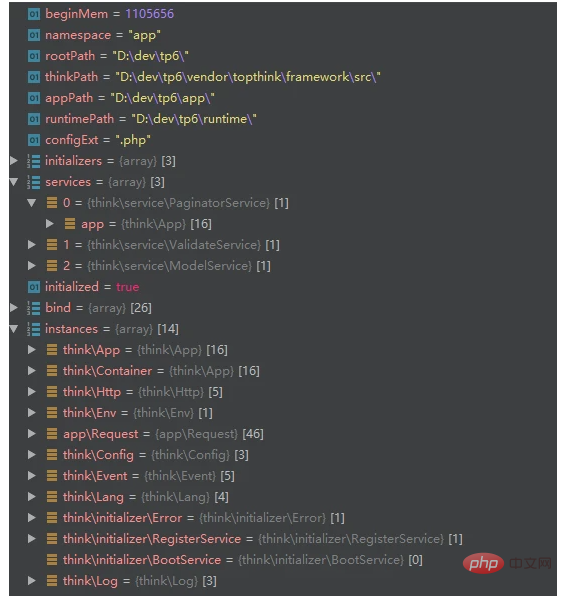
runWithRequest () method
In the run() method of the Http class , after obtaining the instance of the think\\Request class, the program then executes $response = $this->runWithRequest(request);. Among them, the first few lines of the runWithRequest() method are as follows:
protected function runWithRequest(Request $request)
{
$this->initialize();
// 加载全局中间件
$this->loadMiddleware();
.
.
.The first line of this method executes $this->initialize(); to initialize the application , let’s analyze this initialization operation in detail. Http The initialize() method of the class:
protected function initialize()
{
//如果还未初始化,则初始化之
if (!$this->app->initialized()) {
$this->app->initialize();
}
} actually calls the initialize()# of the App class ## method. Code of this method:
public function initialize()
{
// 设置应用状态为已经初始化
$this->initialized = true;
//记录开始时间
$this->beginTime = microtime(true);
//记录起始内存使用量
$this->beginMem = memory_get_usage();
// ==( A )== 加载环境变量
// $this->env跟前面的(new App())->http和$this->config都是同样的套路
if (is_file($this->rootPath . '.env')) {
$this->env->load($this->rootPath . '.env');
}
//设置配置文件后缀
$this->configExt = $this->env->get('config_ext', '.php');
// ==( B )== 设置调试模式
$this->debugModeInit();
// ==( C )== 加载应用文件和配置等操作
$this->load();
// 加载框架默认语言包
$langSet = $this->lang->defaultLangSet();
// 框架目录下对应的语言包
// 比如:D:\dev\tp6\vendor\topthink\framework\src\lang\zh-cn.php
$this->lang->load($this->thinkPath . 'lang' . DIRECTORY_SEPARATOR . $langSet . '.php');
// 加载应用默认语言包
// 这个会扫描「app/lang」里面,对应语言包文件夹的所有「.php」文件
// 比如,app/lang/zh-cn/* 下的所有文件
// 然后加载解析
$this->loadLangPack($langSet);
// 监听AppInit
$this->event->trigger('AppInit');
// 设置时区
date_default_timezone_set($this->config->get('app.default_timezone', 'Asia/Shanghai'));
// ==( D )== 初始化
// 初始化错误和异常处理、注册系统服务和初始化系统服务
foreach ($this->initializers as $initializer) {
$this->make($initializer)->init($this);
}
return $this;
}$this->env->load($this->rootPath . '.env');, among them, $this->env, the principle is the same as the previous (new App())->http (see the first article), it can be obtained Instance of class \think\Env. After obtaining the Env class instance, call the load() method, and the passed-in parameter is the address of the .env file. The load() method is implemented as follows:
public function load(string $file): void
{
$env = parse_ini_file($file, true) ?: [];
$this->set($env);
}.env file, it calls the set() method to The configuration is saved in the $data member variable of the Env class. set() Method code:
public function set($env, $value = null): void
{
if (is_array($env)) {
//全部KEY转为大写字母
$env = array_change_key_case($env, CASE_UPPER);
foreach ($env as $key => $val) {
//有二级配置的,转为KEY1_KEY2 => $v 的形式
if (is_array($val)) {
foreach ($val as $k => $v) {
$this->data[$key . '_' . strtoupper($k)] = $v;
}
} else {
$this->data[$key] = $val;
}
}
//ENV的值不是数组的情况
} else {
$name = strtoupper(str_replace('.', '_', $env));
$this->data[$name] = $value;
}
}.env is probably like this: 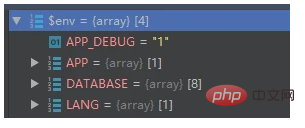
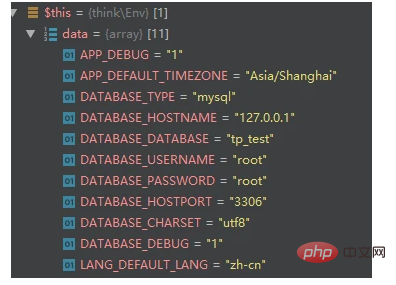
$this->set($env) What you get after that is probably like this:
$this->debugModeInit() See the comments for details on the operating principle.
protected function debugModeInit(): void
{
// 应用调试模式
if (!$this->appDebug) {
$this->appDebug = $this->env->get('app_debug') ? true : false;
// 关闭错误显示
ini_set('display_errors', 'Off');
}
// 如果不是命令行模式
if (!$this->runningInConsole()) {
// 重新申请一块比较大的buffer
// php缓冲控制
// 参考:https://www.php.net/manual/en/ref.outcontrol.php
// https://www.cnblogs.com/saw2012/archive/2013/01/30/2882451.html
// 新版PHP默认开启缓冲区ob_start(),ob_get_level() == 1
if (ob_get_level() > 0) {
// 相当于ob_get_contents() 和 ob_clean()
// 获取缓冲区内容并删除缓冲区内容
$output = ob_get_clean();
}
// 开启新的缓冲区控制
ob_start();
if (!empty($output)) {
// 由于开启了新的缓冲区控制,
// 这里不会直接输出$output
// 而是等到依次执行了ob_flush()和flash()之后才将内容输出到浏览器
echo $output;
}
}
}$this->appDebug = $this->env->get('app\_debug') ? true : false; Get the configuration of debug mode, and then judge: if(!$this->appDebug).
$this->load();, the "load" method is implemented as follows:
protected function load(): void
{
$appPath = $this->getAppPath();
// 加载「app」目录下的「common.php」文件
if (is_file($appPath . 'common.php')) {
include_once $appPath . 'common.php';
}
// 加载核心目录下的「helper.php」文件
// 可以看到,这里的加载顺序:先「common.php」,后「helper.php」
// 且「helper.php」中的函数包裹在「if (!function_exists('xxx'))」下
// 所以可以在「common.php」文件中覆盖系统定义的助手函数
include_once $this->thinkPath . 'helper.php';
$configPath = $this->getConfigPath();
$files = [];
// glob的作用是扫描给定路径模式下的文件,非常好用
// 这里扫描「config」目录下的所有「.php」文件
if (is_dir($configPath)) {
$files = glob($configPath . '*' . $this->configExt);
}
foreach ($files as $file) {
// $this->config 还是同样的套路获得了「Config」类的实例
// 「load」的第二个参数为一级配置名,这里传入一个文件名,所有文件名作为一级配置
// 比如「app.php」配置文件,一级配置为「app」
// 在 「Config」类作用域下的操作:
// 「load」加载文件后,通过「parse」方法解析文件内容
// 最后,通过「set」方法将所有配置合并了「config」成员变量
$this->config->load($file, pathinfo($file, PATHINFO_FILENAME));
}
// 加载「app」目录下的「event.php」文件
if (is_file($appPath . 'event.php')) {
$this->loadEvent(include $appPath . 'event.php');
}
// 注册自定义的服务
if (is_file($appPath . 'service.php')) {
$services = include $appPath . 'service.php';
foreach ($services as $service) {
$this->register($service);
}
}
}$config of the Config class Member variables load the "event.php" file in the "app" directory, and load and register custom services.
foreach ($this->initializers as $initializer) {
$this->make($initializer)->init($this);
}initializers The values of the array are as follows:
protected $initializers = [ Error::class, //错误处理类 RegisterService::class, //注册系统服务类 BootService::class, //启动系统服务 ];
protected $services = [ PaginatorService::class, ValidateService::class, ModelService::class, ];
init method, these services are registered to the system service and merged with the previous custom service. Its main implementation code is:
foreach ($services as $service) {
if (class_exists($service)) {
// 注册到系统服务
$app->register($service);
}
}init method of this class only calls the boot method of the App class. The function of this method is to initialize each system service, that is, to call each service The boot method. The startup system service class is implemented as follows:
class BootService
{
public function init(App $app)
{
$app->boot();
}
}App class’s boot method:
public function boot(): void
{
array_walk($this->services, function ($service) {
$this->bootService($service);
});
}bootService Method:
public function bootService($service)
{
if (method_exists($service, 'boot')) {
return $this->invoke([$service, 'boot']);
}
}boot method of each service separately to initialize the registered service. As you can see from the above code, there are three sources of services registered by the system:
- The system comes with it, such as
- PaginatorService
,ValidateService,ModelService; It is customized in the "service.php" file in the app directory; it is defined in the "service.php" file in the - vendor directory.