 Web Front-end
Web Front-end
 Vue.js
Vue.js
 Analyze the two-way binding principle of observer data in Vue (code sharing)
Analyze the two-way binding principle of observer data in Vue (code sharing)
Analyze the two-way binding principle of observer data in Vue (code sharing)
In the previous article "A brief analysis of some operating methods of Array objects in JS (with code)", we learned about some operating methods of Array objects in JS. The following article will give you an understanding of the two-way binding principle of observer data in Vue. Let's take a look.

vueData two-way binding principle and simple implementation
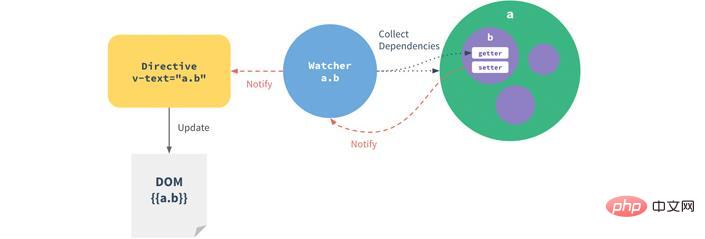
1 )vue data two-way binding principle-observer
2)vue data two-way binding principle-wather
3)vue data Two-way binding principle - parser Complie
vueData two-way binding principle, and simple implementation
Fuck meow's underlying principle, framework core, I only use Jquery when writing code.
Personally, I feel that no matter whether we have been interacting with it for a long time, we should still look at the core things. Learn more about how experts achieve it, so that you can learn more knowledge and grow and progress. If someone asked one day about the implementation principle of a certain kind of frame underwear, they would just be confused.
The ways to implement data binding are roughly as follows:
-
Publisher-Subscriber Pattern (
backbone.js) Dirty value checking (
angular.js)Data hijacking (
vue.js)
vue.js uses data hijacking combined with the publisher-subscriber model to hijack each property through Object.defineProperty() The setter and getter publish messages to subscribers when data changes, triggering corresponding listening callbacks.
If you have written C#winform custom controls, I want to better understand the subsequent logic and implementation principles
When in C# If a property of the control changes, refresh the view
priveate int a ;
public int A
{
get { return a; }
set { if(a!=value){a = value; Invalidate(); } }
}
# 当a的值发生变化, 就重绘视图Let’s take a look at the Object.defineProperty(obj, prop, descriptor) method
Address: https://developer. mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Object/defineProperty
Object.defineProperty()The method will define an object directly New properties, or modify existing properties of an object, and returns the object.
objThe target object that needs to be operatedpropThe target object needs to be defined or modified The name of the attribute.descriptorDescriptor of the attribute to be defined or modified
<strong>descriptor</strong>
configurableIf and only if theconfigurableof this property istrue, this property description The character can be changed and the attribute can be deleted from the corresponding object. Default isfalse.enumerableThis attribute can appear in the object only if theenumerableof the attribute istruein the enumeration properties. Default isfalse. The data descriptor also has the following optional key values:valueThe value corresponding to this attribute. Can be any validJavaScriptvalue (numeric value, object, function, etc.). Default isundefined.writableIf and only if thewritableof the property istrue, the property can be assigned the operator Change. Default isfalse. The access descriptor also has the following optional key values:getA method that provides agetterfor the property, if there is nogetterisundefined. The return value of this method is used as the attribute value. Default isundefined.set is a method that provides
setterto the property. If there is nosetter, it will beundefined. This method will accept a unique parameter and assign the parameter's new value to the property. Default isundefined.
Let’s first implement a simple data hijacking
var A = {};
var a = "";
Object.defineProperty(A, "a", {
set: function (value) {
a = value;
},
get: function () {
return "My name is " + a;
},
});
A.a = "chuchur";
console.log(A.a); // My name is chuchurIt’s not just that simple, let’s take a look at the code of vue
<div id="app">
<input type="text" v-model="word" />
<p>{{word}}</p>
<button v-on:click="sayHi">change model</button>
</div>
<script>
var vm = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
word: "Hello World!",
},
methods: {
sayHi: function () {
this.word = "Hi, everybody!";
},
},
});
</script> For the simple data hijacking that has been implemented, if there are multiple attributes, it is necessary to implement a data listener Observer, which can monitor all attributes of the data object, and a subscriber DepTo collect changes in these attributes to notify subscribers of the
element node’s v-model, v-on:click, you need to implement a command parser Compile , scan and parse the instructions of each element node, replace the data according to the instruction template, and bind the corresponding update function
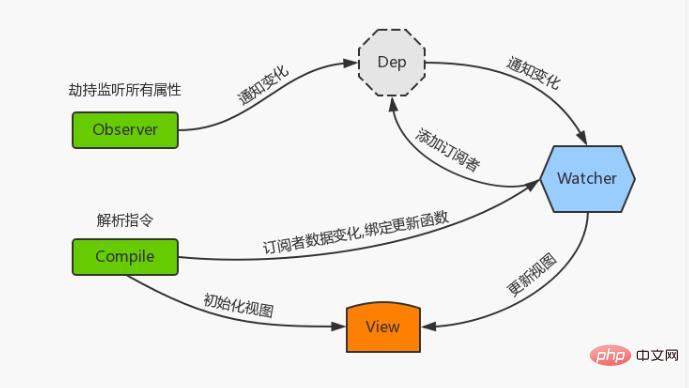
最后实现一个订阅者Watcher,作为连接Observer和Compile的桥梁,能够订阅并收到每个属性变动的通知,执行指令绑定的相应回调函数,从而更新视图
大概的流程图如下:
实现Observer
将需要observe的数据对象进行递归遍历,包括子属性对象的属性,都加上setter和getter这样的话,给这个对象的某个值赋值,就会触发setter,那么就能监听到了数据变化
// observe
function observe(data) {
if (data && typeof data === "object") {
// 取出所有属性遍历
Object.keys(data).forEach(function (key) {
defineReactive(data, key, data[key]);
});
}
return;
}
function defineReactive(data, key, val) {
observe(val); // 监听子属性
Object.defineProperty(data, key, {
enumerable: true, // 可枚举
configurable: false, // 不能再define
get: function () {
return val;
},
set: function (value) {
console.log("监听到值变化了: ", val, "==>", value);
val = value;
},
});
}
var A = {
fristName: "chuchur",
age: 29,
};
observe(A);
A.fristName = "nana"; //监听到值变化了: chuchur ==> nana
A.age = 30; //监听到值变化了: 29 ==> 30这样就实现了多个属性的监听,接下来就是实现订阅器Dep,当这些属性变化的时候,触发通知notify,告诉执行订阅者执行更新函数
//Dep
function Dep() {
this.subs = [];
}
Dep.prototype = {
addSub: function (sub) {
this.subs.push(sub);
},
notify: function () {
this.subs.forEach(function (sub) {
sub.update();
});
},
};把订阅器植入到监听器里
function defineReactive(data, key, val) {
var dep = new Dep()
observe(val); //监听子属性
Object.defineProperty(data, key, {
set: function(value) {
dep.notify() //发出通知, 我被改变了
}
});
}至此,简陋的监听器就实现完成了,接下来继续完成Watcher。
推荐学习:vue.js教程
The above is the detailed content of Analyze the two-way binding principle of observer data in Vue (code sharing). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Using Bootstrap in Vue.js is divided into five steps: Install Bootstrap. Import Bootstrap in main.js. Use the Bootstrap component directly in the template. Optional: Custom style. Optional: Use plug-ins.
 How to add functions to buttons for vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
How to add functions to buttons for vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
You can add a function to the Vue button by binding the button in the HTML template to a method. Define the method and write function logic in the Vue instance.
 How to use watch in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
How to use watch in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
The watch option in Vue.js allows developers to listen for changes in specific data. When the data changes, watch triggers a callback function to perform update views or other tasks. Its configuration options include immediate, which specifies whether to execute a callback immediately, and deep, which specifies whether to recursively listen to changes to objects or arrays.
 What does vue multi-page development mean?
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
What does vue multi-page development mean?
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Vue multi-page development is a way to build applications using the Vue.js framework, where the application is divided into separate pages: Code Maintenance: Splitting the application into multiple pages can make the code easier to manage and maintain. Modularity: Each page can be used as a separate module for easy reuse and replacement. Simple routing: Navigation between pages can be managed through simple routing configuration. SEO Optimization: Each page has its own URL, which helps SEO.
 How to reference js file with vue.js
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
How to reference js file with vue.js
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
There are three ways to refer to JS files in Vue.js: directly specify the path using the <script> tag;; dynamic import using the mounted() lifecycle hook; and importing through the Vuex state management library.
 How to return to previous page by vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
How to return to previous page by vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
Vue.js has four methods to return to the previous page: $router.go(-1)$router.back() uses <router-link to="/" component window.history.back(), and the method selection depends on the scene.
 How to use vue traversal
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
How to use vue traversal
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
There are three common methods for Vue.js to traverse arrays and objects: the v-for directive is used to traverse each element and render templates; the v-bind directive can be used with v-for to dynamically set attribute values for each element; and the .map method can convert array elements into new arrays.
 How to jump to the div of vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 09:18 AM
How to jump to the div of vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 09:18 AM
There are two ways to jump div elements in Vue: use Vue Router and add router-link component. Add the @click event listener and call this.$router.push() method to jump.





