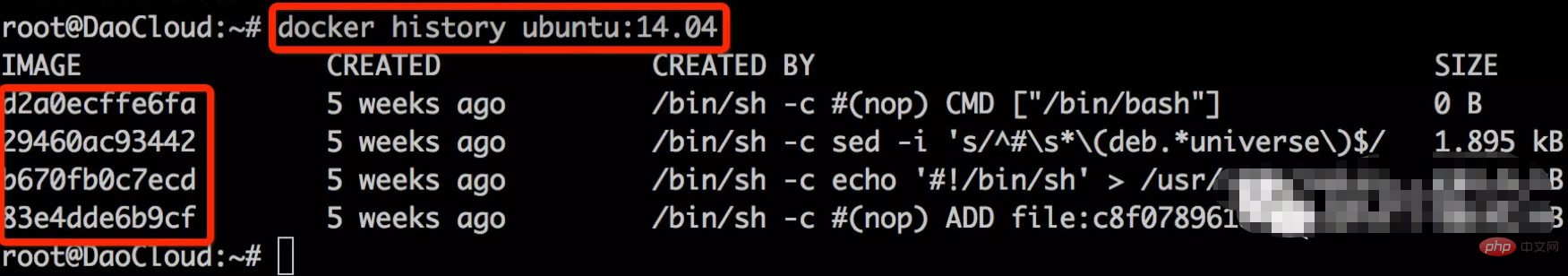
The picture shows that the ubuntu:14.04 image has 4 image layers.
Image layer file content storage
The contents of the Docker image layer are generally under the aufs path of the Docker root directory. is /var/lib/docker/aufs/, the details are as follows:
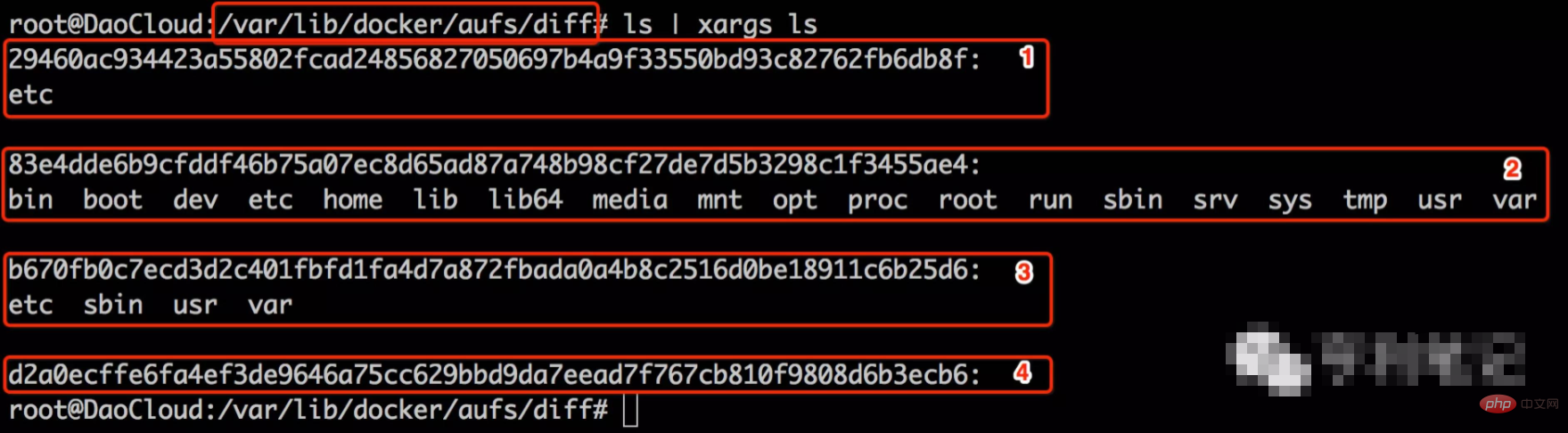
The picture shows the contents of the 4 image layers of the image ubuntu:14.04, and each image layer The first-level directory situation within. An additional note is that there is nothing in the image layer d2a0ecffe6fa.
Mirror json file storage
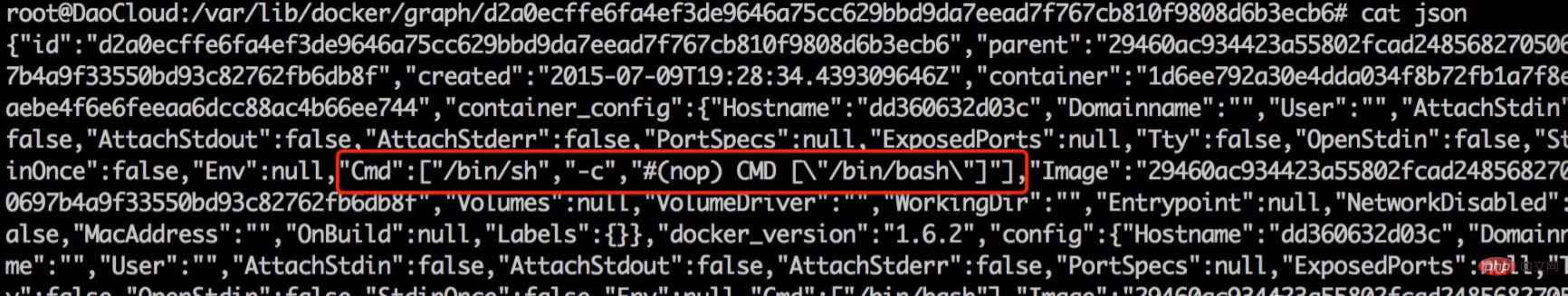
For each image layer, Docker will save a corresponding json file. The json file The storage path is /var/lib/docker/graph, ubuntu:14.04. The json file storage paths of all image layers are shown as follows:
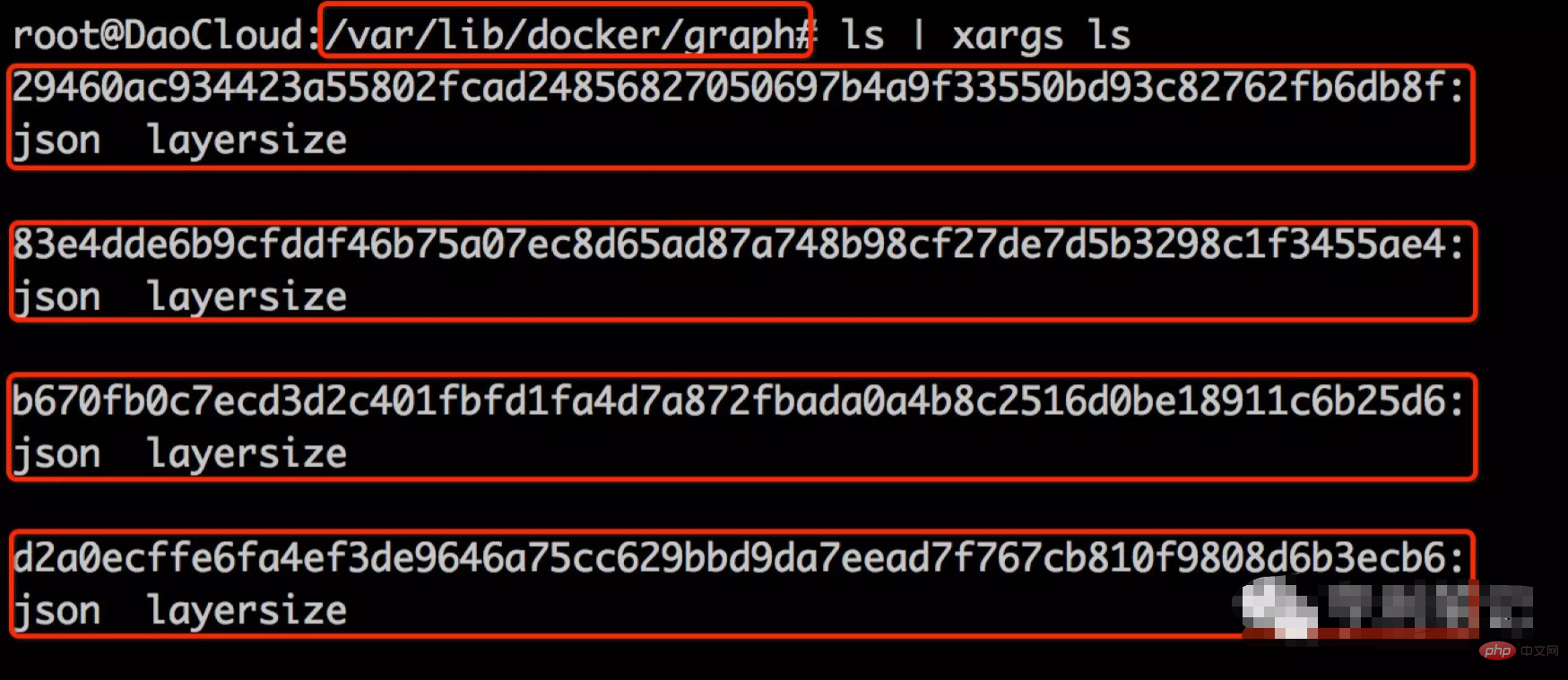
In addition to the json file, you can also see that each image layer also contains a layersize file, which mainly records the total size of the file contents inside the image layer. Now that we have talked about the mirror json file, in order to pave the way for the following, the json file of the ubuntu:14.04 hollow mirror layer d2a0ecffe6fa is posted below:
docker video tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of In which directory is the image compiled by docker placed?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1661
1661
 14
14
 1417
1417
 52
52
 1311
1311
 25
25
 1261
1261
 29
29
 1234
1234
 24
24
 How to exit the container by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:15 PM
How to exit the container by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:15 PM
Four ways to exit Docker container: Use Ctrl D in the container terminal Enter exit command in the container terminal Use docker stop <container_name> Command Use docker kill <container_name> command in the host terminal (force exit)
 How to copy files in docker to outside
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
How to copy files in docker to outside
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
Methods for copying files to external hosts in Docker: Use the docker cp command: Execute docker cp [Options] <Container Path> <Host Path>. Using data volumes: Create a directory on the host, and use the -v parameter to mount the directory into the container when creating the container to achieve bidirectional file synchronization.
 How to start containers by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
How to start containers by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Docker container startup steps: Pull the container image: Run "docker pull [mirror name]". Create a container: Use "docker create [options] [mirror name] [commands and parameters]". Start the container: Execute "docker start [Container name or ID]". Check container status: Verify that the container is running with "docker ps".
 How to restart docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:06 PM
How to restart docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:06 PM
How to restart the Docker container: get the container ID (docker ps); stop the container (docker stop <container_id>); start the container (docker start <container_id>); verify that the restart is successful (docker ps). Other methods: Docker Compose (docker-compose restart) or Docker API (see Docker documentation).
 How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
How to check the name of the docker container
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:21 PM
You can query the Docker container name by following the steps: List all containers (docker ps). Filter the container list (using the grep command). Gets the container name (located in the "NAMES" column).
 How to start mysql by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
How to start mysql by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
The process of starting MySQL in Docker consists of the following steps: Pull the MySQL image to create and start the container, set the root user password, and map the port verification connection Create the database and the user grants all permissions to the database
 How to update the image of docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
How to update the image of docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:03 PM
The steps to update a Docker image are as follows: Pull the latest image tag New image Delete the old image for a specific tag (optional) Restart the container (if needed)
 How to create containers for docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
How to create containers for docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:18 PM
Create a container in Docker: 1. Pull the image: docker pull [mirror name] 2. Create a container: docker run [Options] [mirror name] [Command] 3. Start the container: docker start [Container name]




