An in-depth analysis of non-blocking I/O in Node.js
This article will take you through the non-blocking I/O in Node.js, I hope it will be helpful to you!

How to understand the non-blocking I/O of NodeJs
1. I/O: Input /output refers to the input and output of a system
2. The main difference between non-blocking and blocking is:In the process between receiving input and outputting results, Can you continue to receive other input? [Recommended learning: "nodejs tutorial"]
Example:
For example: Going out to eat
There are usually two ways to go out to eat:
1 Go to the canteen to eat: queue up for food
[Queue] - [Wait for the person in front Someone cooks] - [Cook for yourself] - [Eat]
2 Go to the restaurant to eat
[Sit down] - [Order food ] - [Waiting] - [Eating]
For these two ways of eating:
1 Eating in the canteen: For those who serve meals Generally speaking, you have to wait until the previous person has finished eating before you can order the next person's meal. This process is the blocking mode
2 Eating in a restaurant: Go to a restaurant to eat, and the waiter will finish your order. After the meal, continue to handle the next person's ordering needs. When your meal is ready, the meal will be delivered to you. For the waiter, this process is a non-blocking process
Understanding the key points of non-blocking I/O
1 Determine a to perform I/O operations System, for example: in the above example of cooking, the system that performs I/O is the service staff.
2 Can other I/O be performed while the system is performing I/O operations?
Code Demonstration
In the sample code, we introduced a library glob. This library is mainly used to find files matching conditions. For details, please see https://www.npmjs.com/package/glob
First, we use the synchronization method provided by glob to read the file
const glob = require("glob");
let result = null;
result = glob.sync(__dirname + "/**/*");
console.log(result);The result is a File array :
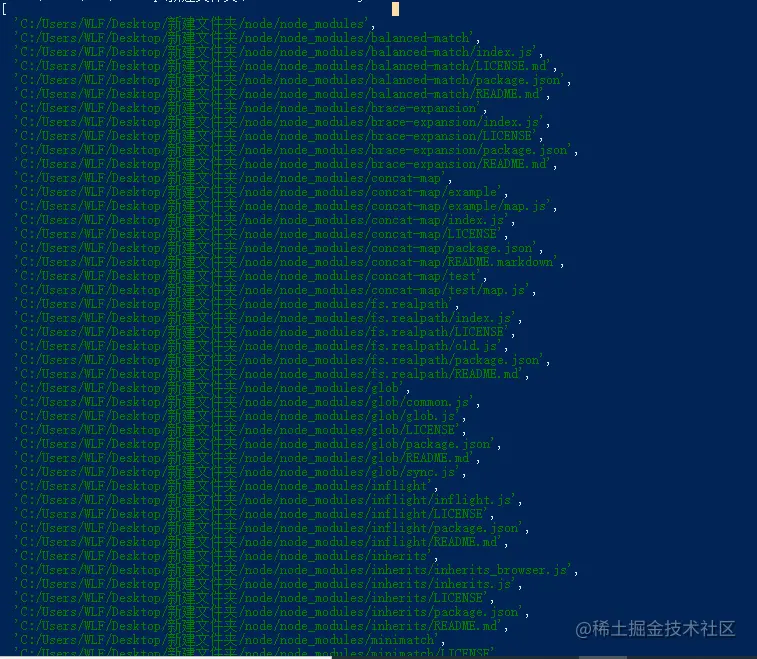
Let’s take a look at the execution time of this synchronization operation:
const glob = require("glob");
let result = null;
console.time("glob");
result = glob.sync(__dirname + "/**/*");
console.timeEnd("glob");Result:
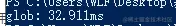
An operation of reading a file will block the process for 33 milliseconds, which is unacceptable!
Next, we use asynchronous method to read the file
let result2 = null;
console.time("glob2");
glob(__dirname + "/**/*", (err, res) => {
console.log("glob over");
});
console.timeEnd("glob2");Result:
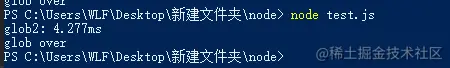
Execute asynchronously Reading the file took a total of 4 milliseconds, and we could also perform other operations while reading the file asynchronously.
Conclusion
After studying, I believe everyone has a deeper understanding of non-blocking I/O, so see you next time. study hard, improve every day!
For more programming related knowledge, please visit: Programming Video! !
The above is the detailed content of An in-depth analysis of non-blocking I/O in Node.js. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Detailed graphic explanation of the memory and GC of the Node V8 engine
Mar 29, 2023 pm 06:02 PM
Detailed graphic explanation of the memory and GC of the Node V8 engine
Mar 29, 2023 pm 06:02 PM
This article will give you an in-depth understanding of the memory and garbage collector (GC) of the NodeJS V8 engine. I hope it will be helpful to you!
 An article about memory control in Node
Apr 26, 2023 pm 05:37 PM
An article about memory control in Node
Apr 26, 2023 pm 05:37 PM
The Node service built based on non-blocking and event-driven has the advantage of low memory consumption and is very suitable for handling massive network requests. Under the premise of massive requests, issues related to "memory control" need to be considered. 1. V8’s garbage collection mechanism and memory limitations Js is controlled by the garbage collection machine
 Let's talk about how to choose the best Node.js Docker image?
Dec 13, 2022 pm 08:00 PM
Let's talk about how to choose the best Node.js Docker image?
Dec 13, 2022 pm 08:00 PM
Choosing a Docker image for Node may seem like a trivial matter, but the size and potential vulnerabilities of the image can have a significant impact on your CI/CD process and security. So how do we choose the best Node.js Docker image?
 Node.js 19 is officially released, let's talk about its 6 major features!
Nov 16, 2022 pm 08:34 PM
Node.js 19 is officially released, let's talk about its 6 major features!
Nov 16, 2022 pm 08:34 PM
Node 19 has been officially released. This article will give you a detailed explanation of the 6 major features of Node.js 19. I hope it will be helpful to you!
 Let's talk in depth about the File module in Node
Apr 24, 2023 pm 05:49 PM
Let's talk in depth about the File module in Node
Apr 24, 2023 pm 05:49 PM
The file module is an encapsulation of underlying file operations, such as file reading/writing/opening/closing/delete adding, etc. The biggest feature of the file module is that all methods provide two versions of **synchronous** and **asynchronous**, with Methods with the sync suffix are all synchronization methods, and those without are all heterogeneous methods.
 Let's talk about the event loop in Node
Apr 11, 2023 pm 07:08 PM
Let's talk about the event loop in Node
Apr 11, 2023 pm 07:08 PM
The event loop is a fundamental part of Node.js and enables asynchronous programming by ensuring that the main thread is not blocked. Understanding the event loop is crucial to building efficient applications. The following article will give you an in-depth understanding of the event loop in Node. I hope it will be helpful to you!
 Let's talk about how to use pkg to package Node.js projects into executable files.
Dec 02, 2022 pm 09:06 PM
Let's talk about how to use pkg to package Node.js projects into executable files.
Dec 02, 2022 pm 09:06 PM
How to package nodejs executable file with pkg? The following article will introduce to you how to use pkg to package a Node project into an executable file. I hope it will be helpful to you!
 Let's talk about the GC (garbage collection) mechanism in Node.js
Nov 29, 2022 pm 08:44 PM
Let's talk about the GC (garbage collection) mechanism in Node.js
Nov 29, 2022 pm 08:44 PM
How does Node.js do GC (garbage collection)? The following article will take you through it.







