In-depth analysis of the key in vue to see what the key can be used for!
What is the use of key? The following article will give you an in-depth analysis of the key in vue to see what the key can be used for. I hope it will be helpful to everyone!

In-depth analysis of key in vue
What is the use of key?
- Let’s look at the official explanation first:
- The key attribute is mainly used in vue's
virtual DOM algorithm (diff algorithm), and is not used when identifying new and old nodes when comparing themVNodes -
key, Vue will use an algorithm that minimizes dynamic elements and tries tomodify/reuse elements of the same typein place as much as possible -
Use key, it will rearrange the order of elements based on key changes, and willremove/destroy elements that have a keythat do not exist
- The key attribute is mainly used in vue's
Faced with these vague concepts, don’t be impatient. Read it once and get an impression. Next, we will analyze in depth step by step what the key is used for. [Related recommendations: "vue.js Tutorial"]
1 vnode virtual node
##vnode: virtual node, virtual node
Document, element, node
Simply put, the node to be rendered by vue on the page is a virtual node
<template id="my-app">
<div class="title" style="font-size: 30px; color: red;">哈哈哈</div>
</template> const vnode = {
type: "div",
props: {
class: "title",
style: {
"font-size": "30px",
color: "red",
},
},
children: "哈哈哈",
}; children: [
{
// 子元素
},
{
// 子元素
}
],2 vDOM Virtual DOM
is the same as real DOM. If there are real nodes, there will be real DOM. Then if there are virtual nodes, then There is a virtual DOM Of course, the same goes for a virtual DOM tree. There is also a VNode tree, which means there is no need to worry about it. It is probably as follows <template id="my-app">
<div>
<div>
<p></p>
<p></p>
<ul>
<li></li>
<li></li>
<li></li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
</template>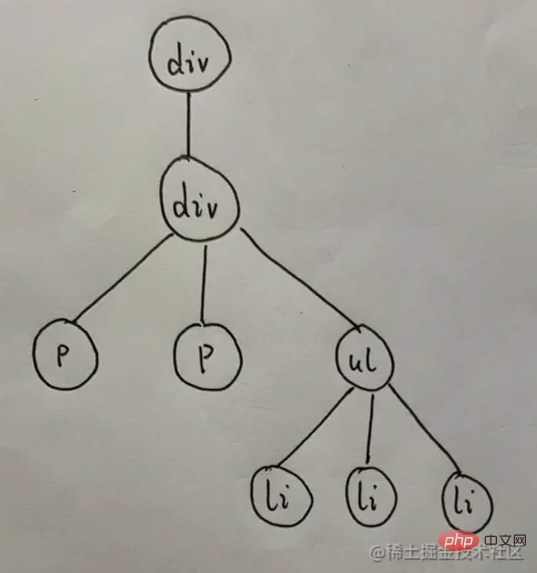
When the virtual DOM is rendered into the real DOM, it is not necessarily exactly the same. This involves components, which I will talk about later when I have the opportunity
3 Rendering process
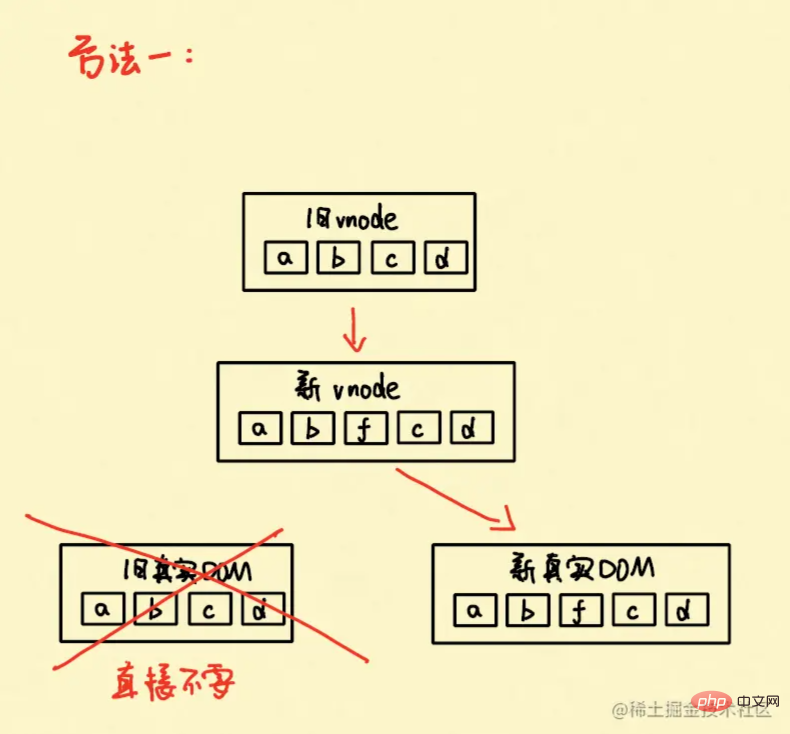
##4 Case: Insert fAfter understanding the previous ones, let’s get down to business. Only one case is needed to fully understand the role of key. Let’s start with
Let’s look at this simple case (without adding key)
<ul>
<li v-for="item in letters">{{item}}</li>
</ul> data() {
return {
letters: ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd']
}
},
methods: {
insertF() {
this.letters.splice(2, 0, 'f');
}
},It can be seen that the purpose of this question is to insert an f
between ab and cd. After understanding this simple case, we started to think about whether there is any way to insert it into the real DOM. What?
There are three following types:
Method one (ordinary method)
 Instructions: Directly Delete the previous dom and re-render it with the new vnode
Instructions: Directly Delete the previous dom and re-render it with the new vnode
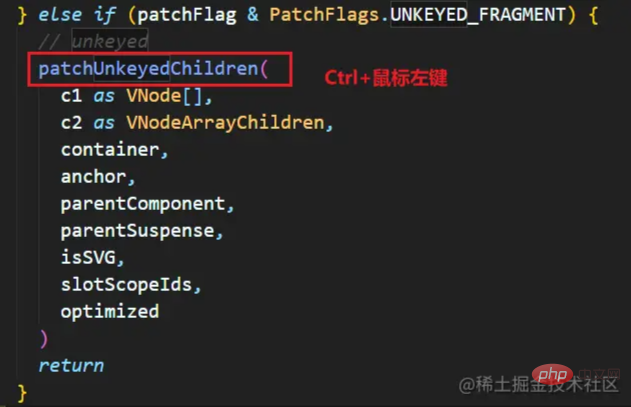 Note: This is vue's default diff algorithm when there is no key. The corresponding source code is as shown in the figure.
Note: This is vue's default diff algorithm when there is no key. The corresponding source code is as shown in the figure.
Vue will judge whether you have brought the key through the judgment statement
 The following is the situation when there is no key
The following is the situation when there is no key
 Then check
Then check
, you can view the execution process of the diff algorithmHere is a brief description:
- Get the old vnode and the new vnode
- Determine which of the two arrays has the smaller length (use the smaller one Patching a larger array will not cause the array to go out of bounds)
- Start patching, as mentioned in the picture, and continue patching until there is no space (at c of the new vnode) , divided into two situations
-
- old vnode
When old vnode > new vnode, uninstall the old vnode node
Similarly, you can view it by following the steps of method two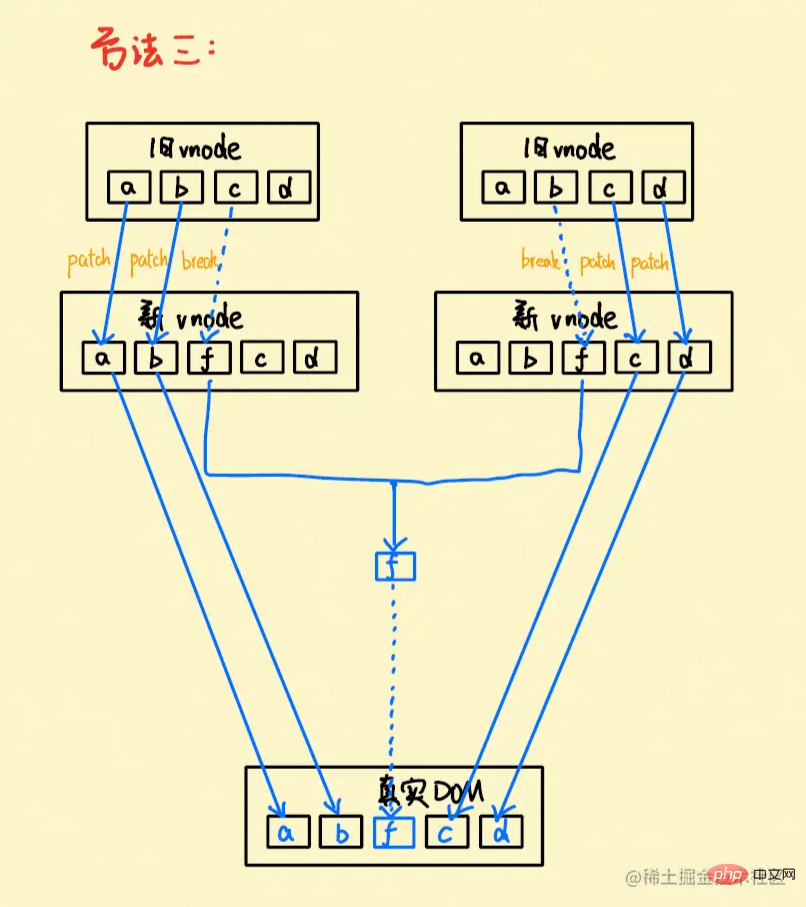 patchKeyedChildren()
patchKeyedChildren()
This method is the essence, it starts to get complicated
-
Patch from the tail, when it is found to be different (here c !== f), break
So far, a, b, c, d have is rendered into the real DOM, the only difference is f, let’s start looking for f
-
to judge:
If the old vnode
If new vnode > old vnode, uninstall the redundant nodes of the old vnode
If new vnode = old vnode, this is very complicated. Regardless of the order, try to patch the same items in it, and then perform uninstall and mount operations
Summary: At this point, the entire case process has been completely gone through. The author can only understand this. This article combines coderwhy’s video and some of my own thoughts (video source: https://ke.qq.com/course /3453141), so there may be something wrong, everyone is welcome to criticize and correct me
[Related recommendations: "vue.js tutorial"]
The above is the detailed content of In-depth analysis of the key in vue to see what the key can be used for!. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1666
1666
 14
14
 1425
1425
 52
52
 1328
1328
 25
25
 1273
1273
 29
29
 1253
1253
 24
24
 How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Using Bootstrap in Vue.js is divided into five steps: Install Bootstrap. Import Bootstrap in main.js. Use the Bootstrap component directly in the template. Optional: Custom style. Optional: Use plug-ins.
 How to add functions to buttons for vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
How to add functions to buttons for vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
You can add a function to the Vue button by binding the button in the HTML template to a method. Define the method and write function logic in the Vue instance.
 How to use watch in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
How to use watch in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
The watch option in Vue.js allows developers to listen for changes in specific data. When the data changes, watch triggers a callback function to perform update views or other tasks. Its configuration options include immediate, which specifies whether to execute a callback immediately, and deep, which specifies whether to recursively listen to changes to objects or arrays.
 How to return to previous page by vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
How to return to previous page by vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
Vue.js has four methods to return to the previous page: $router.go(-1)$router.back() uses <router-link to="/" component window.history.back(), and the method selection depends on the scene.
 What does vue multi-page development mean?
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
What does vue multi-page development mean?
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Vue multi-page development is a way to build applications using the Vue.js framework, where the application is divided into separate pages: Code Maintenance: Splitting the application into multiple pages can make the code easier to manage and maintain. Modularity: Each page can be used as a separate module for easy reuse and replacement. Simple routing: Navigation between pages can be managed through simple routing configuration. SEO Optimization: Each page has its own URL, which helps SEO.
 React vs. Vue: Which Framework Does Netflix Use?
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:19 AM
React vs. Vue: Which Framework Does Netflix Use?
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:19 AM
Netflixusesacustomframeworkcalled"Gibbon"builtonReact,notReactorVuedirectly.1)TeamExperience:Choosebasedonfamiliarity.2)ProjectComplexity:Vueforsimplerprojects,Reactforcomplexones.3)CustomizationNeeds:Reactoffersmoreflexibility.4)Ecosystema
 How to reference js file with vue.js
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
How to reference js file with vue.js
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
There are three ways to refer to JS files in Vue.js: directly specify the path using the <script> tag;; dynamic import using the mounted() lifecycle hook; and importing through the Vuex state management library.
 How to use vue traversal
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
How to use vue traversal
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
There are three common methods for Vue.js to traverse arrays and objects: the v-for directive is used to traverse each element and render templates; the v-bind directive can be used with v-for to dynamically set attribute values for each element; and the .map method can convert array elements into new arrays.




