composer require webonyx/graphql-php
Detailed explanation of how to install and use GraphQL in PHP
This article takes you through GraphQL and introduces in detail how to install and use GraphQL in PHP. It has certain reference value. Friends in need can refer to it. I hope it will be helpful to everyone.

About GraphQL
GraphQL is a modern way to build HTTP API interfaces, and clients can on-demandQuery the required data.
GraphQL can improve the flexibility of API calls. We can request the API to obtain the required data just like writing database query statements. This is very useful for building complex API queries.
Comparison with REST
The core idea of REST is resources. Each resource can be represented by a URL. You can access the URL through a GET request to obtain it. this resource. According to the definition of most APIs today, you are likely to get a data response in JSON format. The whole process is roughly like this:
GET /user/1
{
"username":"姓名",
"age":20,
"sex":"男"
}GET /book/1
{
"book":"书名",
"author":"作者",
"country":"中国"
}As can be seen from the above example, if the front end requires user /1 and book/1 need to call 2 times interface, and if the front end only needs username# in user/1 ##, and the above interface obtains data other than username, then for the front end, data other than username is nowhere available, resulting in a waste of resources.
GraphQL to query, compared with the REST method, we only need to call once and can query the fields we specify , avoiding the waste of resources and being more efficient.
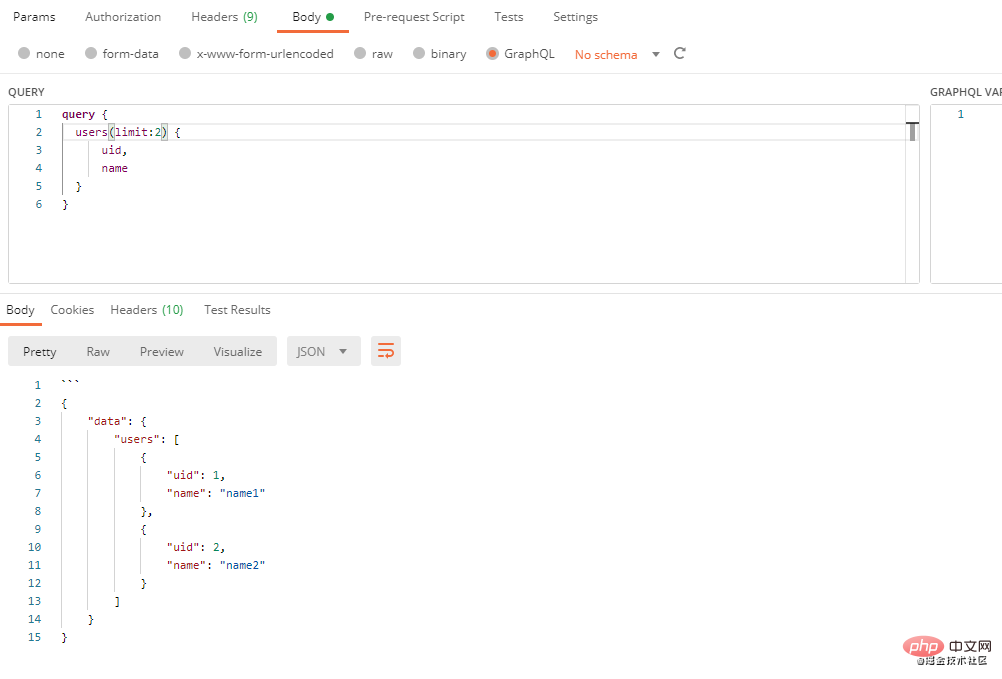
query {
user(id:1) {
username
}
book(id:1){
book,
author,
country
}
}PHP Video Tutorial"
Install the graphql-php packagecomposer require webonyx/graphql-php
Copy after login
composer require webonyx/graphql-php
Start
1. After the installation is complete, we first write a simple example to see how to use graphql-php. The specific code is as follows: In this code, we define a file namedphoneNumber field, and then call the code we wrote through postman.
<?php
require_once __DIR__ . '/vendor/autoload.php';
use GraphQL\Type\Schema;
use GraphQL\Type\Definition\ObjectType;
use GraphQL\Type\Definition\Type;
use GraphQL\GraphQL;
$queryType = new ObjectType([
'name' => 'Query',
'fields' => [
'phoneNumber' => [
'type' => Type::int(),
'resolve' => function () {
return 1875555555;
}
]
],
]);
$schema = new Schema([
'query' => $queryType,
]);
$rawInput = file_get_contents('php://input');
$input = json_decode($rawInput, true);
$query = $input['query'];
$variableValues = isset($input['variables']) ? $input['variables'] : null;
try {
$rootValue = ['prefix' => 'prefix: '];
$result = GraphQL::executeQuery($schema, $query, $rootValue, null, $variableValues);
$output = $result->toArray();
} catch (\Exception $e) {
$output = [
'errors' => [
[
'message' => $e->getMessage()
]
]
];
}
header('Content-Type: application/json');
echo json_encode($output);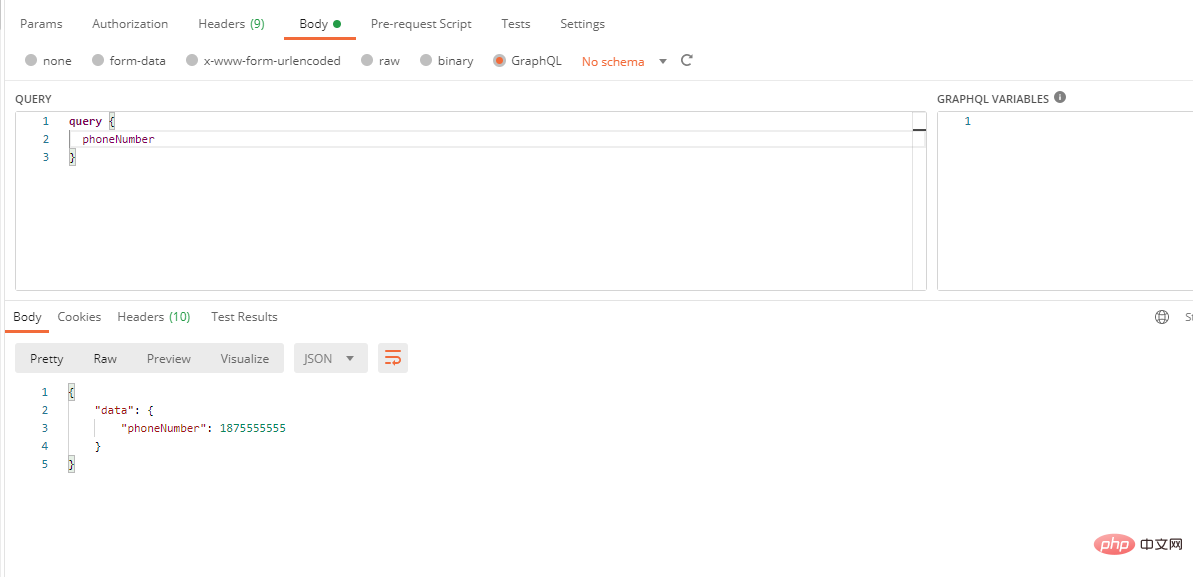
From the above example, we can see that the example mainly introduces 4 classes
use GraphQL\Type\Schema; use GraphQL\Type\Definition\ObjectType; use GraphQL\Type\Definition\Type; use GraphQL\GraphQL;
Schema is a container of type hierarchy. It accepts the root type in the constructor and provides methods for the internal GrahpQL tooling to receive your type information.
Configuration OptionsAn array containing the following options:
| Type | Notes | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ObjectType | | Required. Read the object type containing root-level fields in the API (usually named "Query"), used to read data | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ObjectType | | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ##ObjectType | is reserved for future description implementations. Currently it is graphql-js | Compatible with self-checking queries, used for various clients (such as Relay or GraphiQL)directives | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Directive[] | includes built-in directives @skip | and @include by default. If you pass custom directives and still want to use the built-in directives, add them explicitly. For example: array_merge(GraphQL::getStandardDirectives(), [$myCustomDirective]); ##types | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Object type class table, which cannot be discovered by graphql-php during static schema parsing. | In most cases, the object type is not directly referenced in the field, but it is still used when it is part of the schema, because it implements a call in resolveType to resolve to The interface for this object type. Note that you don't need to pass all types here, it's just a workaround for your specific use case. typeLoader | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
##function($name) Returns the given type instance name . In the case of multiple calls, the same instance must be returned. See the lazy type loading section below. | ObjectType类GraphQL\Type\Definition\ObjectType Copy after login 对象类型是典型的 GraphQL 应用程序中使用最频繁的基元。 配置选项
内置标量类型<?php use GraphQL\Type\Definition\Type; // 内置标量类型 Type::string(); // String 类型 Type::int(); // Int 类型 Type::float(); // Float 类型 Type::boolean(); // Boolean 类型 Type::id(); // ID 类型 Copy after login 字段参数GraphQL 对象类型上的所有字段都有 0 个或多个参数,使用在 args 的字段定义上。每个参数数组参考以下说明:
示例 $queryType = new ObjectType([
'name' => 'Query',
'fields' => [
'phoneNumber' => [
'type' => Type::int(),
'resolve' => function () {
return 1875555555;
}
]
],
]);Copy after login GraphQL 类GraphQL类主要在查询的时候用到,我们可以用 GraphQL::executeQuery 方法来执行查询 executeQuery 方法的参数说明
use GraphQL\GraphQL;
$result = GraphQL::executeQuery(
$schema,
$queryString,
$rootValue = null,
$context = null,
$variableValues = null,
$operationName = null,
$fieldResolver = null,
$validationRules = null
);Copy after login 简单示例我们介绍完GraphQL几个概念之后,用几个简单的示例带大家来体验一下。 普通示例在这个示例中我们定义了2个字段,分别是 <?php
require_once __DIR__ . '/vendor/autoload.php';
use GraphQL\Type\Definition\ObjectType;
use GraphQL\Type\Definition\Type;
use GraphQL\GraphQL;
use GraphQL\Type\Schema;
$queryType = new ObjectType([
'name' => 'Query',
'fields' => [
'phoneNumber' => [
'type' => Type::int(),
'resolve' => function () {
return 1875555555;
}
],
'echo' => [
'type' => Type::string(),
'args' => [
'message' => Type::string(),
],
'resolve' => function ($root, $args) {
return 'echo msg result:' . ($args['message'] ?? 'nothing');
}
],
],
]);
$schema = new Schema([
'query' => $queryType
]);
$rawInput = file_get_contents('php://input');
$input = json_decode($rawInput, true);
$query = $input['query'];
$variableValues = isset($input['variables']) ? $input['variables'] : null;
try {
$rootValue = ['prefix' => 'prefix: '];
$result = GraphQL::executeQuery($schema, $query, $rootValue, null, $variableValues);
$output = $result->toArray();
} catch (\Exception $e) {
$output = [
'errors' => [
[
'message' => $e->getMessage()
]
]
];
}
header('Content-Type: application/json');
echo json_encode($output);Copy after login 执行示例代码结果
我们可以看到,在请求时我们传了 对象示例我们在上面说过,对象类型是典型的 GraphQL 应用程序中使用最频繁的基元,一个对象类型里面可以包含宁外一个对象类型,我们可以新定义一个名为 <?php
require_once __DIR__ . '/vendor/autoload.php';
use GraphQL\Type\Definition\ObjectType;
use GraphQL\Type\Definition\Type;
use GraphQL\GraphQL;
use GraphQL\Type\Schema;
$userType = new ObjectType([
'name' => 'userType',
'description' => '用户详情',
'fields' => [
'uid' => [
'type' => Type::int(),
'description' => '用户ID'
],
'name' => Type::string()
]
]);
$queryType = new ObjectType([
'name' => 'Query',
'fields' => [
'oneUser' => [
'type' => $userType, // 我们这里指定type为我们上面创建的$userType
'description' => '用户列表',
'args' => [
'uid' => [
'type' => Type::int(),
'defaultValue' => 222
]
],
'resolve' => function($root, $args) {
return [
"uid" => $args['user_id'] ?? 3,
"name" => "xzl",
];
}
],
]
]);
$schema = new Schema([
'query' => $queryType
]);
$rawInput = file_get_contents('php://input');
$input = json_decode($rawInput, true);
$query = $input['query'];
$variableValues = isset($input['variables']) ? $input['variables'] : null;
try {
$rootValue = ['prefix' => 'prefix: '];
$result = GraphQL::executeQuery($schema, $query, $rootValue, null, $variableValues);
$output = $result->toArray();
} catch (\Exception $e) {
$output = [
'errors' => [
[
'message' => $e->getMessage()
]
]
];
}
header('Content-Type: application/json');
echo json_encode($output);Copy after login 执行示例代码结果
列表示例在平时的开发请求中,我们从后端接口获取数据的时候,大部分都是以列表的形式返回的,我们可以通过 <?php
require_once __DIR__ . '/vendor/autoload.php';
use GraphQL\Type\Definition\ObjectType;
use GraphQL\Type\Definition\Type;
use GraphQL\GraphQL;
use GraphQL\Type\Schema;
class User
{
// 模拟从数据库取数据
public static function getUserLimit($limit)
{
$user = [
[
"uid" => 1,
"name" => "name1"
],
[
"uid" => 2,
"name" => "name2"
],
[
"uid" => 3,
"name" => "name3"
],
[
"uid" => 4,
"name" => "name4"
]
];
return array_slice($user, 0, $limit);
}
}
$userType = new ObjectType([
'name' => 'userType',
'description' => '用户详情',
'fields' => [
'uid' => [
'type' => Type::int(),
'description' => '用户ID'
],
'name' => Type::string()
]
]);
$queryType = new ObjectType([
'name' => 'Query',
'fields' => [
'users' => [
'type' => Type::listOf($userType),
'description' => '用户列表',
'args' => [
'limit' => [
'type' => Type::int(),
'description' => '限制条数',
'defaultValue' => 10
]
],
'resolve' => function($root, $args) {
return User::getUserLimit($args['limit']);
}
]
]
]);
$schema = new Schema([
'query' => $queryType
]);
$rawInput = file_get_contents('php://input');
$input = json_decode($rawInput, true);
$query = $input['query'];
$variableValues = isset($input['variables']) ? $input['variables'] : null;
try {
$rootValue = ['prefix' => 'prefix: '];
$result = GraphQL::executeQuery($schema, $query, $rootValue, null, $variableValues);
$output = $result->toArray();
} catch (\Exception $e) {
$output = [
'errors' => [
[
'message' => $e->getMessage()
]
]
];
}
header('Content-Type: application/json');
echo json_encode($output);Copy after login 执行示例代码结果
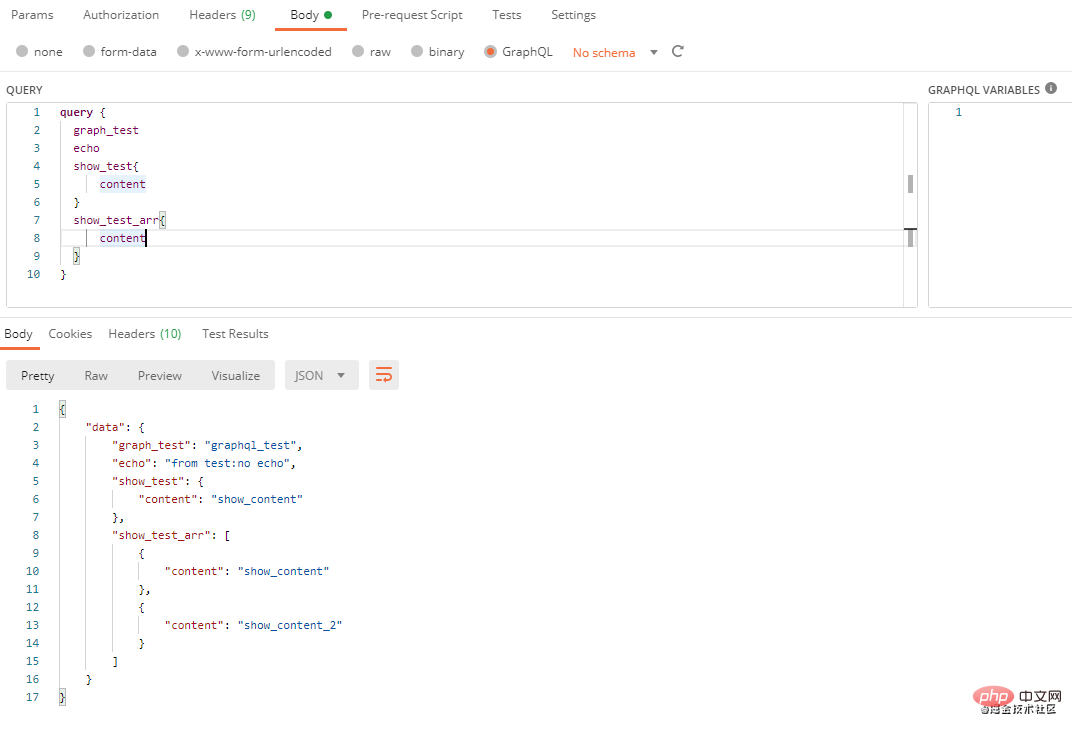
从上面结果可以看到,我们传了 使用类型语言在上面的示例中,如果我们代码返回的数据比较复杂时,需要编写大量的代码,通过GraphQL类型语言,我们可以减少代码量,使代码看上去更加简洁,这是一个用 GraphQL 类型语言定义的简单 Schema示例。 <?php
require_once __DIR__ . '/vendor/autoload.php';
use GraphQL\GraphQL;
use GraphQL\Utils\BuildSchema;
// graph.graphql 文件内容
$graph =
<<<GRAPH
schema {
query: Query
}
type Query {
graph_test: String
echo(message: String): String
show_test: Show
show_test_arr: [Show]
}
type Show {
content: String!
text: String!
}
GRAPH;
$schema = BuildSchema::build($graph);
$rawInput = file_get_contents('php://input');
$input = json_decode($rawInput, true);
$query = $input['query'];
$variableValues = isset($input['variables']) ? $input['variables'] : null;
try {
$rootValue = [
'sum' => function($rootValue, $args, $context) {
return $args['x'] + $args['y'];
},
'echo' => function($rootValue, $args, $context) {
return $rootValue['prefix'] . ($args['message'] ?? 'no echo');
},
'show_test' => function($rootValue, $args, $context) {
return [
'content' => 'show_content',
'text' => 'xxxx xxx'
];
},
'show_test_arr' => function($rootValue, $args, $context) {
return [
[
'content' => 'show_content',
'text' => 'xxxx xxx'
],
[
'content' => 'show_content_2',
'text' => 'xxxx xxx_2'
]
];
},
'prefix' => 'from test:',
"graph_test" => "graphql_test"
];;
$result = GraphQL::executeQuery($schema, $query, $rootValue, null, $variableValues);
$output = $result->toArray();
} catch (\Exception $e) {
\GraphQL\Server\StandardServer::send500Error($e);
}
header('Content-Type: application/json');
echo json_encode($output);Copy after login 执行示例代码结果
参考更多编程相关知识,请访问:编程视频!! The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of how to install and use GraphQL in PHP. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website! Statement of this Website
The content of this article is voluntarily contributed by netizens, and the copyright belongs to the original author. This site does not assume corresponding legal responsibility. If you find any content suspected of plagiarism or infringement, please contact admin@php.cn

Hot AI Tools
Undresser.AI UndressAI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos 
AI Clothes RemoverOnline AI tool for removing clothes from photos. 
Undress AI ToolUndress images for free 
Clothoff.ioAI clothes remover 
Video Face SwapSwap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool! 
Hot Article
How to fix KB5055612 fails to install in Windows 10?
4 weeks ago
By DDD
Roblox: Bubble Gum Simulator Infinity - How To Get And Use Royal Keys
4 weeks ago
By 尊渡假赌尊渡假赌尊渡假赌
Roblox: Grow A Garden - Complete Mutation Guide
3 weeks ago
By DDD
Nordhold: Fusion System, Explained
4 weeks ago
By 尊渡假赌尊渡假赌尊渡假赌
Mandragora: Whispers Of The Witch Tree - How To Unlock The Grappling Hook
3 weeks ago
By 尊渡假赌尊渡假赌尊渡假赌

Hot Tools
Notepad++7.3.1Easy-to-use and free code editor 
SublimeText3 Chinese versionChinese version, very easy to use 
Zend Studio 13.0.1Powerful PHP integrated development environment 
Dreamweaver CS6Visual web development tools 
SublimeText3 Mac versionGod-level code editing software (SublimeText3) 
Hot Topics
Java Tutorial
 1672
1672
 14
14
CakePHP Tutorial
 1428
1428
 52
52
Laravel Tutorial
 1332
1332
 25
25
PHP Tutorial
 1277
1277
 29
29
C# Tutorial
 1257
1257
 24
24
 PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP vs. Python: Understanding the Differences
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:15 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and the choice should be based on project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, with simple syntax and high execution efficiency. 2. Python is suitable for data science and machine learning, with concise syntax and rich libraries.  PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP: A Key Language for Web Development
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:08 AM
PHP is a scripting language widely used on the server side, especially suitable for web development. 1.PHP can embed HTML, process HTTP requests and responses, and supports a variety of databases. 2.PHP is used to generate dynamic web content, process form data, access databases, etc., with strong community support and open source resources. 3. PHP is an interpreted language, and the execution process includes lexical analysis, grammatical analysis, compilation and execution. 4.PHP can be combined with MySQL for advanced applications such as user registration systems. 5. When debugging PHP, you can use functions such as error_reporting() and var_dump(). 6. Optimize PHP code to use caching mechanisms, optimize database queries and use built-in functions. 7  PHP and Python: Comparing Two Popular Programming Languages
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHP and Python: Comparing Two Popular Programming Languages
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and choose according to project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, especially for rapid development and maintenance of websites. 2. Python is suitable for data science, machine learning and artificial intelligence, with concise syntax and suitable for beginners.  PHP in Action: Real-World Examples and Applications
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP in Action: Real-World Examples and Applications
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP is widely used in e-commerce, content management systems and API development. 1) E-commerce: used for shopping cart function and payment processing. 2) Content management system: used for dynamic content generation and user management. 3) API development: used for RESTful API development and API security. Through performance optimization and best practices, the efficiency and maintainability of PHP applications are improved.  The Enduring Relevance of PHP: Is It Still Alive?
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:12 AM
The Enduring Relevance of PHP: Is It Still Alive?
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:12 AM
PHP is still dynamic and still occupies an important position in the field of modern programming. 1) PHP's simplicity and powerful community support make it widely used in web development; 2) Its flexibility and stability make it outstanding in handling web forms, database operations and file processing; 3) PHP is constantly evolving and optimizing, suitable for beginners and experienced developers.  PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP is mainly procedural programming, but also supports object-oriented programming (OOP); Python supports a variety of paradigms, including OOP, functional and procedural programming. PHP is suitable for web development, and Python is suitable for a variety of applications such as data analysis and machine learning.  PHP vs. Other Languages: A Comparison
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP vs. Other Languages: A Comparison
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:19 AM
PHP is suitable for web development, especially in rapid development and processing dynamic content, but is not good at data science and enterprise-level applications. Compared with Python, PHP has more advantages in web development, but is not as good as Python in the field of data science; compared with Java, PHP performs worse in enterprise-level applications, but is more flexible in web development; compared with JavaScript, PHP is more concise in back-end development, but is not as good as JavaScript in front-end development.  PHP and Python: Code Examples and Comparison
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP and Python: Code Examples and Comparison
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP and Python have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice depends on project needs and personal preferences. 1.PHP is suitable for rapid development and maintenance of large-scale web applications. 2. Python dominates the field of data science and machine learning. 
|