Why does redis create 16 databases by default?

In actual development work, we usually use the redis database for caching, distributed locks/message queues, etc. But we usually have this question, why are 16 databases created by default after setting up and configuring the redis server?
Let’s introduce this question to you.

1. The origin of 16 databases
redis is a dictionary-structured storage server. A redis instance provides multiple dictionaries for storing data. , the client can specify in which dictionary the data is stored. This is similar to how multiple databases can be created in a relational database instance (as shown in the figure below), so each dictionary can be understood as an independent database.
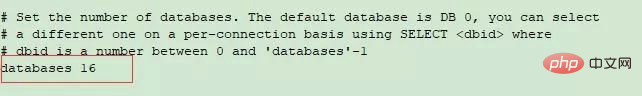
Redis supports 16 databases by default. You can modify this value by adjusting the databases in the redis configuration file redis/redis.conf. After the setting is completed, restart redis and it will be completed. configuration.
#After the client establishes a link with redis, database No. 0 will be selected by default, but you can use the select command to change the database at any time.
# 切换数据库操作:切换到1 127.0.0.1:6379> SELECT 1 OK 127.0.0.1:6379[1]> 127.0.0.1:6379[1]> # 切换到0 127.0.0.1:6379[1]> SELECT 0 OK 127.0.0.1:6379> # 从1号库中获取username 127.0.0.1:6379[1]> get username 。
(Learning video sharing: redis video tutorial)
In actual projects, you can specify the database in the form of a redis configuration file, as shown in the figure below Instructions

2. Correctly understand the "database" concept of redis
Since redis does not support custom database names, all databases Named by number. Developers need to record the correspondence between the stored data and the database themselves. In addition, redis does not support setting different access passwords for each database. All clients can either access all databases or have no permission to access all databases. To correctly understand the "database" concept of redis, we have to mention a command:
Clear the data in all databases in the redis instance
127.0.0.1:6379> FLUSH ALL
Clear the data in a certain redis database The data of other libraries will not be cleared
127.0.0.1:6379> FLUSH db0
This command can clear all database data under the instance, which is different from the relational database we are familiar with. Multiple libraries of relational databases are often used to store data for different applications, and there is no way to clear all library data under the instance at the same time. For redis, these dbs are more like namespaces and are not suitable for storing data from different applications. For example, you can use database No. 0 to store data in the development environment, and use database No. 1 to store data in the test environment. However, it is not suitable to use database No. 0 to store the data of application A and use database No. 1 to store the data of application B. Different environments Different redis instances should be used to store data. Redis is very lightweight. An empty redis instance only occupies about 1M of memory, so there is no need to worry about multiple redis instances taking up a lot of additional memory.
3. Does one instance support multiple DBs in a cluster?
The above are all based on the situation of single redis. In the case of a cluster, the use of the select command to switch db is not supported, because there is only one db0 in redis cluster mode
Recommended learning:redis database tutorial
The above is the detailed content of Why does redis create 16 databases by default?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
How to build the redis cluster mode
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:15 PM
Redis cluster mode deploys Redis instances to multiple servers through sharding, improving scalability and availability. The construction steps are as follows: Create odd Redis instances with different ports; Create 3 sentinel instances, monitor Redis instances and failover; configure sentinel configuration files, add monitoring Redis instance information and failover settings; configure Redis instance configuration files, enable cluster mode and specify the cluster information file path; create nodes.conf file, containing information of each Redis instance; start the cluster, execute the create command to create a cluster and specify the number of replicas; log in to the cluster to execute the CLUSTER INFO command to verify the cluster status; make
 MySQL: An Introduction to the World's Most Popular Database
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL: An Introduction to the World's Most Popular Database
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:18 AM
MySQL is an open source relational database management system, mainly used to store and retrieve data quickly and reliably. Its working principle includes client requests, query resolution, execution of queries and return results. Examples of usage include creating tables, inserting and querying data, and advanced features such as JOIN operations. Common errors involve SQL syntax, data types, and permissions, and optimization suggestions include the use of indexes, optimized queries, and partitioning of tables.
 How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear redis data
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:06 PM
How to clear Redis data: Use the FLUSHALL command to clear all key values. Use the FLUSHDB command to clear the key value of the currently selected database. Use SELECT to switch databases, and then use FLUSHDB to clear multiple databases. Use the DEL command to delete a specific key. Use the redis-cli tool to clear the data.
 Why Use MySQL? Benefits and Advantages
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:17 AM
Why Use MySQL? Benefits and Advantages
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:17 AM
MySQL is chosen for its performance, reliability, ease of use, and community support. 1.MySQL provides efficient data storage and retrieval functions, supporting multiple data types and advanced query operations. 2. Adopt client-server architecture and multiple storage engines to support transaction and query optimization. 3. Easy to use, supports a variety of operating systems and programming languages. 4. Have strong community support and provide rich resources and solutions.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
How to configure Lua script execution time in centos redis
Apr 14, 2025 pm 02:12 PM
On CentOS systems, you can limit the execution time of Lua scripts by modifying Redis configuration files or using Redis commands to prevent malicious scripts from consuming too much resources. Method 1: Modify the Redis configuration file and locate the Redis configuration file: The Redis configuration file is usually located in /etc/redis/redis.conf. Edit configuration file: Open the configuration file using a text editor (such as vi or nano): sudovi/etc/redis/redis.conf Set the Lua script execution time limit: Add or modify the following lines in the configuration file to set the maximum execution time of the Lua script (unit: milliseconds)
 How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to use the redis command line
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
Use the Redis command line tool (redis-cli) to manage and operate Redis through the following steps: Connect to the server, specify the address and port. Send commands to the server using the command name and parameters. Use the HELP command to view help information for a specific command. Use the QUIT command to exit the command line tool.
 How to set the redis expiration policy
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
How to set the redis expiration policy
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:03 PM
There are two types of Redis data expiration strategies: periodic deletion: periodic scan to delete the expired key, which can be set through expired-time-cap-remove-count and expired-time-cap-remove-delay parameters. Lazy Deletion: Check for deletion expired keys only when keys are read or written. They can be set through lazyfree-lazy-eviction, lazyfree-lazy-expire, lazyfree-lazy-user-del parameters.






