Introduction to PHP7.0 installation in Linux environment
 Comparison between PHP7 and HHVM
Comparison between PHP7 and HHVM
The performance of PHP7 in real scenarios is indeed equivalent to that of HHVM, and even exceeds HHVM in some scenarios. The operation and maintenance of HHVM is complex and it is a multi-threaded model. This means that if a thread causes a crash, the entire service will hang and it will not automatically restart. In addition, it uses JIT, which means that it needs to be warmed up after restarting. Without preheating, the performance will be worse. Moreover, the multi-threaded model is difficult to debug, which is very unsuitable for web services that pursue stability.
For versions before Nginx and PHP7.0, please refer to this article: Linux environment Nginx installation and debugging and PHP installation
The official version of PHP7.0 has been released around November 2015, and is currently PHP7.0.2 version, I first started following the first beta version of php7 in August 2015, and now the official version is released.
linux version: 64-bit CentOS 6.6
Nginx version: nginx1.8.0
php version: php-7.0.2
Recommended ( Free): PHP7
##Downloadwget http://php.net/get/php-7.0.2.tar.gz/ from/a/mirror
It is recommended to read the installation help file before installation INSTALLUnzip the installationtar zxvf php-7.0.2.tar .gz
cd php-7.0.2
First check the installation help./configure --help
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/php \
–with-curl –with-freetype-dir
– with-gd
–with-gettext
–with-iconv-dir
–with-kerberos
–with-libdir=lib64
–with-libxml-dir
–with- mysqli
–with-openssl
–with-pcre-regex
–with-pdo-mysql
–with-pdo-sqlite
–with-pear
–with-png- dir
–with-xmlrpc
–with-xsl
–with-zlib
–enable-fpm
–enable-bcmath
–enable-libxml
–enable-inline -optimization
–enable-gd-native-ttf
–enable-mbregex
–enable-mbstring
–enable-opcache
–enable-pcntl
–enable-shmop
–enable-soap
–enable-sockets
–enable-sysvsem
–enable-xml
–enable-zip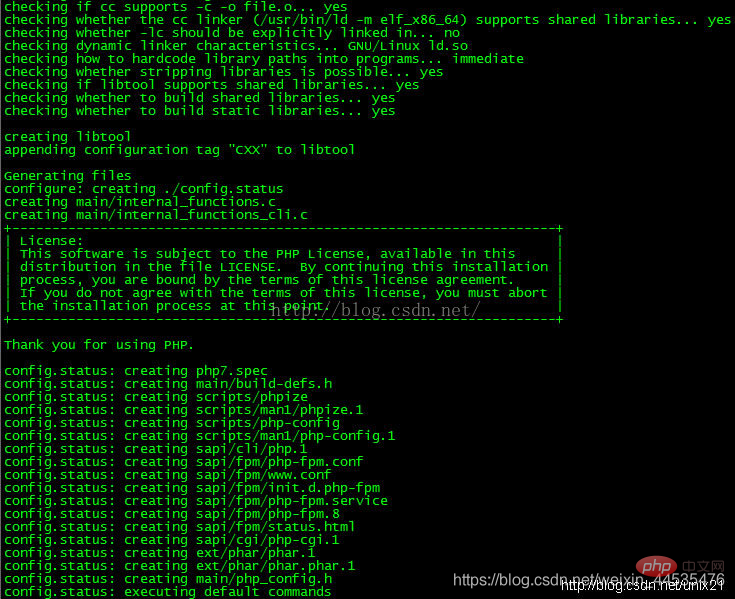 If the configuration is wrong, you need to install the required Module, install dependent libraries directly with yum
If the configuration is wrong, you need to install the required Module, install dependent libraries directly with yum
yum -y install libjpeg libjpeg-devel libpng libpng-devel freetype freetype-devel libxml2 libxml2-devel mysql pcre-devel
Note: There are several configurations that cannot be configured when installing php7beta3. You need to yum it. This is no longer the case with php-7.0.2.yum -y install curl-devel
yum -y install libxslt-devel
Compile and installmake && make install
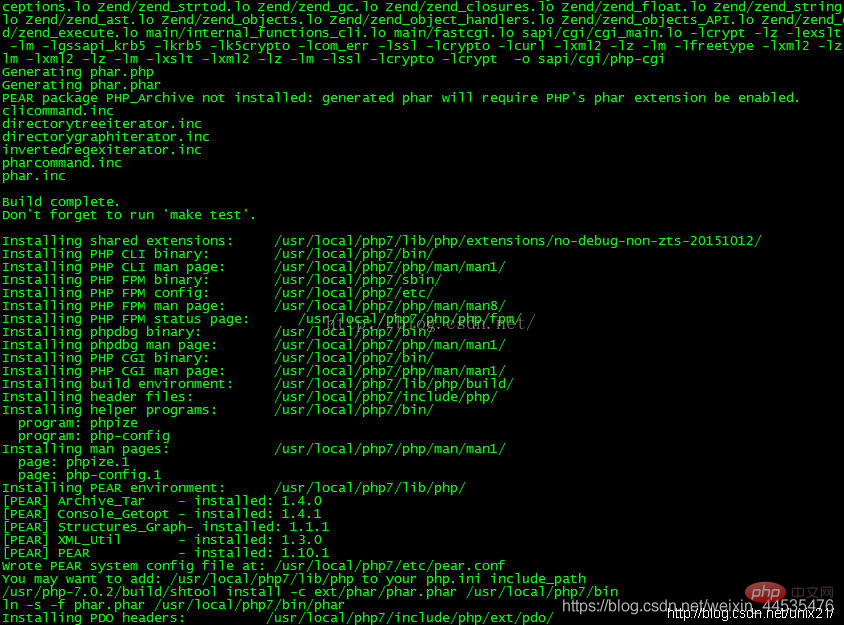
cp php.ini-development /usr/local/php /lib/php.ini
cp /usr/local/php/etc/php-fpm.conf.default /usr/local/php/etc/php-fpm.conf
cp /usr/local/php/etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf.default /usr/local/php/etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf
cp -R ./sapi/fpm/php-fpm /etc/init.d/php-fpm
It should be noted that www in php7 The .conf configuration file configures the port number and other information of phpfpm. If you modify the default 9000 port number, you need to change it here, and then change the nginx configuration Start
/etc/init.d /php-fpm
View phpinfo()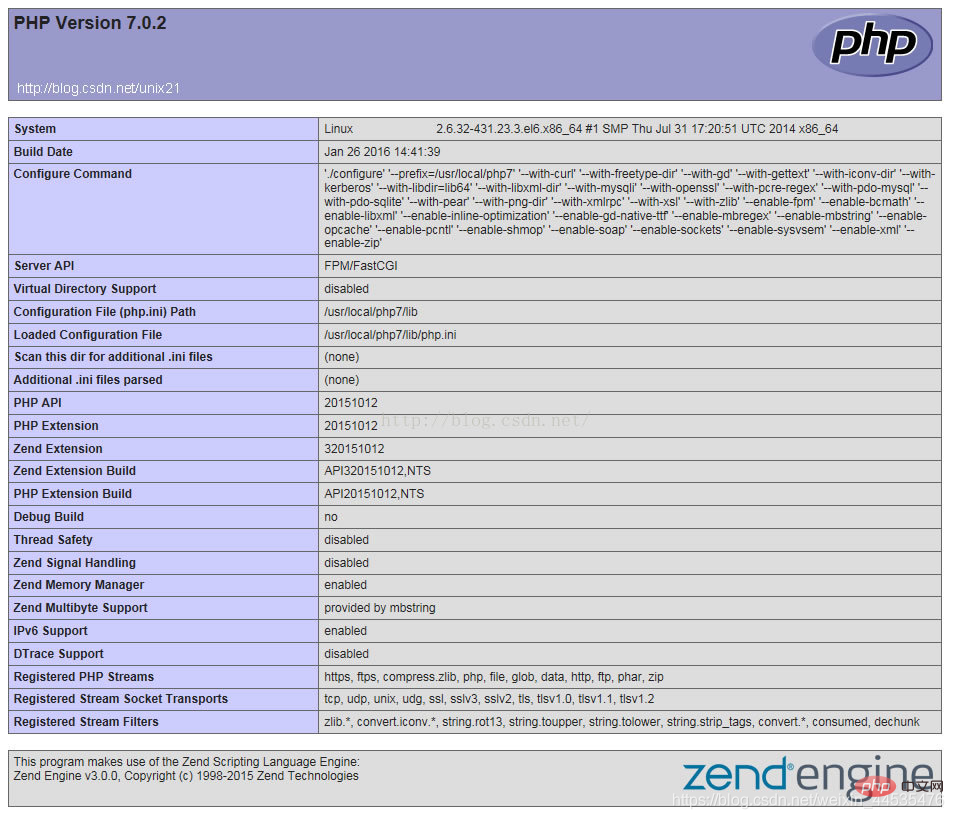
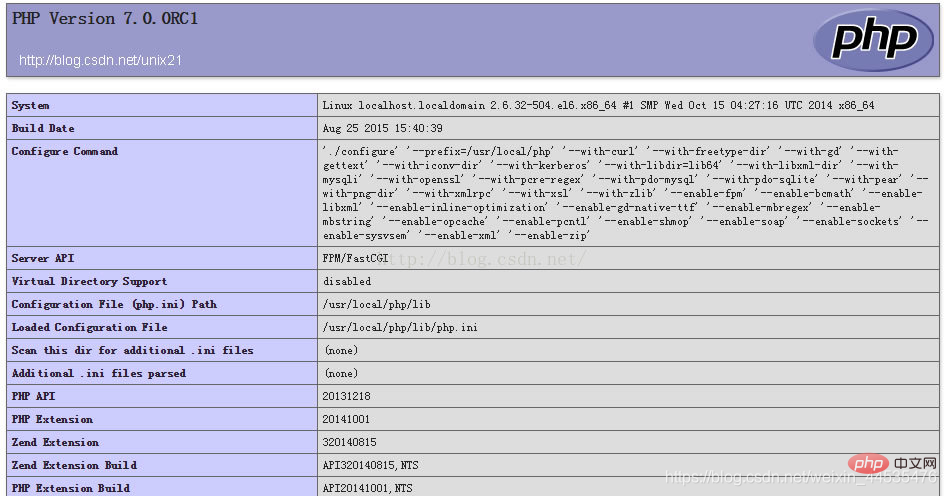
php7 and php5 performance analysis comparison
[root@localhost www5.4.44]# time /usr/local/php5.4.44/bin/php search_by_key.php
user 0m0.300s
sys 0m0.050s
[root@localhost www]# time /usr/local/php/bin/php search_by_key.php
real 0m0.361s
user 0m0.304s
sys 0m0.057s
[root@localhost www7]# time /usr/local/php7/bin/ php search_by_key.php
real 0m0.114s
user 0m0.097s
sys 0m0.017s
Official website address: http://php.net/opcache
Use the following recommended settings to obtain better performance:
opcache.memory_consumption=128
opcache.interned_strings_buffer=8
opcache.max_accelerated_files=4000
opcache.revalidate_freq=60
opcache.fast_shutdown=1
opcache.enable_cli=1
You can also disable opcache.save_comments and enable opcache.enable_file_override. It should be reminded that the above configuration must be rigorously tested before being used in a production environment. Because there is a known issue with the above configuration, it will cause exceptions in some frameworks and applications, especially when there are documents using comment annotations.
vim /usr/local/php7/etc/php.ini
Join
zend_extension=/usr/local/php7/lib/php /extensions/no-debug-non-zts-20141001/opcache.so
restart
killall php-fpm
/etc /init.d/php-fpm
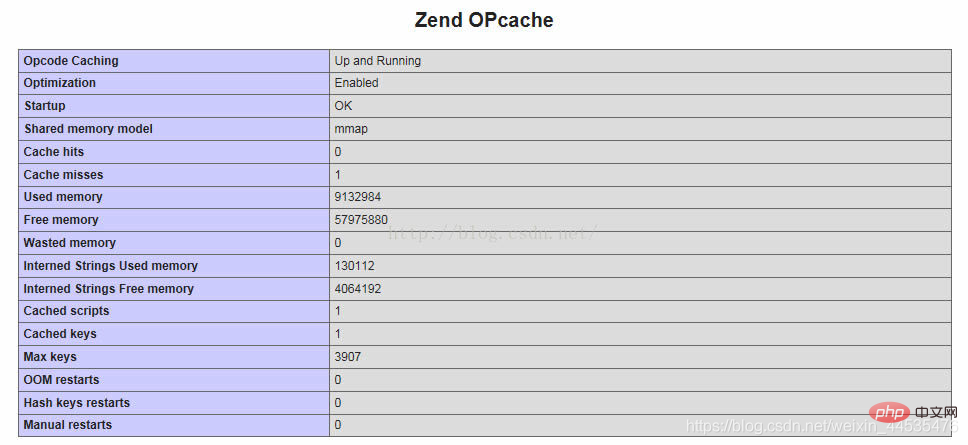
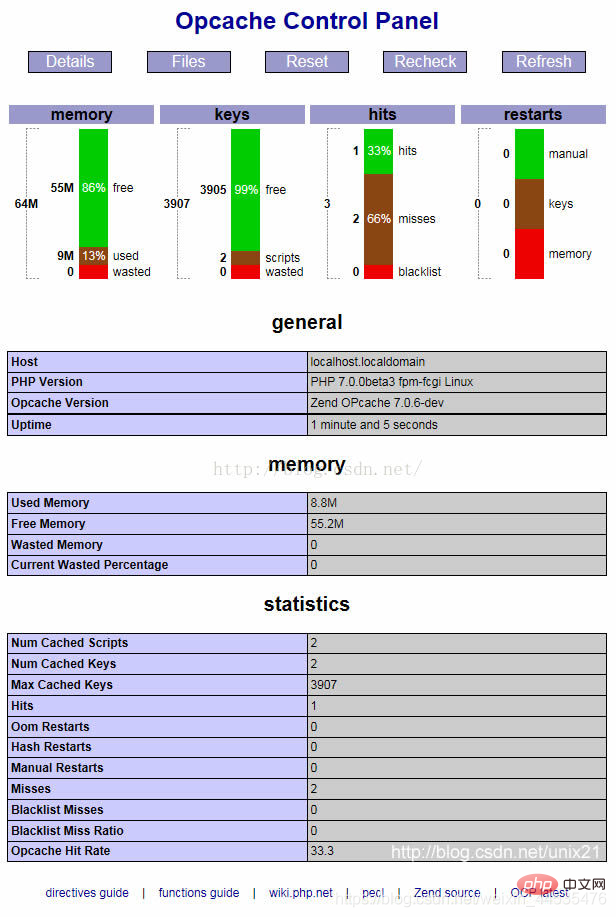
Opcache status test code (https://gist.github.com/ck-on/4959032) Give a demo:
<?php /*
OCP - Opcache Control Panel (aka Zend Optimizer+ Control Panel for PHP)
Author: _ck_ (with contributions by GK, stasilok)
Version: 0.1.6
Free for any kind of use or modification, I am not responsible for anything, please share your improvements
* revision history
0.1.6 2013-04-12 moved meta to footer so graphs can be higher and reduce clutter
0.1.5 2013-04-12 added graphs to visualize cache state, please report any browser/style bugs
0.1.4 2013-04-09 added "recheck" to update files when using large revalidate_freq (or validate_timestamps=Off)
0.1.3 2013-03-30 show host and php version, can bookmark with hashtag ie. #statistics - needs new layout asap
0.1.2 2013-03-25 show optimization levels, number formatting, support for start_time in 7.0.2
0.1.1 2013-03-18 today Zend completely renamed Optimizer+ to OPcache, adjusted OCP to keep working
0.1.0 2013-03-17 added group/sort indicators, replaced "accelerator_" functions with "opcache_"
0.0.6 2013-03-16 transition support as Zend renames product and functions for PHP 5.5 (stasilok)
0.0.5 2013-03-10 added refresh button (GK)
0.0.4 2013-02-18 added file grouping and sorting (click on headers) - code needs cleanup but gets the job done
0.0.2 2013-02-14 first public release
* known problems/limitations:
Unlike APC, the Zend OPcache API
- cannot determine when a file was put into the cache
- cannot change settings on the fly
- cannot protect opcache functions by restricting execution to only specific scripts/paths
* todo:
Extract variables for prefered ordering and better layout instead of just dumping into tables
File list filter
*/
// ini_set('display_errors',1); error_reporting(-1);
if ( count(get_included_files())>1 || php_sapi_name()=='cli' || empty($_SERVER['REMOTE_ADDR']) ) { die; } // weak block against indirect access
$time=time();
define('CACHEPREFIX',function_exists('opcache_reset')?'opcache_':(function_exists('accelerator_reset')?'accelerator_':''));
if ( !empty($_GET['RESET']) ) {
if ( function_exists(CACHEPREFIX.'reset') ) { call_user_func(CACHEPREFIX.'reset'); }
header( 'Location: '.str_replace('?'.$_SERVER['QUERY_STRING'],'',$_SERVER['REQUEST_URI']) );
exit;
}
if ( !empty($_GET['RECHECK']) ) {
if ( function_exists(CACHEPREFIX.'invalidate') ) {
$recheck=trim($_GET['RECHECK']); $files=call_user_func(CACHEPREFIX.'get_status');
if (!empty($files['scripts'])) {
foreach ($files['scripts'] as $file=>$value) {
if ( $recheck==='1' || strpos($file,$recheck)===0 ) call_user_func(CACHEPREFIX.'invalidate',$file);
}
}
header( 'Location: '.str_replace('?'.$_SERVER['QUERY_STRING'],'',$_SERVER['REQUEST_URI']) );
} else { echo 'Sorry, this feature requires Zend Opcache newer than April 8th 2013'; }
exit;
}
?>nbsp;html>
<p>
</p><h1 id="a-Opcache-Control-Panel-a"><a>Opcache Control Panel</a></h1>
<p>
<a>Details</a>
<a>Files</a>
<a>Reset</a>
<?php if ( function_exists(CACHEPREFIX.'invalidate') ) { ?>
<a>Recheck</a>
<?php } ?>
<a>Refresh</a>
</p>
<?php
if ( !function_exists(CACHEPREFIX.'get_status') ) { echo '<h2>Opcache not detected?'; die; }
if ( !empty($_GET['FILES']) ) { echo '<h2 id="files-cached">files cached</h2>'; files_display(); echo 'The above is the detailed content of Introduction to PHP7.0 installation in Linux environment. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What computer configuration is required for vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
What computer configuration is required for vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
VS Code system requirements: Operating system: Windows 10 and above, macOS 10.12 and above, Linux distribution processor: minimum 1.6 GHz, recommended 2.0 GHz and above memory: minimum 512 MB, recommended 4 GB and above storage space: minimum 250 MB, recommended 1 GB and above other requirements: stable network connection, Xorg/Wayland (Linux)
 Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
Linux Architecture: Unveiling the 5 Basic Components
Apr 20, 2025 am 12:04 AM
The five basic components of the Linux system are: 1. Kernel, 2. System library, 3. System utilities, 4. Graphical user interface, 5. Applications. The kernel manages hardware resources, the system library provides precompiled functions, system utilities are used for system management, the GUI provides visual interaction, and applications use these components to implement functions.
 vscode terminal usage tutorial
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
vscode terminal usage tutorial
Apr 15, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
vscode built-in terminal is a development tool that allows running commands and scripts within the editor to simplify the development process. How to use vscode terminal: Open the terminal with the shortcut key (Ctrl/Cmd). Enter a command or run the script. Use hotkeys (such as Ctrl L to clear the terminal). Change the working directory (such as the cd command). Advanced features include debug mode, automatic code snippet completion, and interactive command history.
 How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
How to check the warehouse address of git
Apr 17, 2025 pm 01:54 PM
To view the Git repository address, perform the following steps: 1. Open the command line and navigate to the repository directory; 2. Run the "git remote -v" command; 3. View the repository name in the output and its corresponding address.
 Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Where to write code in vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
Writing code in Visual Studio Code (VSCode) is simple and easy to use. Just install VSCode, create a project, select a language, create a file, write code, save and run it. The advantages of VSCode include cross-platform, free and open source, powerful features, rich extensions, and lightweight and fast.
 How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
How to run java code in notepad
Apr 16, 2025 pm 07:39 PM
Although Notepad cannot run Java code directly, it can be achieved by using other tools: using the command line compiler (javac) to generate a bytecode file (filename.class). Use the Java interpreter (java) to interpret bytecode, execute the code, and output the result.
 What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
What is the main purpose of Linux?
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:19 AM
The main uses of Linux include: 1. Server operating system, 2. Embedded system, 3. Desktop operating system, 4. Development and testing environment. Linux excels in these areas, providing stability, security and efficient development tools.
 How to run sublime after writing the code
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:51 AM
How to run sublime after writing the code
Apr 16, 2025 am 08:51 AM
There are six ways to run code in Sublime: through hotkeys, menus, build systems, command lines, set default build systems, and custom build commands, and run individual files/projects by right-clicking on projects/files. The build system availability depends on the installation of Sublime Text.






