 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 Vue.js
Vue.js
 How to get started with Vue's new state management Pinia, read this article!
How to get started with Vue's new state management Pinia, read this article!
How to get started with Vue's new state management Pinia, read this article!
Pinia is a new state management library developed by Vue, so how can novices get started with Pinia? The following article will introduce you to Pinia and introduce its core features and simple usage. I hope it will be helpful to you!

Vuex is an old Vue state management library that everyone is familiar with
Pinia is a brand new one developed specifically for Vue by members of the Vue.js team State management library, and has been included in the official github
Why do we need to develop another Pinia when there is Vuex?
Let’s take a picture first to look at the proposal for Vuex5 at that time, which is what the next generation Vuex5 should look like. [Related recommendations: vuejs video tutorial]
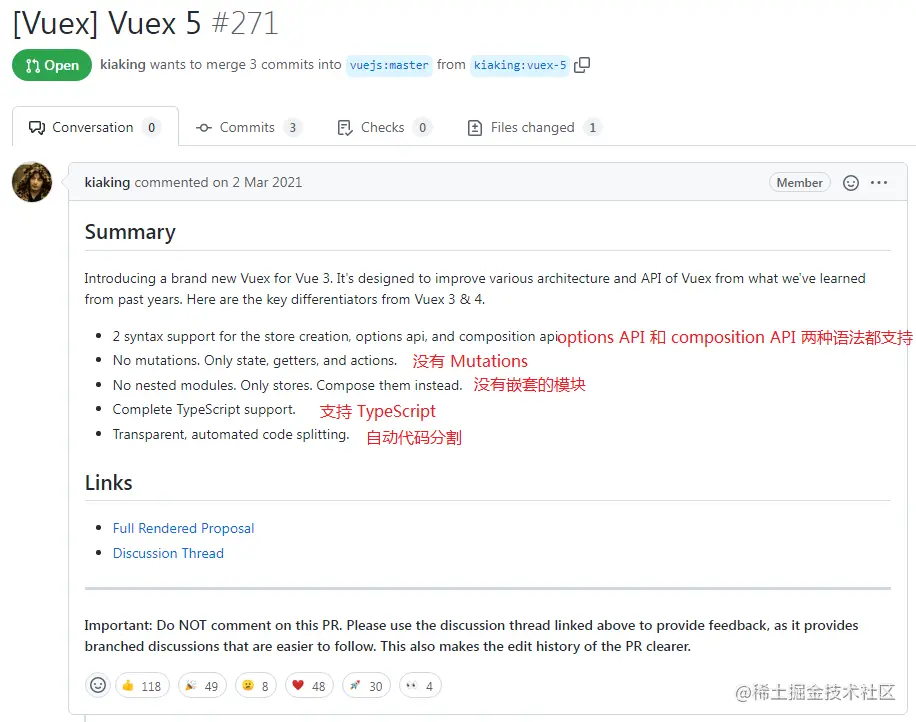
Vuex: State, Gettes, Mutations(synchronization), Actions(Asynchronous)
Pinia: State、Gettes、Actions(Synchronous Asynchronous All supported)
4.x
- Vuex4 for Vue3
- Vuex3 for Vue2
2.x
- It supports both Vue2 and Vue3
- Pinia does not have
- Mutations
- Actions
Supports synchronous and asynchronousNested structure without modules - Pinia provides a flat structure by design, which means that each store is Independent of each other, no one belongs to anyone, that is, flat, better code separation and no namespace. Of course you can also implicitly nest stores by importing another module in one module, and even have circular dependencies of stores
Better- TypeScript
Support- No need to create custom complex wrappers to support TypeScript. Everything is typed, and the API is designed to use TS type inference as much as possible
No need to inject, import functions, call them, enjoy automatic completion, making our development more convenient - No need to manually add the store, its module is automatically registered by default when it is created
- Vue2 Both support Vue3 and
- Except for initial installation and SSR configuration, the API used by both is the same
Support- Vue DevTools
- Track the timeline of actions and mutations
- You can observe the module itself in the component that uses the module
- Support time-travel for easier debugging
- In Vue2, Pinia will use all interfaces of Vuex, so they cannot be used together
- But the debugging tool support for Vue3 is not perfect enough, for example, there is no time-travel function
Hot module update - You can modify the module without reloading the page
- Any existing status will be maintained during hot update
Support Use plug-ins to extend Pinia functions- Support server-side rendering
Vue3 TypeScript as an example
npm install pinia
main.ts Initialization configuration
import { createPinia } from 'pinia'createApp(App).use(createPinia()).mount('#app')user.ts in the store directory. For example, we first define and export a name The module for user
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
export const userStore = defineStore('user', {
state: () => {
return {
count: 1,
arr: []
}
},
getters: { ... },
actions: { ... }
})defineStore receives two parameters
The second parameter is an object, and the options inside are similar to Vuex
- 其中
state用来存储全局状态,它必须是箭头函数,为了在服务端渲染的时候避免交叉请求导致的数据状态污染所以只能是函数,而必须用箭头函数则为了更好的 TS 类型推导 getters就是用来封装计算属性,它有缓存的功能actions就是用来封装业务逻辑,修改 state
访问 state
比如我们要在页面中访问 state 里的属性 count
由于 defineStore 会返回一个函数,所以要先调用拿到数据对象,然后就可以在模板中直接使用了
<template>
<div>{{ user_store.count }}</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { userStore } from '../store'
const user_store = userStore()
// 解构
// const { count } = userStore()
</script>比如像注释中的解构出来使用,是完全没有问题的,只是注意了,这样拿到的数据不是响应式的,如果要解构还保持响应式就要用到一个方法 storeToRefs(),示例如下
<template>
<div>{{ count }}</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { storeToRefs } from 'pinia'
import { userStore } from '../store'
const { count } = storeToRefs(userStore)
</script>原因就是 Pinia 其实是把 state 数据都做了 reactive 处理,和 Vue3 的 reactive 同理,解构出来的也不是响应式,所以需要再做 ref 响应式代理
getters
这个和 Vuex 的 getters 一样,也有缓存功能。如下在页面中多次使用,第一次会调用 getters,数据没有改变的情况下之后会读取缓存
<template>
<div>{{ myCount }}</div>
<div>{{ myCount }}</div>
<div>{{ myCount }}</div>
</template>注意两种方法的区别,写在注释里了
getters: {
// 方法一,接收一个可选参数 state
myCount(state){
console.log('调用了') // 页面中使用了三次,这里只会执行一次,然后缓存起来了
return state.count + 1
},
// 方法二,不传参数,使用 this
// 但是必须指定函数返回值的类型,否则类型推导不出来
myCount(): number{
return this.count + 1
}
}更新和 actions
更新 state 里的数据有四种方法,我们先看三种简单的更新,说明都写在注释里了
<template>
<div>{{ user_store.count }}</div>
<button @click="handleClick">按钮</button>
</template>
<script setup>
import { userStore } from '../store'
const user_store = userStore()
const handleClick = () => {
// 方法一
user_store.count++
// 方法二,需要修改多个数据,建议用 $patch 批量更新,传入一个对象
user_store.$patch({
count: user_store.count1++,
// arr: user_store.arr.push(1) // 错误
arr: [ ...user_store.arr, 1 ] // 可以,但是还得把整个数组都拿出来解构,就没必要
})
// 使用 $patch 性能更优,因为多个数据更新只会更新一次视图
// 方法三,还是$patch,传入函数,第一个参数就是 state
user_store.$patch( state => {
state.count++
state.arr.push(1)
})
}
</script>第四种方法就是当逻辑比较多或者请求的时候,我们就可以封装到示例中 store/user.ts 里的 actions 里
可以传参数,也可以通过 this.xx 可以直接获取到 state 里的数据,需要注意的是不能用箭头函数定义 actions,不然就会绑定外部的 this 了
actions: {
changeState(num: number){ // 不能用箭头函数
this.count += num
}
}调用
const handleClick = () => {
user_store.changeState(1)
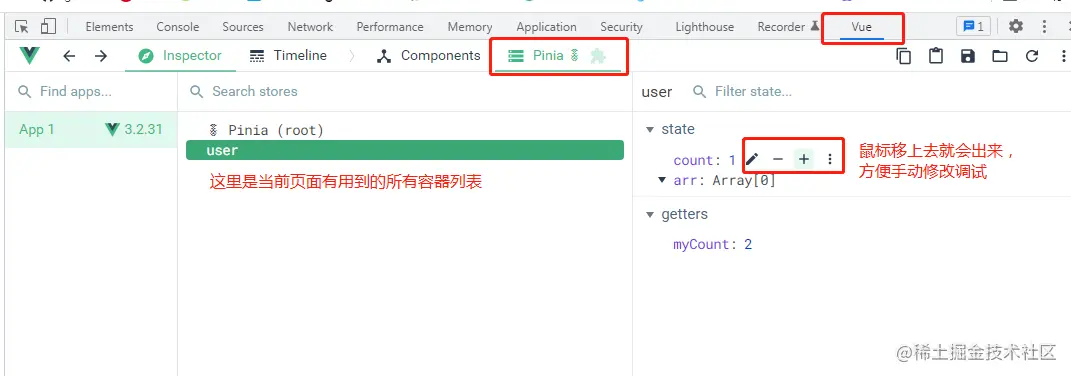
}支持 VueDevtools
打开开发者工具的 Vue Devtools 就会发现 Pinia,而且可以手动修改数据调试,非常方便
模拟调用接口
示例:
我们先定义示例接口 api/user.ts
// 接口数据类型
export interface userListType{
id: number
name: string
age: number
}
// 模拟请求接口返回的数据
const userList = [
{ id: 1, name: '张三', age: 18 },
{ id: 2, name: '李四', age: 19 },
]
// 封装模拟异步效果的定时器
async function wait(delay: number){
return new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, delay))
}
// 接口
export const getUserList = async () => {
await wait(100) // 延迟100毫秒返回
return userList
}然后在 store/user.ts 里的 actions 封装调用接口
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
import { getUserList, userListType } from '../api/user'
export const userStore = defineStore('user', {
state: () => {
return {
// 用户列表
list: [] as userListType // 类型转换成 userListType
}
},
actions: {
async loadUserList(){
const list = await getUserList()
this.list = list
}
}
})页面中调用 actions 发起请求
<template>
<ul>
<li v-for="item in user_store.list"> ... </li>
</ul>
</template>
<script setup>
import { userStore } from '../store'
const user_store = userStore()
user_store.loadUserList() // 加载所有数据
</script>跨模块修改数据
在一个模块的 actions 里需要修改另一个模块的 state 数据
示例:比如在 chat 模块里修改 user 模块里某个用户的名称
// chat.ts
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
import { userStore } from './user'
export const chatStore = defineStore('chat', {
actions: {
someMethod(userItem){
userItem.name = '新的名字'
const user_store = userStore()
user_store.updateUserName(userItem)
}
}
})user 模块里
// user.ts
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
export const userStore = defineStore('user', {
state: () => {
return {
list: []
}
},
actions: {
updateUserName(userItem){
const user = this.list.find(item => item.id === userItem.id)
if(user){
user.name = userItem.name
}
}
}
})The above is the detailed content of How to get started with Vue's new state management Pinia, read this article!. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1662
1662
 14
14
 1419
1419
 52
52
 1313
1313
 25
25
 1263
1263
 29
29
 1236
1236
 24
24
 How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Using Bootstrap in Vue.js is divided into five steps: Install Bootstrap. Import Bootstrap in main.js. Use the Bootstrap component directly in the template. Optional: Custom style. Optional: Use plug-ins.
 How to add functions to buttons for vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
How to add functions to buttons for vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
You can add a function to the Vue button by binding the button in the HTML template to a method. Define the method and write function logic in the Vue instance.
 How to use watch in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
How to use watch in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
The watch option in Vue.js allows developers to listen for changes in specific data. When the data changes, watch triggers a callback function to perform update views or other tasks. Its configuration options include immediate, which specifies whether to execute a callback immediately, and deep, which specifies whether to recursively listen to changes to objects or arrays.
 What does vue multi-page development mean?
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
What does vue multi-page development mean?
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Vue multi-page development is a way to build applications using the Vue.js framework, where the application is divided into separate pages: Code Maintenance: Splitting the application into multiple pages can make the code easier to manage and maintain. Modularity: Each page can be used as a separate module for easy reuse and replacement. Simple routing: Navigation between pages can be managed through simple routing configuration. SEO Optimization: Each page has its own URL, which helps SEO.
 How to return to previous page by vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
How to return to previous page by vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
Vue.js has four methods to return to the previous page: $router.go(-1)$router.back() uses <router-link to="/" component window.history.back(), and the method selection depends on the scene.
 React vs. Vue: Which Framework Does Netflix Use?
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:19 AM
React vs. Vue: Which Framework Does Netflix Use?
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:19 AM
Netflixusesacustomframeworkcalled"Gibbon"builtonReact,notReactorVuedirectly.1)TeamExperience:Choosebasedonfamiliarity.2)ProjectComplexity:Vueforsimplerprojects,Reactforcomplexones.3)CustomizationNeeds:Reactoffersmoreflexibility.4)Ecosystema
 How to use vue traversal
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
How to use vue traversal
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
There are three common methods for Vue.js to traverse arrays and objects: the v-for directive is used to traverse each element and render templates; the v-bind directive can be used with v-for to dynamically set attribute values for each element; and the .map method can convert array elements into new arrays.
 How to reference js file with vue.js
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
How to reference js file with vue.js
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
There are three ways to refer to JS files in Vue.js: directly specify the path using the <script> tag;; dynamic import using the mounted() lifecycle hook; and importing through the Vuex state management library.



