How to compile and install php5.6.31
How to compile and install php5.6.31: 1. Add epel source; 2. Install dependencies; 3. Download and decompress php5.6.31; 4. Modify php-fpm.conf; 5. Start php-fpm. Can.

The operating environment of this article: CentOS 7 system, php version: 5.6.31 nginx version: 1.7.3 mysql version: 5.6.62, DELL G3 computer
How to compile and install php5.6.31?
CentOS 7 Compile and install PHP5.6.31:
There are already nginx and mysql on the server, so I decided to use PHP Nginx mysql For this combination, I read a lot of information on the Internet. Since I don’t know much about Linux and PHP, and I don’t know how PHP is related to nginx and mysql, I encountered various reasons (either PHP was installed incorrectly, or the package was not installed), It took a lot of time, but after the deployment, I found that these three are installed separately (well~~ can they be installed together), you only need to configure PHP after installation, and configure nginx (associated with PHP). Ran. As for mysql, as long as it is turned on and the connection database in the php project is configured, you can connect directly. So this article mainly focuses on the installation of php.
Regarding the installation of nginx and mysql, some development libraries for Linux need to be installed before starting the installation. I will not repeat them here. They are all in the reference link.
PHP installation configuration
nginx itself cannot handle PHP. It is just a WEB server. When a request is received, if it is a PHP request, it is sent to the PHP interpreter for processing and the result is returned. to the client.
nginx generally sends the request to the fastcgi management process for processing. The fastcgi management process selects the cgi sub-process processing result and returns it to nginx.
What is PHP-FPM? PHP-FPM is a FASTCGI manager for PHP. It is only used for PHP. The new version has integrated php-fpm. php-fpm provides better php process management, can effectively control memory and processes, and can smoothly reload php configuration. . When configuring, you can enable php-fpm with the -enable-fpm parameter. Other parameters can be found here. As for what fastcgi is and its relationship with php-fpm, please refer to the link https://segmentfault.com/q/1010000000256516
Preparation before installation
Add epel source
rpm -Uvh http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/x86_64/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
Installation dependencies
yum install gcc bison bison-devel zlib-devel libmcrypt-devel mcrypt mhash-devel openssl-devel libxml2-devel libcurl-devel bzip2-devel readline-devel libedit-devel sqlite-develyum -y install gcc gcc-c++ glibcyum -y install libmcrypt-devel mhash-devel libxslt-devel \ libjpeg libjpeg-devel libpng libpng-devel freetype freetype-devel libxml2 libxml2-devel \ zlib zlib-devel glibc glibc-devel glib2 glib2-devel bzip2 bzip2-devel \ ncurses ncurses-devel curl curl-devel e2fsprogs e2fsprogs-devel \ krb5 krb5-devel libidn libidn-devel openssl openssl-devel
Downloadphp-5.6.31
1) Unzip the installation package to /usr/local/src
cd /usr/local/srctar -zvxf php-5.6.31.tar.gz
2) Enter the installation directory, Installation
cd php-5.6.31./configure --prefix=/usr/local/php --enable-fpm --with-mcrypt \--enable-mbstring --enable-pdo --with-curl --disable-debug --disable-rpath \--enable-inline-optimization --with-bz2 --with-zlib --enable-sockets \--enable-sysvsem --enable-sysvshm --enable-pcntl --enable-mbregex \--with-mhash --enable-zip --with-pcre-regex --with-mysql --with-mysqli \--with-gd --with-jpeg-dir --with-freetype-dir --enable-calendarmake && make install
CentOS 中下载php: wget http://php.net/get/php-5.6.30.tar.gz/from/this/mirror
The above completes the installation of php-fpm. The installation process will take some time.
About php configuration
1. Provide configuration files for php
cp php.ini-production /usr/local/php/etc/php.ini
Note: php.ini-production is still in /usr/local/src/php-5.6. 31 directory
2. Provide configuration file for php-fpm
cd /usr/local/phpcp etc/php-fpm.conf.default etc/php-fpm.conf vim etc/php-fpm.conf
Modify php-fpm.conf
user = www group = www
If the www user does not exist, add the www user first ( The default running user is nobody)
groupadd www useradd -g www www
If this step is not configured, the browser will report an error when opening the php file
"The page you are looking for is temporarily unavailable . Please try again later”
Modify
pm.max_children = 150 pm.start_servers = 8 pm.min_spare_servers = 5 pm.max_spare_servers = 10 pid = /usr/local/php/var/run/php-fpm.pid
3. Start php-fpm
Execute
/usr/local/php/sbin/php-fpm
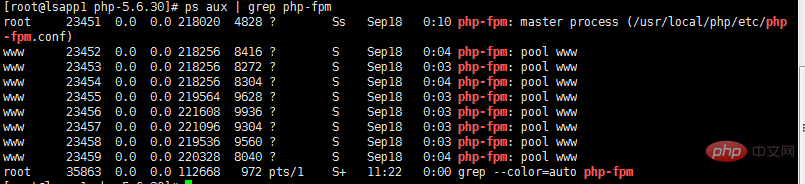
Use the following command to verify ( If there are several php-fpm processes in the output of this command, it means the startup is successful):
ps aux | grep php-fpm
The result is as shown below:
3, nginx and php -fpm integration
Edit nginx configuration file
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
The initial content is as follows:
# nginx运行的用户名
user nginx;
# nginx启动进程,通常设置成和cpu的数量相等,这里为自动
worker_processes auto;
# errorlog文件位置
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
# pid文件地址,记录了nginx的pid,方便进程管理
pid /run/nginx.pid;
# Load dynamic modules. See /usr/share/nginx/README.dynamic.
# 用来加载其他动态模块的配置
include /usr/share/nginx/modules/*.conf;
# 工作模式和连接数上限
events {
# 每个worker_processes的最大并发链接数
# 并发总数:worker_processes*worker_connections
worker_connections 1024;
}
# 与提供http服务相关的一些配置参数类似的还有mail
http {
# 设置日志的格式
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
# access_log记录访问的用户、页面、浏览器、ip和其他的访问信息
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;
# 这部分下面会单独解释
# 设置nginx是否使用sendfile函数输出文件
sendfile on;
# 数据包最大时发包(使用Nagle算法)
tcp_nopush on;
# 立刻发送数据包(禁用Nagle算法)
tcp_nodelay on;
# 链接超时时间
keepalive_timeout 65;
# 这个我也不清楚...
types_hash_max_size 2048;
# 引入文件扩展名与文件类型映射表
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
# 默认文件类型
default_type application/octet-stream;
# Load modular configuration files from the /etc/nginx/conf.d directory.
# See http://nginx.org/en/docs/ngx_core_module.html#include
# for more information.
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
# http服务上支持若干虚拟主机。
# 每个虚拟主机一个对应的server配置项
# 配置项里面包含该虚拟主机相关的配置。
server {
# 端口
listen 80 default_server;
listen [::]:80 default_server;
# 访问的域名
server_name _;
# 默认网站根目录(www目录)
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
# Load configuration files for the default server block.
include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf;
# 默认请求
location / {
}
# 错误页(404)
error_page 404 /404.html;
location = /40x.html {
}
# 错误页(50X)
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
}
}
}We only need to change the configurationserver## The # part is fine. Enter vim editing mode, or use FlashFXP to share the configuration file to the desktop to make changes.
server {
listen 80 default_server;
listen [::]:80 default_server;
# 这里改动了,也可以写你的域名,我用的是IP地址
server_name 192.168.0.222;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
# Load configuration files for the default server block.
include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf;
location / {
# 这里改动了 定义首页索引文件的名称
index index.php index.html index.htm;
}
error_page 404 /404.html;
location = /40x.html {
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
}
# 这里新加的
# PHP 脚本请求全部转发到 FastCGI处理. 使用FastCGI协议默认配置.
# Fastcgi服务器和程序(PHP,Python)沟通的协议.
location ~ \.php$ {
# 设置监听端口
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# 设置脚本文件请求的路径
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
# 引入fastcgi的配置文件
include fastcgi_params;
}
}nginx -s reload
As mentioned before, /usr/share/nginx/html is the root directory of Nginx website. We can create a php test script in this directory.
vi /usr/share/nginx/html/phpinfo.php
<?php phpinfo();// 测试信息?>
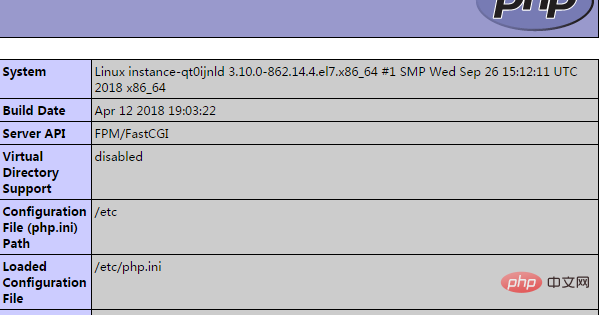
At this point, PHP has been configured. I wish you a smooth installation. By the way, I wish you all a Happy New Year in advance!
Recommended learning: "PHP Video Tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of How to compile and install php5.6.31. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1665
1665
 14
14
 1423
1423
 52
52
 1321
1321
 25
25
 1269
1269
 29
29
 1249
1249
 24
24
 What are the backup methods for GitLab on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 05:33 PM
What are the backup methods for GitLab on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 05:33 PM
Backup and Recovery Policy of GitLab under CentOS System In order to ensure data security and recoverability, GitLab on CentOS provides a variety of backup methods. This article will introduce several common backup methods, configuration parameters and recovery processes in detail to help you establish a complete GitLab backup and recovery strategy. 1. Manual backup Use the gitlab-rakegitlab:backup:create command to execute manual backup. This command backs up key information such as GitLab repository, database, users, user groups, keys, and permissions. The default backup file is stored in the /var/opt/gitlab/backups directory. You can modify /etc/gitlab
 Centos shutdown command line
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
Centos shutdown command line
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
The CentOS shutdown command is shutdown, and the syntax is shutdown [Options] Time [Information]. Options include: -h Stop the system immediately; -P Turn off the power after shutdown; -r restart; -t Waiting time. Times can be specified as immediate (now), minutes ( minutes), or a specific time (hh:mm). Added information can be displayed in system messages.
 Difference between centos and ubuntu
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:09 PM
Difference between centos and ubuntu
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:09 PM
The key differences between CentOS and Ubuntu are: origin (CentOS originates from Red Hat, for enterprises; Ubuntu originates from Debian, for individuals), package management (CentOS uses yum, focusing on stability; Ubuntu uses apt, for high update frequency), support cycle (CentOS provides 10 years of support, Ubuntu provides 5 years of LTS support), community support (CentOS focuses on stability, Ubuntu provides a wide range of tutorials and documents), uses (CentOS is biased towards servers, Ubuntu is suitable for servers and desktops), other differences include installation simplicity (CentOS is thin)
 How to optimize CentOS HDFS configuration
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
How to optimize CentOS HDFS configuration
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:15 PM
Improve HDFS performance on CentOS: A comprehensive optimization guide to optimize HDFS (Hadoop distributed file system) on CentOS requires comprehensive consideration of hardware, system configuration and network settings. This article provides a series of optimization strategies to help you improve HDFS performance. 1. Hardware upgrade and selection resource expansion: Increase the CPU, memory and storage capacity of the server as much as possible. High-performance hardware: adopts high-performance network cards and switches to improve network throughput. 2. System configuration fine-tuning kernel parameter adjustment: Modify /etc/sysctl.conf file to optimize kernel parameters such as TCP connection number, file handle number and memory management. For example, adjust TCP connection status and buffer size
 Centos configuration IP address
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:06 PM
Centos configuration IP address
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:06 PM
Steps to configure IP address in CentOS: View the current network configuration: ip addr Edit the network configuration file: sudo vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 Change IP address: Edit IPADDR= Line changes the subnet mask and gateway (optional): Edit NETMASK= and GATEWAY= Lines Restart the network service: sudo systemctl restart network verification IP address: ip addr
 What are the common misunderstandings in CentOS HDFS configuration?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
What are the common misunderstandings in CentOS HDFS configuration?
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:12 PM
Common problems and solutions for Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) configuration under CentOS When building a HadoopHDFS cluster on CentOS, some common misconfigurations may lead to performance degradation, data loss and even the cluster cannot start. This article summarizes these common problems and their solutions to help you avoid these pitfalls and ensure the stability and efficient operation of your HDFS cluster. Rack-aware configuration error: Problem: Rack-aware information is not configured correctly, resulting in uneven distribution of data block replicas and increasing network load. Solution: Double check the rack-aware configuration in the hdfs-site.xml file and use hdfsdfsadmin-printTopo
 What steps are required to configure CentOS in HDFS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
What steps are required to configure CentOS in HDFS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
Building a Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) on a CentOS system requires multiple steps. This article provides a brief configuration guide. 1. Prepare to install JDK in the early stage: Install JavaDevelopmentKit (JDK) on all nodes, and the version must be compatible with Hadoop. The installation package can be downloaded from the Oracle official website. Environment variable configuration: Edit /etc/profile file, set Java and Hadoop environment variables, so that the system can find the installation path of JDK and Hadoop. 2. Security configuration: SSH password-free login to generate SSH key: Use the ssh-keygen command on each node
 How to install mysql in centos7
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:30 PM
How to install mysql in centos7
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:30 PM
The key to installing MySQL elegantly is to add the official MySQL repository. The specific steps are as follows: Download the MySQL official GPG key to prevent phishing attacks. Add MySQL repository file: rpm -Uvh https://dev.mysql.com/get/mysql80-community-release-el7-3.noarch.rpm Update yum repository cache: yum update installation MySQL: yum install mysql-server startup MySQL service: systemctl start mysqld set up booting




