How to configure C language environment using VSCode
本篇文章给大家介绍使用VSCode配置C语言环境的方法。有一定的参考价值,有需要的朋友可以参考一下,希望对大家有所帮助。

安装相关插件
打卡后进入如下界面,选择这个C/C++的,然后点击install进行安装,大概几秒钟就好了,安装完成后install按钮会变成uninstall(卸载):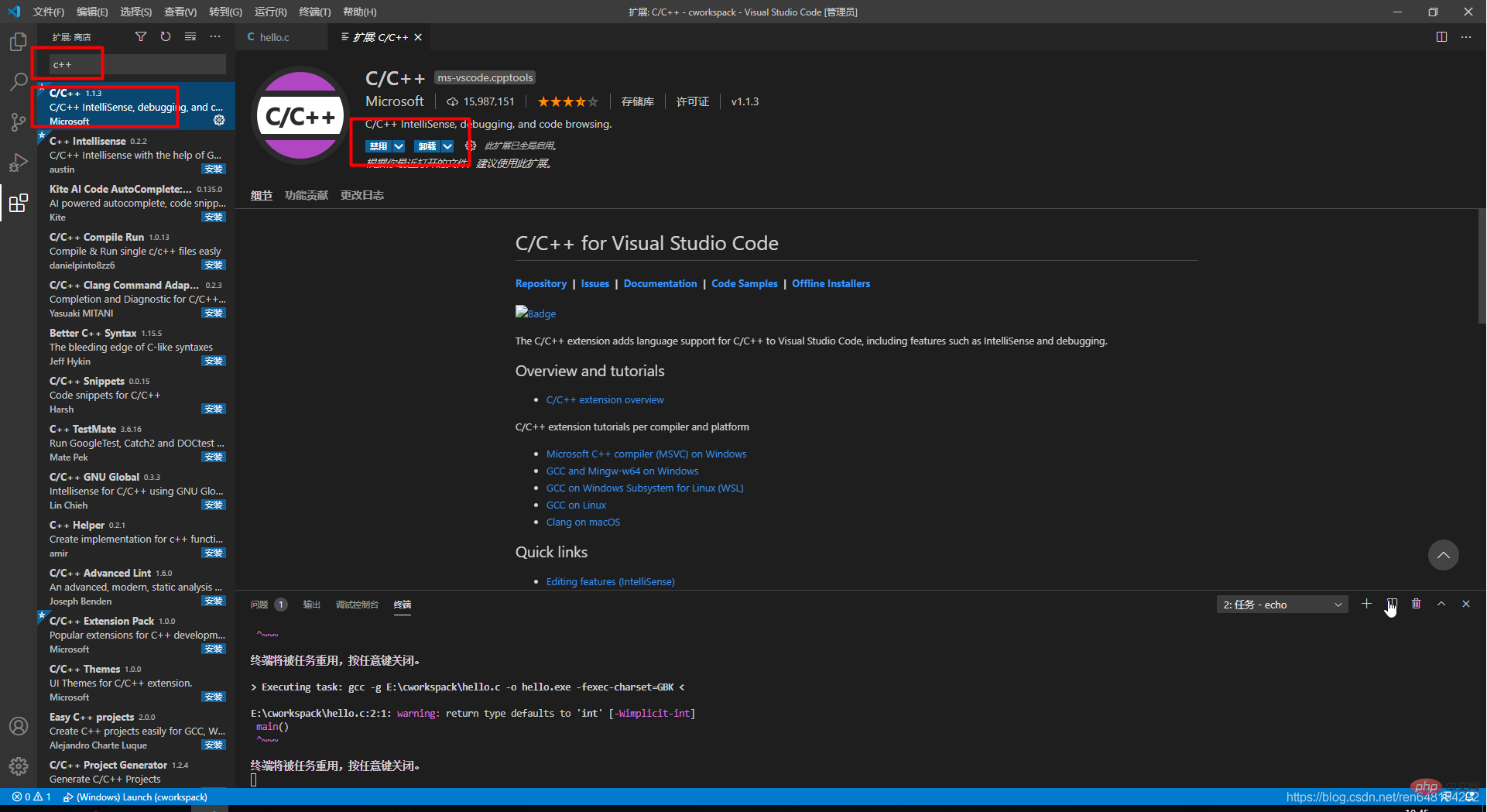
安装编译器(MinGW-W64 GCC)
下载完成后解压:
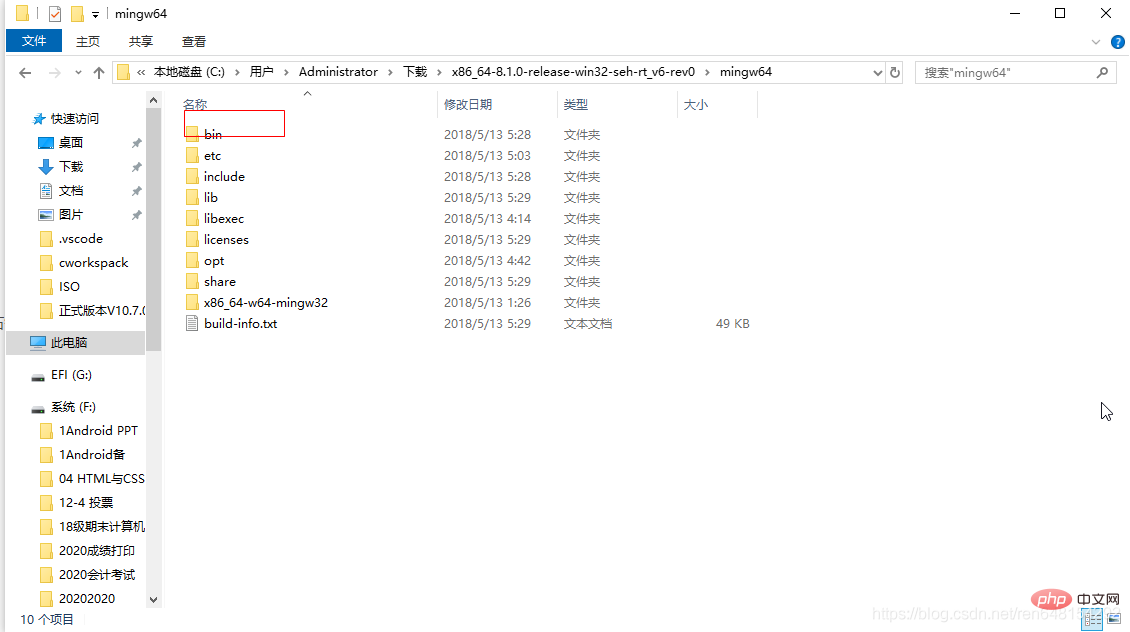
然后配置环境变量
找到这个文件夹内的一个叫bin的文件夹:
然后把它的地址复制一下,找到此电脑(或者我的电脑)——>右键——>属性
然后进入到下面这个页面,打开高级系统设置:
在弹出的页面中选择“高级”分页,找到环境变量,单击打开:
然后在环境变量中的系统变量中,找到Path变量:
打开之后将刚刚复制的地址添加进去:
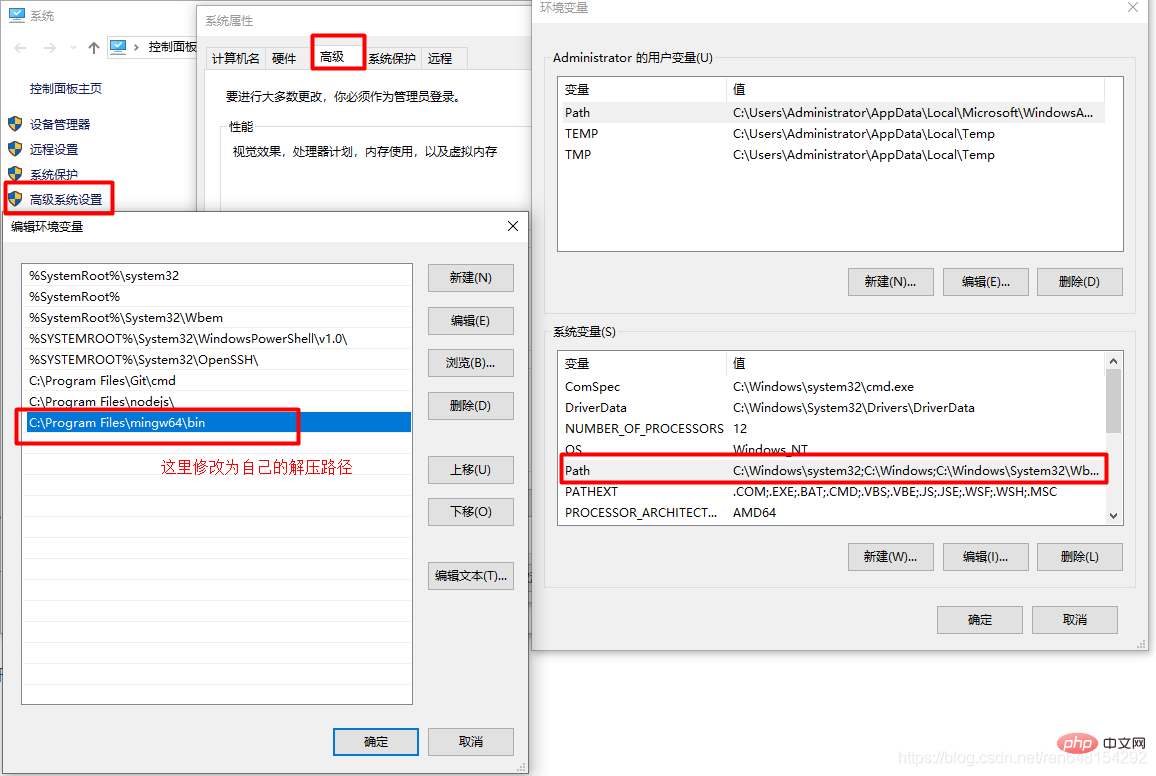
然后点确定,之前弹出的所有页面都点击确定。然后测试环境配置是否成功:
crtl+R快捷键打开运行窗口,在里面输入cmd,回车打开cmd.exe
在cmd.exe中输入如下命令:
gcc -v -E -x c++ -
如果运行结果像下方图片中这样,就配置成功了。
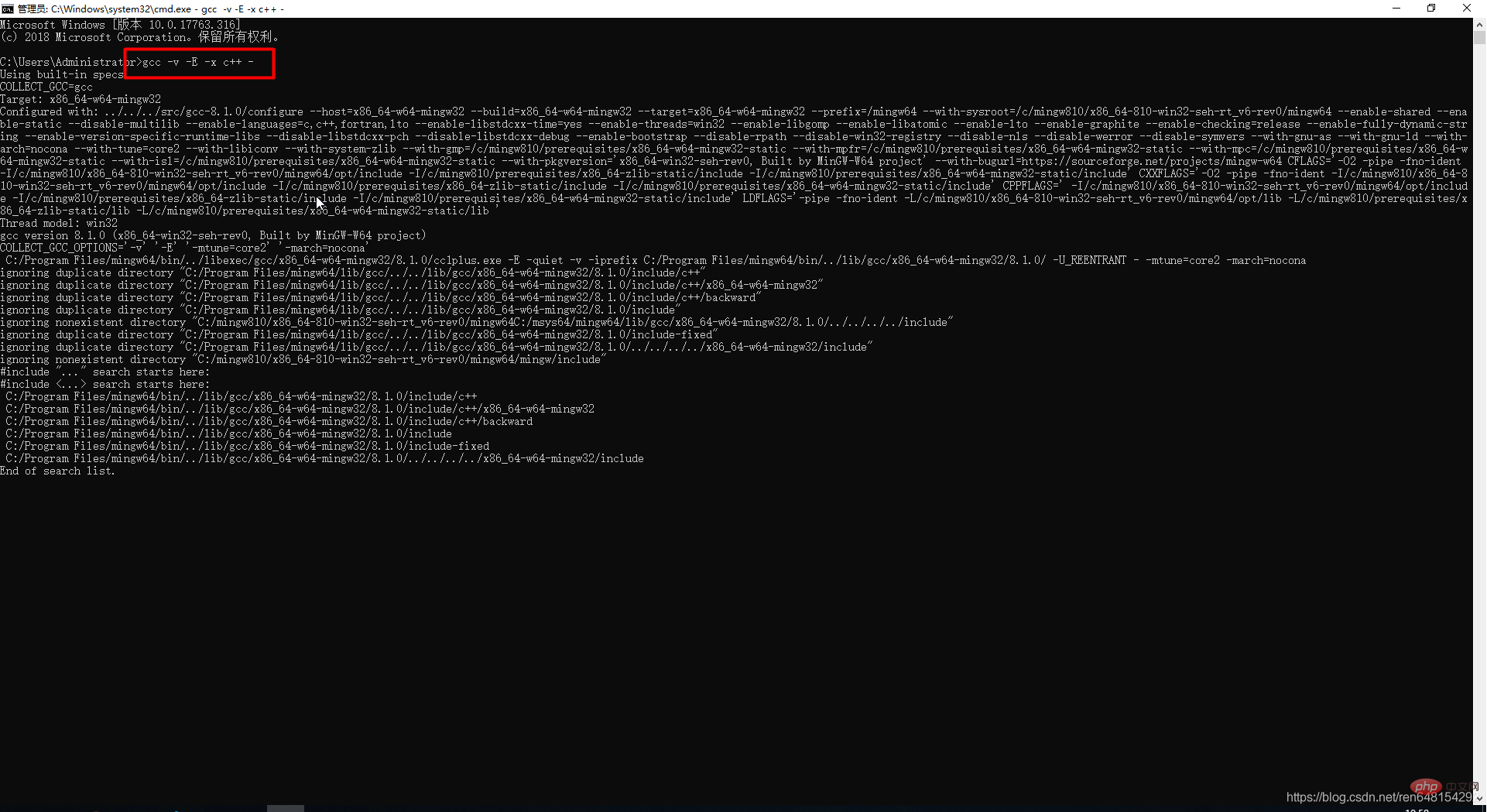
配置
最后在VSCode中进行相关配置:
先新建一个文件夹作为C语言项目文件,然后点击菜单栏中的File——>Open Folder,找到刚才新建的文件夹,然后点击选择文件夹打开这个项目文件。
然后在里面新建一个hello.c文件(名字随便起,以.c结尾就行了)
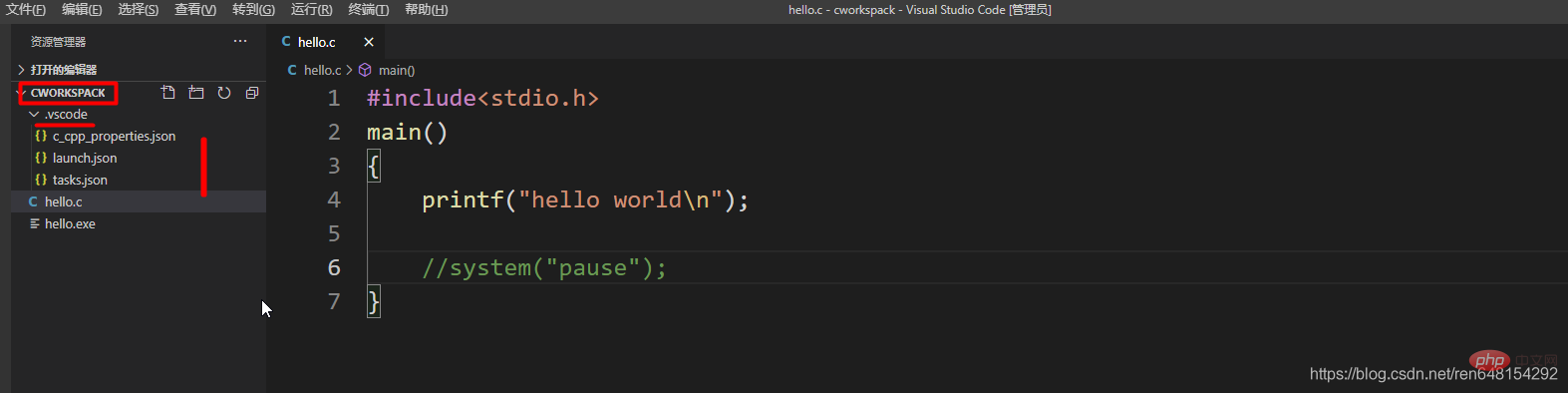
然后再建一个
.vscode文件夹(注意前面有个点),在里面建三个文件,c_cpp_properties.json、launch.json、tasks.json
- c_cpp_properties.json:将这段代码复制进去
{
"configurations": [
{
"name": "Win32",
"includePath": [
"${workspaceRoot}",
"C:/Program Files/mingw64/include/**",
"C:/Program Files/mingw64/bin/../lib/gcc/x86_64-w64-mingw32/8.1.0/include/c++",
"C:/Program Files/mingw64/bin/../lib/gcc/x86_64-w64-mingw32/8.1.0/include/c++/x86_64-w64-mingw32",
"C:/Program Files/mingw64/bin/../lib/gcc/x86_64-w64-mingw32/8.1.0/include/c++/backward",
"C:/Program Files/mingw64/bin/../lib/gcc/x86_64-w64-mingw32/8.1.0/include",
"C:/Program Files/mingw64/bin/../lib/gcc/x86_64-w64-mingw32/8.1.0/include-fixed",
"C:/Program Files/mingw64/bin/../lib/gcc/x86_64-w64-mingw32/8.1.0/../../../../x86_64-w64-mingw32/include"
],
"defines": [
"_DEBUG",
"UNICODE",
"__GNUC__=6",
"__cdecl=__attribute__((__cdecl__))"
],
"intelliSenseMode": "msvc-x64",
"browse": {
"limitSymbolsToIncludedHeaders": true,
"databaseFilename": "",
"path": [
"${workspaceRoot}",
"C:/Program Files/mingw64/include/**",
"C:/Program Files/mingw64/bin/../lib/gcc/x86_64-w64-mingw32/8.1.0/include/c++",
"C:/Program Files/mingw64/bin/../lib/gcc/x86_64-w64-mingw32/8.1.0/include/c++/x86_64-w64-mingw32",
"C:/Program Files/mingw64/bin/../lib/gcc/x86_64-w64-mingw32/8.1.0/include/c++/backward",
"C:/Program Files/mingw64/bin/../lib/gcc/x86_64-w64-mingw32/8.1.0/include",
"C:/Program Files/mingw64/bin/../lib/gcc/x86_64-w64-mingw32/8.1.0/include-fixed",
"C:/Program Files/mingw64/bin/../lib/gcc/x86_64-w64-mingw32/8.1.0/../../../../x86_64-w64-mingw32/include"
]
}
}
],
"version": 4
}然后,下方红框里的内容需要修改,将所有的 改为自己的安装路径,就是我们之前下载的编译器的地址:
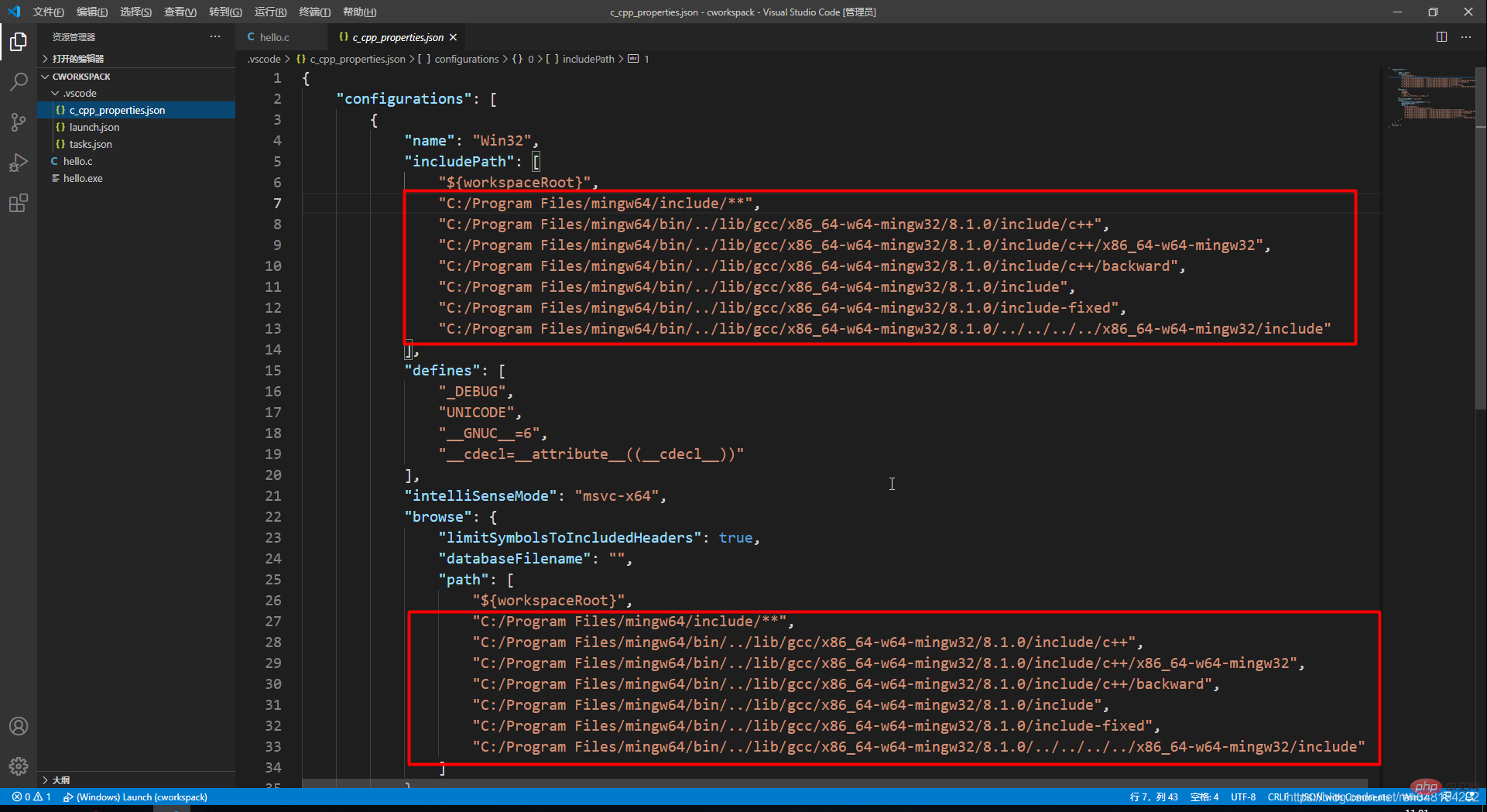
把你的MinGW-W64 GCC解压后的文件中的mingw64的地址复制下来,替换代码里所有的 D:/Program Files (x86)/softwareFactory/x86_64-8.1.0-release-win32-sjlj-rt_v6-rev0/mingw64/ :
- launch.json:复制粘贴,然后miDebuggerPath属性里的内容也要改成自己的路径
{
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "(Windows) Launch",
"type": "cppvsdbg",
"request": "launch",
"program": "cmd",
"preLaunchTask": "echo",
"args": [
"/C",
"${fileDirname}\\${fileBasenameNoExtension}.exe",
"&",
"echo.",
"&",
"pause"
],
"stopAtEntry": false,
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}",
"environment": [],
"externalConsole":true
},
{
"name": "(gdb) Launch",
"type": "cppdbg",
"request": "launch",
"program": "${workspaceFolder}/${fileBasenameNoExtension}.exe",
"args": [],
"stopAtEntry": false,
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}",
"environment": [],
"externalConsole": true,
"MIMode": "gdb",
"miDebuggerPath": "C:\\Program Files\\mingw64\\bin\\gdb.exe",// 自己电脑的gdb
"preLaunchTask": "echo",//这里和task.json的label相对应
"setupCommands": [
{
"description": "Enable pretty-printing for gdb",
"text": "-enable-pretty-printing",
"ignoreFailures": true
}
]
}
]
}- tasks.json:复制粘贴
{
// See https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=733558
// for the documentation about the tasks.json format
"version": "2.0.0",
"tasks": [
{
"label": "echo",
"type": "shell",
"command": "gcc",
"args": [
"-g",
"${file}",
"-o",
"${fileBasenameNoExtension}.exe",
"-fexec-charset=GBK"//解决中文乱码
]
}
],
"presentation": {
"echo": true,
"reveal": "always",
"focus": false,
"panel": "shared",
"showReuseMessage": true,
"clear": false
}
}然后就可以在之前建的hello.c文件里面写程序啦,比如我们熟悉的hello world:
#include<stdio.h>
main()
{
printf("hello world\n");
//system("pause");
}f5运行结果:
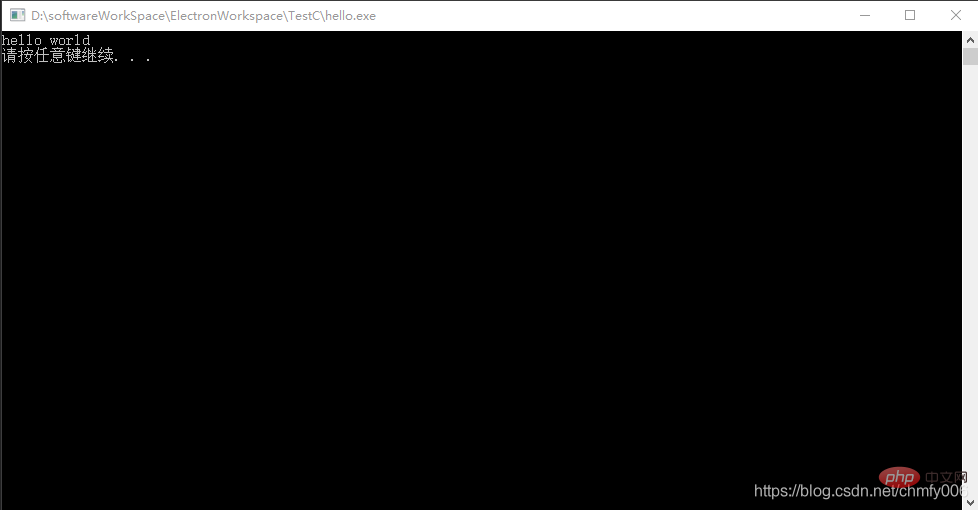
vscode配置c环境就配置完成。
推荐学习:《vscode教程》
The above is the detailed content of How to configure C language environment using VSCode. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What computer configuration is required for vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
What computer configuration is required for vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
VS Code system requirements: Operating system: Windows 10 and above, macOS 10.12 and above, Linux distribution processor: minimum 1.6 GHz, recommended 2.0 GHz and above memory: minimum 512 MB, recommended 4 GB and above storage space: minimum 250 MB, recommended 1 GB and above other requirements: stable network connection, Xorg/Wayland (Linux)
 vscode terminal usage tutorial
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
vscode terminal usage tutorial
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
vscode built-in terminal is a development tool that allows running commands and scripts within the editor to simplify the development process. How to use vscode terminal: Open the terminal with the shortcut key (Ctrl/Cmd). Enter a command or run the script. Use hotkeys (such as Ctrl L to clear the terminal). Change the working directory (such as the cd command). Advanced features include debug mode, automatic code snippet completion, and interactive command history.
 Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Writing code in Visual Studio Code (VSCode) is simple and easy to use. Just install VSCode, create a project, select a language, create a file, write code, save and run it. The advantages of VSCode include cross-platform, free and open source, powerful features, rich extensions, and lightweight and fast.
 How to solve the problem of vscode Chinese annotations becoming question marks
Apr 15, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
How to solve the problem of vscode Chinese annotations becoming question marks
Apr 15, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
How to solve the problem that Chinese comments in Visual Studio Code become question marks: Check the file encoding and make sure it is "UTF-8 without BOM". Change the font to a font that supports Chinese characters, such as "Song Style" or "Microsoft Yahei". Reinstall the font. Enable Unicode support. Upgrade VSCode, restart the computer, and recreate the source file.
 Common commands for vscode terminal
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
Common commands for vscode terminal
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
Common commands for VS Code terminals include: Clear the terminal screen (clear), list the current directory file (ls), change the current working directory (cd), print the current working directory path (pwd), create a new directory (mkdir), delete empty directory (rmdir), create a new file (touch) delete a file or directory (rm), copy a file or directory (cp), move or rename a file or directory (mv) display file content (cat) view file content and scroll (less) view file content only scroll down (more) display the first few lines of the file (head)
 vscode terminal command cannot be used
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
vscode terminal command cannot be used
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
Causes and solutions for the VS Code terminal commands not available: The necessary tools are not installed (Windows: WSL; macOS: Xcode command line tools) Path configuration is wrong (add executable files to PATH environment variables) Permission issues (run VS Code as administrator) Firewall or proxy restrictions (check settings, unrestrictions) Terminal settings are incorrect (enable use of external terminals) VS Code installation is corrupt (reinstall or update) Terminal configuration is incompatible (try different terminal types or commands) Specific environment variables are missing (set necessary environment variables)
 How to use VSCode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 11:21 PM
How to use VSCode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 11:21 PM
Visual Studio Code (VSCode) is a cross-platform, open source and free code editor developed by Microsoft. It is known for its lightweight, scalability and support for a wide range of programming languages. To install VSCode, please visit the official website to download and run the installer. When using VSCode, you can create new projects, edit code, debug code, navigate projects, expand VSCode, and manage settings. VSCode is available for Windows, macOS, and Linux, supports multiple programming languages and provides various extensions through Marketplace. Its advantages include lightweight, scalability, extensive language support, rich features and version
 vscode Previous Next Shortcut Key
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
vscode Previous Next Shortcut Key
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:51 PM
VS Code One-step/Next step shortcut key usage: One-step (backward): Windows/Linux: Ctrl ←; macOS: Cmd ←Next step (forward): Windows/Linux: Ctrl →; macOS: Cmd →






