What is the difference between ssr and vue
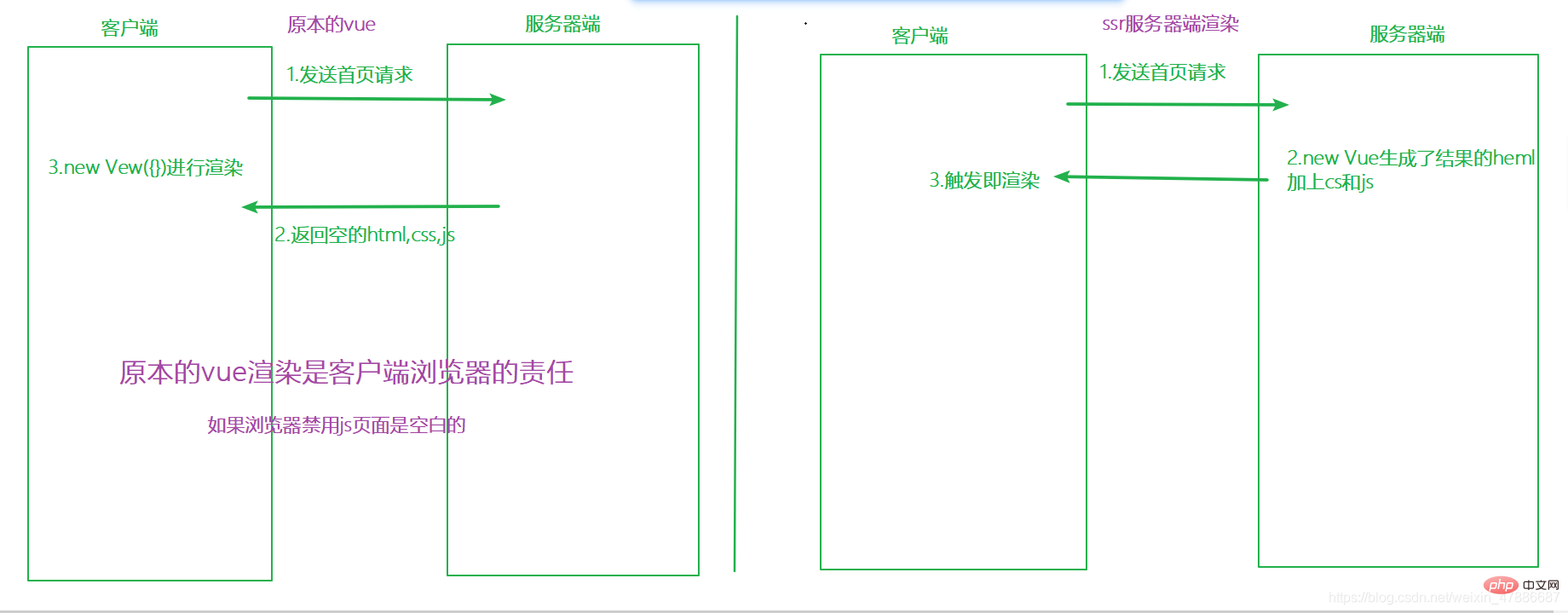
The difference between ssr and vue is: ssr is returned after the server renders the component into an HTML string, while vue is after the client sends a request, the server returns empty HTML, css, js, etc., and the component is The client renders.

The operating environment of this article: Windows 10 system, Vue version 2.9.6, DELL G3 computer.
What is the difference between ssr and vue?
ssr is the server-side rendering technology of vue, nuxt is a A framework used for ssr server-side rendering development. ssr is the technical foundation, nuxt is the encapsulation
1. What is SSR
Vue.js is a framework for building client applications. By default, Vue components can be output in the browser to generate DOM and operate DOM. All operations are run on the client side. In this case, nothing can be seen before the life cycle mounted, or if our client browser has js disabled function, it will be blank
However, vuejs can also render the same vue component directly on the server side as HTML characters Strings, send them directly to the browser, and finally "activate" these static tags into fully interactive applications on the client
2. The difference between ssr and ordinary vue
Normalvue means that after the client sends a request, the server returns empty HTML, css, js, etc., which are rendered on the client. ssr is rendered on the server. Return the string
3. Render a vue instance
Initialization
npm init
Download and install
npm install vue vue-server-renderer --save
Create a js
// 第 1 步:创建一个 Vue 实例
const Vue = require('vue')
const app = new Vue({
template: `<div>Hello World</div>`
})
// 第 2 步:创建一个 renderer
const renderer = require('vue-server-renderer').createRenderer()
// 第 3 步:将 Vue 实例渲染为 HTML
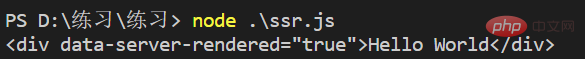
renderer.renderToString(app, (err, html) => {
if (err) throw err
console.log(html)
// => <div>Hello World</div>
})
// 在 2.5.0+,如果没有传入回调函数,则会返回 Promise:
renderer.renderToString(app).then(html => {
console.log(html)
}).catch(err => {
console.error(err)
})Output the terminal display effect
node file name, display<p>Hello World</p>
4. Integrate with the server
Download and install
npm install express --save
js
// 第 1 步:创建一个 Vue 实例
const Vue = require('vue')
const express = require('express')//创建服务器
const app = new Vue({
template: `<div>Hello World</div>`
})
const server = express()
// 第 2 步:创建一个 renderer
const renderer = require('vue-server-renderer').createRenderer()
// 在 2.5.0+,如果没有传入回调函数,则会返回 Promise:
renderer.renderToString(app).then(html => {
console.log(html)
}).catch(err => {
console.error(err)
})
server.get("*", (req, res) => {
// 第 3 步:将 Vue 实例渲染为 HTML
renderer.renderToString(app, (err, html) => {
if (err) throw err
console.log(html)
res.send(html)
// => <div>Hello World</div>
})
})
//打开服务器,监听端口等待浏览器访问
server.listen(8080, (err) => {
console.log("ok");
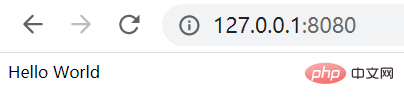
})Effect
Input127.0.0.1:8080
4. Why/should you use server-side rendering (SSR)?
Compared with traditional SPA (Single-Page Application), the main advantages of server-side rendering (SSR) are:
- Better SEO, due to Search engine crawlers can view fully rendered pages directly.
- Faster time-to-content, especially for slow network conditions or slow devices. Instead of waiting for all JavaScript to finish downloading and executing, your users will see a fully rendered page much faster.
There are also some trade-offs when using server-side rendering (SSR): - Limited development conditions. Browser-specific code can only be used in certain lifecycle hooks; some external libraries may require special handling to run in server-rendered applications.
- More requirements involving build setup and deployment. Unlike fully static single-page applications (SPA), which can be deployed on any static file server, server-rendered applications require a Node.js server runtime environment.
- More server-side load. Rendering a complete application in Node.js will obviously take up more CPU resources (CPU-intensive) than a server that just serves static files, so if you expect to use it in a high traffic environment (high traffic), please Prepare server loads accordingly and employ caching strategies wisely.
Before using server-side rendering (SSR) for your application, the first question you should ask is whether you really need it. This mainly depends on how important time-to-content is to the application. For example, if you're building an internal dashboard, a few extra hundred milliseconds on initial load won't matter, and using server-side rendering (SSR) would be a no-brainer. However, time-to-content requirements are an absolutely critical metric, and in this case, server-side rendering (SSR) can help you achieve optimal initial load performance.
[Related recommendations: "vue.js tutorial"]
The above is the detailed content of What is the difference between ssr and vue. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Using Bootstrap in Vue.js is divided into five steps: Install Bootstrap. Import Bootstrap in main.js. Use the Bootstrap component directly in the template. Optional: Custom style. Optional: Use plug-ins.
 How to add functions to buttons for vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
How to add functions to buttons for vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
You can add a function to the Vue button by binding the button in the HTML template to a method. Define the method and write function logic in the Vue instance.
 How to use watch in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
How to use watch in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
The watch option in Vue.js allows developers to listen for changes in specific data. When the data changes, watch triggers a callback function to perform update views or other tasks. Its configuration options include immediate, which specifies whether to execute a callback immediately, and deep, which specifies whether to recursively listen to changes to objects or arrays.
 What does vue multi-page development mean?
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
What does vue multi-page development mean?
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Vue multi-page development is a way to build applications using the Vue.js framework, where the application is divided into separate pages: Code Maintenance: Splitting the application into multiple pages can make the code easier to manage and maintain. Modularity: Each page can be used as a separate module for easy reuse and replacement. Simple routing: Navigation between pages can be managed through simple routing configuration. SEO Optimization: Each page has its own URL, which helps SEO.
 How to reference js file with vue.js
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
How to reference js file with vue.js
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
There are three ways to refer to JS files in Vue.js: directly specify the path using the <script> tag;; dynamic import using the mounted() lifecycle hook; and importing through the Vuex state management library.
 How to return to previous page by vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
How to return to previous page by vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
Vue.js has four methods to return to the previous page: $router.go(-1)$router.back() uses <router-link to="/" component window.history.back(), and the method selection depends on the scene.
 How to use vue traversal
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
How to use vue traversal
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
There are three common methods for Vue.js to traverse arrays and objects: the v-for directive is used to traverse each element and render templates; the v-bind directive can be used with v-for to dynamically set attribute values for each element; and the .map method can convert array elements into new arrays.
 How to jump to the div of vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 09:18 AM
How to jump to the div of vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 09:18 AM
There are two ways to jump div elements in Vue: use Vue Router and add router-link component. Add the @click event listener and call this.$router.push() method to jump.






