How to perform type conversion in mysql
Conversion method: 1. Use the " " operator, the syntax is "SELECT 1 'String';"; 2. Use the CAST() function to convert any type to a specified type, the syntax is "CAST(expr AS type)"; 3. Use the DATE_FORMAT() function to convert the date into a string according to the given pattern.

The operating environment of this tutorial: windows7 system, mysql8 version, Dell G3 computer.
1. The concept of implicit type conversion and explicit type conversion
Implicit type conversion:
To perform operations or comparisons between two values, the data types must first be consistent. Implicit type conversion occurs when two data types are found to be inconsistent. For example, convert a string into a number, or vice versa:
SELECT 1+'1'; – 字符串1转成数字 SELECT concat(2,'test'); – 数字2转成字符串
Explicit type conversion:
Use functions to convert data types
2.Cast function
##CAST(expr AS type)
- BINARY[(N)]: binary string, the length after conversion is less than N bytes (if the length is less than N, 0x00 will be added at the end)
- CHAR[(N)]: String, the length after conversion is less than N characters
- DATE: Date
- DATETIME: Date and time
- DECIMAL[(M[,N])]: Floating point number, M is the total number of digits (including the integer part and the decimal part) , N is the number of digits after the decimal point ##SIGNED [INTEGER]: Signed integer
- TIME: Time
- UNSIGNED [INTEGER]: Unsigned integer
When converting to decimal, scan characters from the beginning String up to the first non-numeric character. Round the truncated digit
1) By default, M and N are not limited, converted to an integer, and rounded to the first decimal place:SELECT cast(‘28.82abc’ AS DECIMAL);

SELECT cast(‘28.82abc’ AS DECIMAL(4));
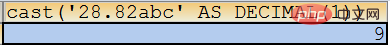
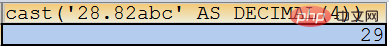 If M When the length is less than the actual number of digits, it will be converted to the maximum value of the set number of digits. In the following conversion, M is 1, that is, the two-digit number 29 cannot be displayed, and the largest one-digit number, 9
If M When the length is less than the actual number of digits, it will be converted to the maximum value of the set number of digits. In the following conversion, M is 1, that is, the two-digit number 29 cannot be displayed, and the largest one-digit number, 9
SELECT cast(‘28.82abc’ AS DECIMAL(1));
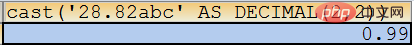
 , is limited to M and N, which must be First satisfy N decimal places after the decimal point. In the following example, 1 decimal place is satisfied first, and then 1 integer is taken:
, is limited to M and N, which must be First satisfy N decimal places after the decimal point. In the following example, 1 decimal place is satisfied first, and then 1 integer is taken:
SELECT cast(‘28.82abc’ AS DECIMAL(2,1));
 2 decimal places are satisfied first, and the integer part is not taken:
2 decimal places are satisfied first, and the integer part is not taken:
SELECT cast(‘28.82abc’ AS DECIMAL(2,2));
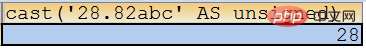
SELECT cast(‘28.82abc’ AS UNSIGNED);
SELECT cast(’-28abc’ AS SIGNED);
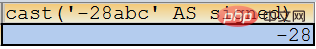
SELECT cast(‘2007-12-25’ AS DATETIME);
SELECT cast(‘2007-12-25’ AS DATE);
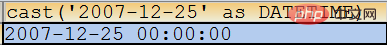
SELECT cast(‘20:20:20’ AS TIME);

The date format must be 'YYYY-MM-DD'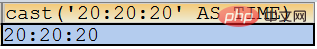
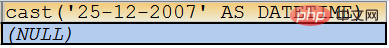
SELECT cast(‘25-12-2007’ AS DATETIME); SELECT cast(‘2007-may-25’ AS DATETIME);

SELECT cast(123 AS CHAR);
SELECT cast(123 AS BINARY);
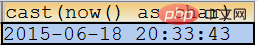
SELECT cast(now() AS CHAR);
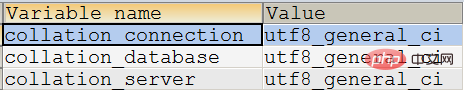
二进制字符串:二进制字符串被视为一个连续的字节序列,与字符集无关。非二进制字符串(即我们通常所说的字符串)被视为一个连续排列的字符序列,与字符集有关。所谓与字符集无关,是指与MySQL自己的字符集无关,而是按照操作系统的字符集把字符串转换成字节进行存储 两种字符串的比较方式:二进制字符串的比较方式是一个字节一个字节进行的,比较的依据是两个字节的二进制值。因为同一个字母的大小写的数值编码是不一样的,因此它是区分大小写的。另外,由于它和字符集无关,因此也就没有大写和小写字母一说 非二进制字符串的比较方式是一个字符一个字符进行的,比较的依据是两个字符在字符集中的先后顺序。根据使用的校对不同,可以进行区分大小写的比较和不区分大小写的比较 使用CAST(str AS BINARY)将字符串转换成二进制字符串时,通常使用它的快捷方式写法: BINARY str 查看当前字符集和校对规则设置 在比较表达式中,binary影响后面所有的字符串,并且不会忽略字符串的尾部空格 Cast(col_name as date_type) 将指定的列或者表达式转换为指定的数据类型 使用场景:当两个值进行比较,但是数据源的表中列的数据不一致,这个时候可以使用cast函数进行转化 3.Convert函数 CONVERT(expr, type), CONVERT(expr USING sharset_name) convert函数的作用和cast函数几乎相同,但是它可以把字符串从一种字符集转换成另一种字符集。下例将字符串’abc’从默认的字符集转换成utf8字符集 如果目标字符集不能表示该字符,则返回乱码 日期字符串转换函数 DATE_FORMAT(date, format) 将日期date按照给定的模式format转换成字符串。format中可使用以下模式元素 TIME_FORMAT(date, format) format中只可使用时、分、秒和微秒模式元素 STR_TO_DATE(str, format) 将字符串str以指定的模式format转换成日期。format中可以包含模式元素和字面量,字面量必须匹配str中的字面量: 【相关推荐:mysql视频教程】 The above is the detailed content of How to perform type conversion in mysql. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!SHOW VARIABLES LIKE ‘collation_%’;
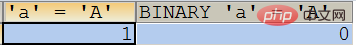
SELECT ‘a’ = ‘A’ ,BINARY ‘a’ = ‘A’;
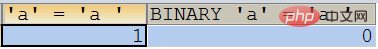
SELECT ‘a’ = 'a ',BINARY ‘a’ = 'a ';
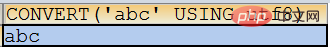
SELECT convert(‘abc’ USING utf8);
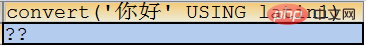
SELECT convert(‘你好’ USING gbk);

SELECT convert(‘你好’ USING latin1);
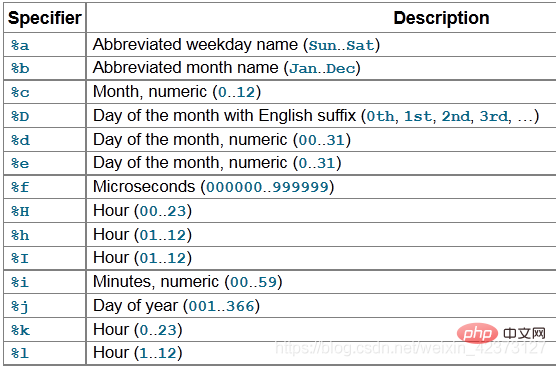
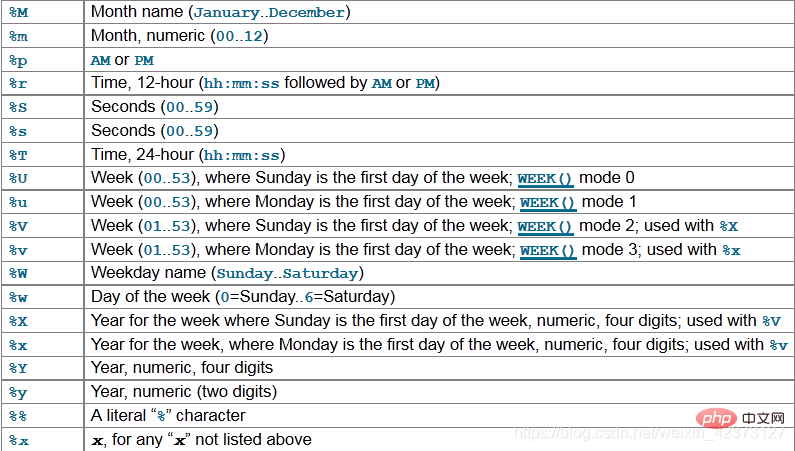
SELECT date_format(‘2009-10-04 22:23:00’, ‘%W %M %Y’);

SELECT date_format(now(), ‘%W %M %Y’);
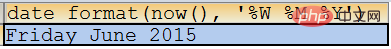
SELECT date_format(‘2007-10-04 22:23:00’, ‘%H:%i:%s’);

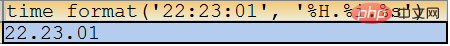
SELECT time_format(‘22:23:01’, ‘%H.%i.%s’);
SELECT str_to_date(‘01,5,2013’,’%d,%m,%Y’);
SELECT str_to_date(‘May 1, 2013’,’%M %d,%Y’);

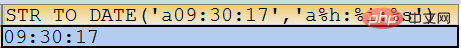
以下在会话变量@@sql_mode设置中包含no_zero_date和no_zero_in_date时转换失败,没有包含这些设置时转换成功SELECT str_to_date(‘a09:30:17’,‘a%h:%i:%s’);
SELECT str_to_date(‘09:30:17a’,’%h:%i:%s’);


Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1655
1655
 14
14
 1413
1413
 52
52
 1306
1306
 25
25
 1252
1252
 29
29
 1226
1226
 24
24
 MySQL's Role: Databases in Web Applications
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
MySQL's Role: Databases in Web Applications
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
The main role of MySQL in web applications is to store and manage data. 1.MySQL efficiently processes user information, product catalogs, transaction records and other data. 2. Through SQL query, developers can extract information from the database to generate dynamic content. 3.MySQL works based on the client-server model to ensure acceptable query speed.
 How to start mysql by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
How to start mysql by docker
Apr 15, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
The process of starting MySQL in Docker consists of the following steps: Pull the MySQL image to create and start the container, set the root user password, and map the port verification connection Create the database and the user grants all permissions to the database
 Laravel Introduction Example
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
Laravel Introduction Example
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:45 PM
Laravel is a PHP framework for easy building of web applications. It provides a range of powerful features including: Installation: Install the Laravel CLI globally with Composer and create applications in the project directory. Routing: Define the relationship between the URL and the handler in routes/web.php. View: Create a view in resources/views to render the application's interface. Database Integration: Provides out-of-the-box integration with databases such as MySQL and uses migration to create and modify tables. Model and Controller: The model represents the database entity and the controller processes HTTP requests.
 Solve database connection problem: a practical case of using minii/db library
Apr 18, 2025 am 07:09 AM
Solve database connection problem: a practical case of using minii/db library
Apr 18, 2025 am 07:09 AM
I encountered a tricky problem when developing a small application: the need to quickly integrate a lightweight database operation library. After trying multiple libraries, I found that they either have too much functionality or are not very compatible. Eventually, I found minii/db, a simplified version based on Yii2 that solved my problem perfectly.
 Laravel framework installation method
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
Laravel framework installation method
Apr 18, 2025 pm 12:54 PM
Article summary: This article provides detailed step-by-step instructions to guide readers on how to easily install the Laravel framework. Laravel is a powerful PHP framework that speeds up the development process of web applications. This tutorial covers the installation process from system requirements to configuring databases and setting up routing. By following these steps, readers can quickly and efficiently lay a solid foundation for their Laravel project.
 How to install mysql in centos7
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:30 PM
How to install mysql in centos7
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:30 PM
The key to installing MySQL elegantly is to add the official MySQL repository. The specific steps are as follows: Download the MySQL official GPG key to prevent phishing attacks. Add MySQL repository file: rpm -Uvh https://dev.mysql.com/get/mysql80-community-release-el7-3.noarch.rpm Update yum repository cache: yum update installation MySQL: yum install mysql-server startup MySQL service: systemctl start mysqld set up booting
 MySQL and phpMyAdmin: Core Features and Functions
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:12 AM
MySQL and phpMyAdmin: Core Features and Functions
Apr 22, 2025 am 12:12 AM
MySQL and phpMyAdmin are powerful database management tools. 1) MySQL is used to create databases and tables, and to execute DML and SQL queries. 2) phpMyAdmin provides an intuitive interface for database management, table structure management, data operations and user permission management.
 MySQL vs. Other Databases: Comparing the Options
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:08 AM
MySQL vs. Other Databases: Comparing the Options
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:08 AM
MySQL is suitable for web applications and content management systems and is popular for its open source, high performance and ease of use. 1) Compared with PostgreSQL, MySQL performs better in simple queries and high concurrent read operations. 2) Compared with Oracle, MySQL is more popular among small and medium-sized enterprises because of its open source and low cost. 3) Compared with Microsoft SQL Server, MySQL is more suitable for cross-platform applications. 4) Unlike MongoDB, MySQL is more suitable for structured data and transaction processing.




