What is the difference between map and foreach in es6
Difference: 1. The forEach() method will not return the execution result, and the return value is "undefined", while the map() method will return the operation result and an array; 2. the forEach() method will modify The original array, and the map() method does not modify the original array.

The operating environment of this tutorial: Windows 7 system, ECMAScript version 6, Dell G3 computer.
foreEach() method: Execute the provided function for each element.
map() method: Create a new array in which each element is obtained by calling the provided function on each element in the array.
Difference
The forEach() method will not return the execution result, but undefined. In other words, forEach() will modify the original array. The map() method will get a new array and return it.
Example:
Make the square of an array
There is an array as follows
let arr =[1,2,3,4,5,6]
Use forEach() and Map respectively below ()
forEach()
Note that forEach will not return a meaningful value.
We directly modify the value of arr in the callback function.
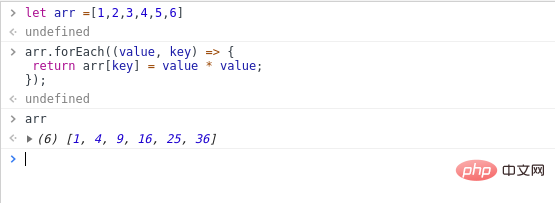
arr.forEach((value, key) => {
return arr[key] = value * value;
});The execution results are as follows:
Map()
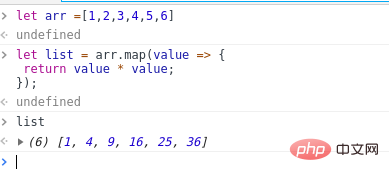
let list = arr.map(value => {
return value * value;
});The execution results are as follows:
Execution speed comparison
Execution speed of forEach() How to use forEach is suitable when you don’t plan to change the data, but just want to do something with the data Things – like saving to a database or printing. map() is suitable when you want to change the data value. Not only is it faster, but it returns a new array. The advantage of this is that you can use composition (combination of map(), filter(), reduce(), etc.) to create more tricks. We first use map to multiply each element by itself, and then filter out those elements greater than 10. The final result is assigned to arr2. Summary What forEach() can do, map() can do the same. The reverse is also true. map() will allocate memory space to store the new array and return it, while forEach() will not return data. forEach() allows the callback to change the elements of the original array. map() returns a new array. 【Related recommendations: javascript video tutorial, web front-end】 The above is the detailed content of What is the difference between map and foreach in es6. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!let arr = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'];
arr.forEach((letter) => {
console.log(letter);
});
// a
// b
// c
// dlet arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
let arr2 = arr.map(value => value * value).filter(value => value > 10);
// arr2 = [16, 25]

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1666
1666
 14
14
 1425
1425
 52
52
 1327
1327
 25
25
 1273
1273
 29
29
 1253
1253
 24
24
 How does springboot read lists, arrays, map collections and objects in yml files?
May 11, 2023 am 10:46 AM
How does springboot read lists, arrays, map collections and objects in yml files?
May 11, 2023 am 10:46 AM
application.yml defines the list collection. The first way is to use the @ConfigurationProperties annotation to obtain all the values of the list collection type:code:status:-200-300-400-500. Write the entity class corresponding to the configuration file. What needs to be noted here is that defining the list Collection, first define a configuration class Bean, and then use the annotation @ConfigurationProperties annotation to obtain the list collection value. Here we will explain the role of the relevant annotations. @Component hands over the entity class to Spring management @ConfigurationPropertie
 What is the difference between using foreach and iterator to delete elements when traversing Java ArrayList?
Apr 27, 2023 pm 03:40 PM
What is the difference between using foreach and iterator to delete elements when traversing Java ArrayList?
Apr 27, 2023 pm 03:40 PM
1. The difference between Iterator and foreach is the polymorphic difference (the bottom layer of foreach is Iterator) Iterator is an interface type, it does not care about the type of collection or array; both for and foreach need to know the type of collection first, even the type of elements in the collection; 1. Why is it said that the bottom layer of foreach is the code written by Iterator: Decompiled code: 2. The difference between remove in foreach and iterator. First, look at the Alibaba Java Development Manual, but no error will be reported in case 1, and an error will be reported in case 2 (java. util.ConcurrentModificationException) first
 How to determine the number of foreach loop in php
Jul 10, 2023 pm 02:18 PM
How to determine the number of foreach loop in php
Jul 10, 2023 pm 02:18 PM
The steps for PHP to determine the number of the foreach loop: 1. Create an array of "$fruits"; 2. Create a counter variable "$counter" with an initial value of 0; 3. Use "foreach" to loop through the array, and Increase the value of the counter variable in the loop body, and then output each element and their index; 4. Output the value of the counter variable outside the "foreach" loop to confirm which element the loop reaches.
 How to set expiration time map in Java
May 04, 2023 am 10:13 AM
How to set expiration time map in Java
May 04, 2023 am 10:13 AM
1. Technical background In actual project development, we often use caching middleware (such as redis, MemCache, etc.) to help us improve the availability and robustness of the system. But in many cases, if the project is relatively simple, there is no need to specifically introduce middleware such as Redis to increase the complexity of the system in order to use caching. So does Java itself have any useful lightweight caching components? The answer is of course yes, and there is more than one way. Common solutions include: ExpiringMap, LoadingCache and HashMap-based packaging. 2. Technical effects to realize common functions of cache, such as outdated deletion strategy, hotspot data warm-up 3. ExpiringMap3.
 Is async for es6 or es7?
Jan 29, 2023 pm 05:36 PM
Is async for es6 or es7?
Jan 29, 2023 pm 05:36 PM
async is es7. async and await are new additions to ES7 and are solutions for asynchronous operations; async/await can be said to be syntactic sugar for co modules and generator functions, solving js asynchronous code with clearer semantics. As the name suggests, async means "asynchronous". Async is used to declare that a function is asynchronous; there is a strict rule between async and await. Both cannot be separated from each other, and await can only be written in async functions.
 PHP returns an array with key values flipped
Mar 21, 2024 pm 02:10 PM
PHP returns an array with key values flipped
Mar 21, 2024 pm 02:10 PM
This article will explain in detail how PHP returns an array after key value flipping. The editor thinks it is quite practical, so I share it with you as a reference. I hope you can gain something after reading this article. PHP Key Value Flip Array Key value flip is an operation on an array that swaps the keys and values in the array to generate a new array with the original key as the value and the original value as the key. Implementation method In PHP, you can perform key-value flipping of an array through the following methods: array_flip() function: The array_flip() function is specially used for key-value flipping operations. It receives an array as argument and returns a new array with the keys and values swapped. $original_array=[
 How to convert objects to Maps in Java - using BeanMap
May 08, 2023 pm 03:49 PM
How to convert objects to Maps in Java - using BeanMap
May 08, 2023 pm 03:49 PM
There are many ways to convert javabeans and maps, such as: 1. Convert beans to json through ObjectMapper, and then convert json to map. However, this method is complicated and inefficient. After testing, 10,000 beans were converted in a loop. , it takes 12 seconds! ! ! Not recommended. 2. Obtain the attributes and values of the bean class through Java reflection, and then convert them into the key-value pairs corresponding to the map. This method is the second best, but it is a little more troublesome. 3. Through net.sf.cglib.beans.BeanMap Method in the class, this method is extremely efficient. The difference between it and the second method is that because of the use of cache, the bean needs to be initialized when it is first created.
 Optimize the performance of Go language map
Mar 23, 2024 pm 12:06 PM
Optimize the performance of Go language map
Mar 23, 2024 pm 12:06 PM
Optimizing the performance of Go language map In Go language, map is a very commonly used data structure, used to store a collection of key-value pairs. However, map performance may suffer when processing large amounts of data. In order to improve the performance of map, we can take some optimization measures to reduce the time complexity of map operations, thereby improving the execution efficiency of the program. 1. Pre-allocate map capacity. When creating a map, we can reduce the number of map expansions and improve program performance by pre-allocating capacity. Generally, we





