 Operation and Maintenance
Operation and Maintenance
 Linux Operation and Maintenance
Linux Operation and Maintenance
 How to check whether vsftpd is installed in Linux
How to check whether vsftpd is installed in Linux
How to check whether vsftpd is installed in Linux
Linux method to check whether vsftpd is installed: 1. Execute the "rpm -qa | grep vsftpd" command. If the relevant information about vsftpd is output, it means it has been installed, otherwise it is not installed; 2. Execute "vsftpd -v" command, if the version information of vsftpd is output, it means installation.

#The operating environment of this tutorial: CentOS 6 system, Dell G3 computer.
Check whether vsftpd is installed
Method 1: Use the rpm -qa | grep vsftpd command to Detection
If there is output related information about vsftpd, it means vsftpd has been installed, otherwise it means it has not been installed
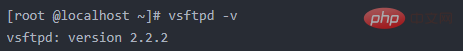
Method 2: Use the vsftpd -v command to detect the installation version by viewing it
If the version information of vsftpd is output, it means it is installed, otherwise it means it is not installed

If vsftpd is not installed, you can use yum to install it
Since the vsftpd software depends on some other software and software libraries, it is installed using yum. Relatively easy
1. Configure the yum source
Network: When connected to the Internet, no other configuration is required
Cannot be connected to the Internet: You can configure the local yum source, The Centos system disk can be configured as u pan yum source
2. Install vsftpd
For installing software using yum method, you usually need to use Only root users can install. Installation command: yum -y install vsftpd
[root@localhost ~]# yum -y install vsftpd Loaded plugins: fastestmirror, security Setting up Install Process Determining fastest mirrors * base: centos.ustc.edu.cn * extras: centos.ustc.edu.cn * updates: mirror.bit.edu.cn base | 3.7 kB 00:00 base/primary_db | 4.7 MB 00:01 extras | 3.4 kB 00:00 extras/primary_db | 29 kB 00:00 updates | 3.4 kB 00:00 updates/primary_db | 1.4 MB 00:00 Resolving Dependencies --> Running transaction check ---> Package vsftpd.x86_64 0:2.2.2-24.el6 will be installed --> Finished Dependency Resolution Dependencies Resolved ============================================================================================================================= Package Arch Version Repository Size ============================================================================================================================= Installing: vsftpd x86_64 2.2.2-24.el6 base 156 k Transaction Summary ============================================================================================================================= Install 1 Package(s) Total download size: 156 k Installed size: 340 k Downloading Packages: vsftpd-2.2.2-24.el6.x86_64.rpm | 156 kB 00:00 Running rpm_check_debug Running Transaction Test Transaction Test Succeeded Running Transaction Installing : vsftpd-2.2.2-24.el6.x86_64 1/1 Verifying : vsftpd-2.2.2-24.el6.x86_64 1/1 Installed: vsftpd.x86_64 0:2.2.2-24.el6 Complete!
The installation is successful. You can use the sftpd -v command to check the version
3. Default configuration
3.1 Configuration file location
The vsftpd service configuration file is in the /etc/vsftp directory by default, and the core configuration file is vsftpd.conf.
[root@localhost ~]# ll /etc/vsftpd/ total 28 -rw-------. 1 root root 125 May 11 2016 ftpusers -rw-------. 1 root root 361 May 11 2016 user_list -rw-------. 1 root root 4599 May 11 2016 vsftpd.conf -rwxr--r--. 1 root root 338 May 11 2016 vsftpd_conf_migrate.sh -rw-------. 1 root root 4647 Jun 20 20:07 vsftpd.conf.rpmsave [root@localhost ~]#
3.2 Default root directory
The default root directory of vsftp service is /var/ftp. The owner and group of this directory are both root.
[root@localhost ~]# ll -d /var/ftp/ drwxr-xr-x. 3 root root 4096 Jul 1 16:58 /var/ftp/ [root@localhost ~]# ll /var/ftp/ total 4 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 4096 May 11 2016 pub [root@localhost ~]#
3.3 Default anonymous user
During the installation process of vsftpd, an ftp user will be created as a proxy user for anonymous users. The ftp user cannot log in to the system.
[root@localhost ~]# id ftp uid=14(ftp) gid=50(ftp) groups=50(ftp) [root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/passwd | grep ftp ftp:x:14:50:FTP User:/var/ftp:/sbin/nologin [root@localhost ~]#
3.4 Default permissions
Under the default configuration, the vsftpd service is allowed Anonymous user access, using the Linux system user as the user source, allowing system users to log in.
Anonymous user permissions: root directory /var/ftp, readable, downloadable, unable to upload files, No new folders can be created, no files can be deleted/renamed
System user permissions: The root directory is the user's home directory, you can jump out of the user's home directory, and the permissions on files are controlled by linux user permissions.
System configuration
After installing vsftpd, you need to make some modifications to the system
ftp_home_dir: Solve non-root user login error: OOPS: child died
- ##allow_ftpd_full_access: Solve the problem of unable to upload files
- selinux: To solve the problem of not being able to log in to OOPS: priv_sock_get_cmd
[root@localhost vsftpd] setsebool -P ftp_home_dir on [root@localhost vsftpd] setsebool allow_ftpd_full_access on [root@localhost vsftpd]# vim /etc/selinux/config # This file controls the state of SELinux on the system. # SELINUX= can take one of these three values: # enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced. # permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing. # disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded. SELINUX=permissive # SELINUXTYPE= can take one of these two values: # targeted - Targeted processes are protected, # mls - Multi Level Security protection. SELINUXTYPE=targeted
Server startup
Centos series can start the server through the service command. Stop, restart1. Start the server
[root@localhost ~]# service vsftpd start Starting vsftpd for vsftpd: [ OK ] [root@localhost ~]#
2. Restart the server
[root@localhost ~]# service vsftpd restart Shutting down vsftpd: [ OK ] Starting vsftpd for vsftpd: [ OK ] [root@localhost ~]#
3. Stop the server
[root@localhost ~]# service vsftpd stop Shutting down vsftpd: [ OK ] [root@localhost ~]#
4. Set auto-start at boot
You can choose to set the vsftpd service to auto-start at boot. You can use the chkconfig command or customize it. Startup script. I use the chkconfig command. chkconfig can set the boot startup for each run level of Linux.- 0: means shutdown 1: single-user mode2: Multi-user command line mode without network connection 3: Multi-user command line mode with network connection 4: Not available 5: With graphical interface Multi-user mode6: Restart
[root@localhost ~]# chkconfig | grep vsftpd vsftpd 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:off 4:off 5:off 6:off [root@localhost ~]#
- We only set the boot level to 35 to automatically start the vsftpd service.
[root@localhost ~]# chkconfig --level 35 vsftpd on [root@localhost ~]# chkconfig | grep vsftpd vsftpd 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:on 4:off 5:on 6:off [root@localhost ~]#
vsftpd firewall settings
- vsftpd service listens to ports 20 and 21 by default. If other computers want to access, they need to release the firewall port or close the firewall. Turning off the firewall is not recommended. vsftpd uses the PASV security mode by default to transmit data, so it needs to be set PASV port upper and lower limits, and release the port
1. Set the PASV port upper and lower limits
Edit the configuration file: /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf, Append two lines at the end of the file:#设定PASV 端口下限 pasv_min_port=61000 #设定PASV 端口上限 pasv_max_port=62000
2. Release the firewall port
Edit the configuration file: /etc/sysconfig/iptables, add the following configuration to the file:
-A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 20 -j ACCEPT -A OUTPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 20 -j ACCEPT -A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 21 -j ACCEPT -A OUTPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 21 -j ACCEPT -A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 61000:62000 -j ACCEPT -A OUTPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 61000:62000 -j ACCEPT
3. Restart the service
Restart the vsftpd service and firewall[root@localhost ~]# service vsftpd restart Shutting down vsftpd: [ OK ] Starting vsftpd for vsftpd: [ OK ] [root@localhost ~]# service iptables restart iptables: Setting chains to policy ACCEPT: filter [ OK ] iptables: Flushing firewall rules: [ OK ] iptables: Unloading modules: [ OK ] iptables: Applying firewall rules: [ OK ] [root@localhost ~]#
相关推荐:《Linux视频教程》
The above is the detailed content of How to check whether vsftpd is installed in Linux. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1663
1663
 14
14
 1420
1420
 52
52
 1313
1313
 25
25
 1266
1266
 29
29
 1239
1239
 24
24
 Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
The five basic components of the Linux system are: 1. Kernel, 2. System library, 3. System utilities, 4. Graphical user interface, 5. Applications. The kernel manages hardware resources, the system library provides precompiled functions, system utilities are used for system management, the GUI provides visual interaction, and applications use these components to implement functions.
 How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
To view the Git repository address, perform the following steps: 1. Open the command line and navigate to the repository directory; 2. Run the "git remote -v" command; 3. View the repository name in the output and its corresponding address.
 vscode Previous Next Shortcut Key
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
vscode Previous Next Shortcut Key
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
VS Code One-step/Next step shortcut key usage: One-step (backward): Windows/Linux: Ctrl ←; macOS: Cmd ←Next step (forward): Windows/Linux: Ctrl →; macOS: Cmd →
 What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
The main uses of Linux include: 1. Server operating system, 2. Embedded system, 3. Desktop operating system, 4. Development and testing environment. Linux excels in these areas, providing stability, security and efficient development tools.
 How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
Although Notepad cannot run Java code directly, it can be achieved by using other tools: using the command line compiler (javac) to generate a bytecode file (filename.class). Use the Java interpreter (java) to interpret bytecode, execute the code, and output the result.
 How to run sublime after writing the code
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:51 AM
How to run sublime after writing the code
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:51 AM
There are six ways to run code in Sublime: through hotkeys, menus, build systems, command lines, set default build systems, and custom build commands, and run individual files/projects by right-clicking on projects/files. The build system availability depends on the installation of Sublime Text.
 laravel installation code
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:30 PM
laravel installation code
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:30 PM
To install Laravel, follow these steps in sequence: Install Composer (for macOS/Linux and Windows) Install Laravel Installer Create a new project Start Service Access Application (URL: http://127.0.0.1:8000) Set up the database connection (if required)
 git software installation
Apr 17, 2025 am 11:57 AM
git software installation
Apr 17, 2025 am 11:57 AM
Installing Git software includes the following steps: Download the installation package and run the installation package to verify the installation configuration Git installation Git Bash (Windows only)



